SLLSEI8D June 2014 – April 2015 ISO7310C , ISO7310FC
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- D|8
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage(2) | VCC1 , VCC2 | –0.5 | 6 | V | ||
| Voltage (2) | IN, OUT | –0.5 | VCC+0.5(3) | V | ||
| Output current | IO | ±15 | mA | |||
| Junction temperature | TJ | 150 | °C | |||
| Storage temperature | Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values are with respect to network ground terminal and are peak voltage values.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±4000 | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | ||||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC1, VCC2 | Supply voltage | 3 | 5.5 | V | |
| IOH | High-level output current | –4 | mA | ||
| IOL | Low-level output current | 4 | mA | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2 | 5.5 | V | |
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0 | 0.8 | V | |
| tui | Input pulse duration | 40 | ns | ||
| 1 / tui | Signaling rate | 0 | 25 | Mbps | |
| TJ(1) | Junction temperature | 136 | °C | ||
| TA | Ambient temperature | -40 | 25 | 125 | °C |
(1) To maintain the recommended operating conditions for TJ, see the Thermal Information table.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | D PACKAGE | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (8) PINS | ||||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 119.9 | °C/W | |
| RθJCtop | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 65.2 | ||
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 61.3 | ||
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 19.3 | ||
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 60.7 | ||
| RθJCbot | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | N/A | ||
| PD | Maximum power dissipation | VCC1 = VCC2 = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, CL = 15 pF, Input a 12.5 MHz 50% duty-cycle square wave |
34 | mW |
| PD1 | Power dissipation by Side-1 | 7.9 | ||
| PD2 | Power dissipation by Side-2 | 26.1 | ||
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
VCC1 and VCC2 at 5 V ± 10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –4 mA; see Figure 9 | VCC2 – 0.5 | 4.7 | V | ||
| IOH = –20 μA; see Figure 9 | VCC2 – 0.1 | 5 | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 4 mA; see Figure 9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | ||
| IOL = 20 μA; see Figure 9 | 0 | 0.1 | |||||
| VI(HYS) | Input threshold voltage hysteresis | 480 | mV | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current | IN = VCC | 10 | μA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current | IN = 0 V | –10 | μA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | VI = VCC or 0 V; see Figure 11. | 25 | 65 | kV/μs | ||
| SUPPLY CURRENT (All inputs switching with square wave clock signal for dynamic ICC measurement) | |||||||
| ICC1 | Supply current for VCC1 and VCC2 | DC to 1 Mbps | DC Input: VI = VCC or 0 V, AC Input: CL = 15pF |
0.3 | 0.6 | mA | |
| ICC2 | 1.6 | 2.4 | |||||
| ICC1 | 10 Mbps | CL = 15pF | 0.5 | 1 | |||
| ICC2 | 2.2 | 3.2 | |||||
| ICC1 | 25 Mbps | CL = 15pF | 0.8 | 1.3 | |||
| ICC2 | 3 | 4.2 | |||||
6.6 Switching Characteristics
VCC1 and VCC2 at 5 V ± 10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH, tPHL | Propagation delay time | See Figure 9 | 20 | 32 | 58 | ns |
| PWD(1) | Pulse width distortion |tPHL – tPLH| | 4 | ns | |||
| tsk(pp)(2) | Part-to-part skew time | 24 | ns | |||
| tr | Output signal rise time | See Figure 9 | 2.5 | ns | ||
| tf | Output signal fall time | 2 | ns | |||
| tfs | Fail-safe output delay time from input power loss | See Figure 10 | 7.5 | μs | ||
(1) Also known as pulse skew.
(2) tsk(pp) is the magnitude of the difference in propagation delay times between any terminals of different devices switching in the same direction while operating at identical supply voltages, temperature, input signals and loads.
6.7 Electrical Characteristics
VCC1 and VCC2 at 3.3 V ± 10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –4 mA; see Figure 9 | VCC2 – 0.5 | 3 | V | ||
| IOH = –20 μA; see Figure 9 | VCC2 – 0.1 | 3.3 | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 4 mA; see Figure 9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | ||
| IOL = 20 μA; see Figure 9 | 0 | 0.1 | |||||
| VI(HYS) | Input threshold voltage hysteresis | 450 | mV | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current | IN = VCC | 10 | μA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input curre | IN = 0 V | -10 | μA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | VI = VCC or 0 V; see Figure 11 | 25 | 50 | kV/μs | ||
| SUPPLY CURRENT (All inputs switching with square wave clock signal for dynamic ICC measurement) | |||||||
| ICC1 | Supply current for VCC1 and VCC2 | DC to 1 Mbps | DC Input: VI = VCC or 0 V, AC Input: CL = 15pF |
0.2 | 0.4 | mA | |
| ICC2 | 1.2 | 1.8 | |||||
| ICC1 | 10 Mbps | CL = 15pF | 0.3 | 0.5 | |||
| ICC2 | 1.6 | 2.2 | |||||
| ICC1 | 25 Mbps | CL = 15pF | 0.5 | 0.8 | |||
| ICC2 | 2.1 | 3 | |||||
6.8 Switching Characteristics
VCC1 and VCC2 at 3.3 V ± 10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH, tPHL | Propagation delay time | See Figure 9 | 22 | 36 | 67 | ns |
| PWD(1) | Pulse width distortion |tPHL – tPLH| | 3.5 | ns | |||
| tsk(pp)(2) | Part-to-part skew time | 28 | ns | |||
| tr | Output signal rise time | See Figure 9 | 3.2 | ns | ||
| tf | Output signal fall time | 2.7 | ns | |||
| tfs | Fail-safe output delay time from input power loss | See Figure 10 | 7.4 | μs | ||
(1) Also known as pulse skew.
(2) tsk(pp) is the magnitude of the difference in propagation delay times between any terminals of different devices switching in the same direction while operating at identical supply voltages, temperature, input signals and loads.
6.9 Typical Characteristics
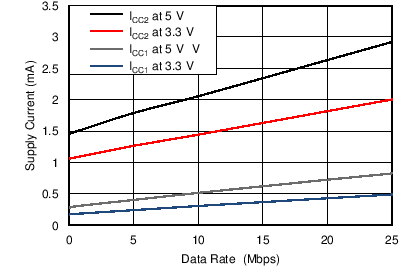
| TA = 25°C | CL = 15 pF |
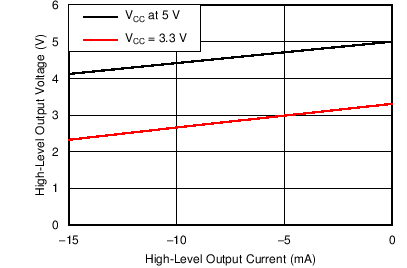
| TA = 25°C |
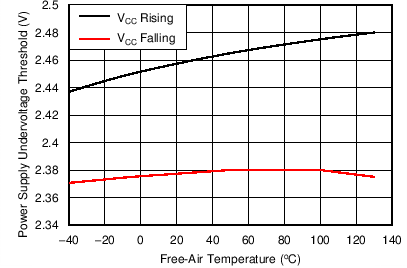
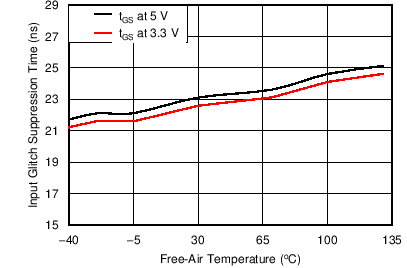
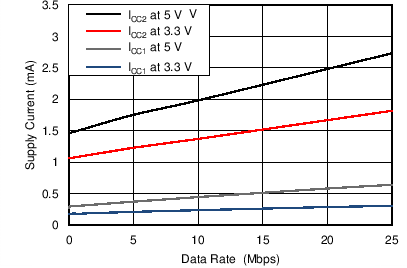
| TA = 25°C | CL = No Load |
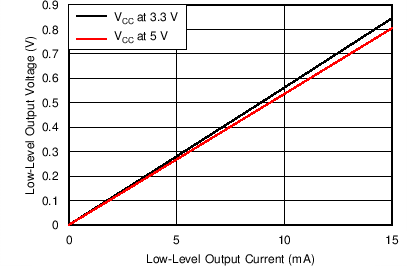
| TA = 25°C |
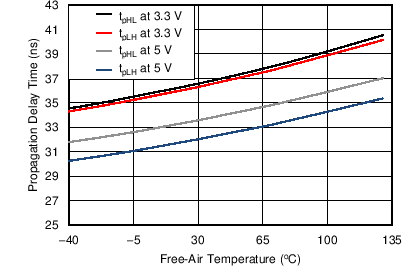
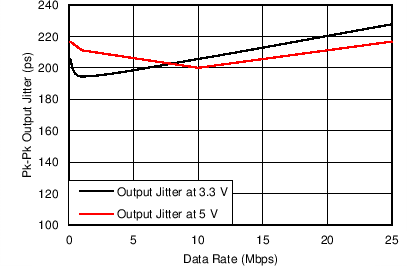
| TA = 25°C |