SLLSEP8B July 2015 – June 2016 ISO7831
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Rating
- 6.6 Insulation Characteristics
- 6.7 Regulatory Information
- 6.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics—5-V Supply
- 6.10 Supply Current Characteristics—5-V Supply
- 6.11 Electrical Characteristics—3.3-V Supply
- 6.12 Supply Current Characteristics—3.3-V Supply
- 6.13 Electrical Characteristics—2.5-V Supply
- 6.14 Supply Current Characteristics—2.5-V Supply
- 6.15 Switching Characteristics—5-V Supply
- 6.16 Switching Characteristics—3.3-V Supply
- 6.17 Switching Characteristics—2.5-V Supply
- 6.18 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.19 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DWW|16
- DW|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
See (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC1
VCC2 |
Supply voltage(2) | –0.5 | 6 | V | |
| V | Voltage at INx, OUTx, or ENx | –0.5 | VCCx + 0.5(3) | V | |
| IO | Output current | –15 | 15 | mA | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values except differential I/O bus voltages are with respect to the local ground terminal (GND1 or GND2) and are peak voltage values.
(3) Maximum voltage must not exceed 6 V
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±6000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC1, VCC2 | Supply voltage | 2.25 | 5.5 | V | ||
| IOH | High-level output current | VCCO(1) = 5 V | –4 | mA | ||
| VCCO(1) = 3.3 V | –2 | |||||
| VCCO(1) = 2.5 V | –1 | |||||
| IOL | Low-level output current | VCCO(1) = 5 V | 4 | mA | ||
| VCCO(1) = 3.3 V | 2 | |||||
| VCCO(1) = 2.5 V | 1 | |||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × VCCI(1) | VCCI(1) | V | ||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0 | 0.3 × VCCI(1) | V | ||
| DR | Signaling rate | 0 | 100 | Mbps | ||
| TA | Ambient temperature | –55 | 25 | 125 | °C | |
(1) VCCI = Input-side VCC; VCCO = Output-side VCC.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | ISO7831 | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DW (SOIC) | DWW (SOIC) | ||||
| 16 PINS | 16 PINS | ||||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 81.1 | 83.4 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case(top) thermal resistance | 43.8 | 45.2 | °C/W | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 45.7 | 54.1 | °C/W | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 17.0 | 17.6 | °C/W | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 45.2 | 53.3 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(bottom) | Junction-to-case(bottom) thermal resistance | — | — | °C/W | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Power Rating
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Maximum power dissipation | VCC1 = VCC2 = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, CL = 15 pF, input a 50 MHz 50% duty cycle square wave |
150 | mW | ||
| PD1 | Maximum power dissipation by side-1 | 50 | mW | |||
| PD2 | Maximum power dissipation by side-2 | 100 | mW | |||
6.6 Insulation Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | SPECIFICATION | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DW | DWW | ||||
| CLR | External clearance(1) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance through air | >8 | >14.5 | mm |
| CPG | External creepage(1) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance across the package surface | >8 | >14.5 | mm |
| DTI | Distance through the insulation | Minimum internal gap (internal clearance) | >21 | >21 | μm |
| CTI | Comparative tracking index | DIN EN 60112 (VDE 0303-11); IEC 60112; UL 746A | >600 | >600 | V |
| Material group | I | I | |||
| Overvoltage category per IEC 60664-1 | Rated mains voltage ≤ 600 VRMS | I–IV | I–IV | ||
| Rated mains voltage ≤ 1000 VRMS | I–III | I–IV | |||
| DIN V VDE V 0884–10 (VDE V 0884–10):2006-12(2) | |||||
| VIOWM | Maximum isolation working voltage | Time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) Test; see Figure 1 and Figure 2 | 1500 | 2000 | VRMS |
| 2121 | 2828 | VDC | |||
| VIOTM | Maximum transient isolation voltage | VTEST = VIOTM
t = 60 s (qualification) t= 1 s (100% production) |
8000 | 8000 | VPK |
| VIOSM | Maximum surge isolation voltage for reinforced insulation(3) | Test method per IEC 60065, 1.2/50 µs waveform, VTEST = 1.6 × VIOSM = 12800 VPK (qualification) |
8000 | 8000 | VPK |
| VIORM | Maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage | 2121 | 2828 | VPK | |
| VPR | Input-to-output test voltage | Method a, After Input/Output safety test subgroup 2/3, VPR = VIORM × 1.2, t = 10 s, Partial discharge < 5 pC |
2545 | 3394 | VPK |
| Method a, After environmental tests subgroup 1, VPR = VIORM × 1.6, t = 10 s, Partial Discharge < 5 pC |
3394 | 4525 | |||
| Method b1, VPR = VIORM × 1.875, t = 1 s (100% Production test) Partial discharge < 5 pC |
3977 | 5303 | |||
| CIO | Barrier capacitance, input to output(4) | VIO = 0.4 × sin (2πft), f = 1 MHz | ~1 | ~1 | pF |
| RIO | Isolation resistance, input to output(4) | VIO = 500 V, TA = 25°C | >1012 | >1012 | Ω |
| VIO = 500 V, 100°C ≤ TA ≤ max | >1011 | >1011 | Ω | ||
| RS | Isolation resistance | VIO = 500 V at TS | >109 | >109 | Ω |
| Pollution degree | 2 | 2 | |||
| Climatic category | 55/125/21 | 55/125/21 | |||
| UL 1577 | |||||
| VISO | Withstanding isolation voltage | VTEST = VISO = 5700 VRMS, t = 60 s (qualification), VTEST = 1.2 × VISO = 6840 VRMS, t = 1 s (100% production) |
5700 | 5700 | VRMS |
(1) Creepage and clearance requirements should be applied according to the specific equipment isolation standards of an application. Care should be taken to maintain the creepage and clearance distance of a board design to ensure that the mounting pads of the isolator on the printed-circuit board do not reduce this distance. Creepage and clearance on a printed-circuit board become equal in certain cases. Techniques such as inserting grooves and/or ribs on a printed circuit board are used to help increase these specifications
(2) This coupler is suitable for safe electrical insulation only within the safety ratings. Compliance with the safety ratings shall be ensured by means of suitable protective circuits.
(3) Testing is carried out in air or oil to determine the intrinsic surge immunity of the isolation barrier.
(4) All pins on each side of the barrier tied together creating a two-terminal device.
6.7 Regulatory Information
All DW package certifications are complete. DWW package certifications are complete for UL, VDE and TUV and planned for CSA and CQC.| VDE | CSA | UL | CQC | TUV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certified according to DIN V VDE V 0884–10 (VDE V 0884–10):2006-12 and DIN EN 60950-1 (VDE 0805 Teil 1):2011-01 | Approved under CSA Component Acceptance Notice 5A, IEC 60950-1 and IEC 60601-1 | Certified according to UL 1577 Component Recognition Program | Certified according to GB 4943.1-2011 | Certified according to EN 61010-1:2010 (3rd Ed) and EN 60950-1:2006/A11:2009/A1:2010/ A12:2011/A2:2013 |
| Reinforced insulation Maximum transient isolation voltage, 8000 VPK; Maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage, 2121 VPK (DW), 2828 VPK (DWW); Maximum surge isolation voltage, 8000 VPK |
Reinforced insulation per CSA 60950-1-07+A1+A2 and IEC 60950-1 2nd Ed., 800 VRMS (DW) and 1450 VRMS (DWW) maximum working voltage (pollution degree 2, material group I); | Single protection, 5700 VRMS | Reinforced Insulation, Altitude ≤ 5000 m, Tropical Climate, 250 VRMS maximum working voltage | 5700 VRMS Reinforced insulation per EN 61010-1:2010 (3rd Ed) up to working voltage of 600 VRMS (DW package) and 1000 VRMS (DWW package) |
| 2 MOPP (Means of Patient Protection) per CSA 60601-1:14 and IEC 60601-1 Ed. 3.1, 250 VRMS (354 VPK) maximum working voltage | 5700 VRMS Reinforced insulation per EN 60950-1:2006/A11:2009/A1:2010/ A12:2011/A2:2013 up to working voltage of 800 VRMS (DW package) and 1450 VRMS (DWW package) |
|||
| Certificate number: 40040142 | Master contract number: 220991 | File number: E181974 | Certificate number: CQC15001121716 | Client ID number: 77311 |
6.8 Safety Limiting Values
Safety limiting intends to minimize potential damage to the isolation barrier upon failure of input or output circuitry. A failure of the I/O can allow low resistance to ground or the supply and, without current limiting, dissipate sufficient power to overheat the die and damage the isolation barrier potentially leading to secondary system failures.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DW PACKAGE | ||||||
| IS | Safety input, output, or supply current | RθJA = 81.1°C/W, VI = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 3 | 280 | mA | ||
| RθJA = 81.1°C/W, VI = 3.6 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 3 | 428 | |||||
| RθJA = 81.1°C/W, VI = 2.75 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 3 | 560 | |||||
| PS | Safety input, output, or total power | RθJA = 81.1°C/W, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 5 | 1541 | mW | ||
| TS | Maximum safety temperature | 150 | °C | |||
| DWW PACKAGE | ||||||
| IS | Safety input, output, or supply current | RθJA = 83.4°C/W, VI = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 4 | 273 | mA | ||
| RθJA = 83.4°C/W, VI = 3.6 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 4 | 416 | |||||
| RθJA = 83.4°C/W, VI = 2.75 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 4 | 545 | |||||
| PS | Safety input, output, or total power | RθJA = 83.4°C/W, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 6 | 1499 | mW | ||
| TS | Maximum safety temperature | 150 | °C | |||
The maximum safety temperature is the maximum junction temperature specified for the device. The power dissipation and junction-to-air thermal impedance of the device installed in the application hardware determines the junction temperature. The assumed junction-to-air thermal resistance in the Thermal Information is that of a device installed on a high-K test board for leaded surface mount packages. The power is the recommended maximum input voltage times the current. The junction temperature is then the ambient temperature plus the power times the junction-to-air thermal resistance.
6.9 Electrical Characteristics—5-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 5 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –4 mA; see Figure 13 | VCCO(1) – 0.4 | VCCO – 0.2 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 4 mA; see Figure 13 | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | ||
| VI(HYS) | Input threshold voltage hysteresis | 0.1 × VCCI(1) | V | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current | VIH = VCCI at INx or ENx | 10 | μA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current | VIL = 0 V at INx or ENx | –10 | μA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | VI = VCCI or 0 V, VCM = 1500 V; see Figure 16 | 100 | kV/μs | |||
| CI | Input capacitance (2) | VI = VCC / 2 + 0.4 × sin (2πft), f = 1 MHz, VCC = 5 V | 2 | pF | |||
(1) VCCI = Input-side VCC; VCCO = Output-side VCC.
(2) Measured from input pin to ground.
6.10 Supply Current Characteristics—5-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 5 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | SUPPLY CURRENT | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply current - disable | EN1 = EN2 = 0 V, VI = 0 V (Devices with suffix F), VI = VCCI (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 1 | 1.6 | mA | ||
| ICC2 | 0.8 | 1.3 | |||||
| EN2 = 0 V, VI = VCCI (Devices with suffix F), VI = 0 V (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 3.3 | 4.8 | ||||
| ICC2 | 2 | 2.9 | |||||
| Supply current - DC signal | VI = 0 V (Devices with suffix F), VI = VCCI (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 1.4 | 2.3 | |||
| ICC2 | 1.7 | 2.6 | |||||
| VI = VCCI (Devices with suffix F), VI = 0 V (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 3.8 | 5.6 | ||||
| ICC2 | 3 | 4.3 | |||||
| Supply current - AC signal | All channels switching with square wave clock input; CL = 15 pF |
1 Mbps | ICC1 | 2.6 | 4 | ||
| ICC2 | 2.4 | 3.6 | |||||
| 10 Mbps | ICC1 | 3.2 | 4.5 | ||||
| ICC2 | 3.4 | 4.6 | |||||
| 100 Mbps | ICC1 | 8.7 | 10.5 | ||||
| ICC2 | 13.2 | 15.8 | |||||
6.11 Electrical Characteristics—3.3-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 3.3 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –2 mA; see Figure 13 | VCCO(1) – 0.4 | VCCO – 0.2 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 2 mA; see Figure 13 | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | ||
| VI(HYS) | Input threshold voltage hysteresis | 0.1 × VCCI(1) | V | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current | VIH = VCCI at INx or ENx | 10 | μA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current | VIL = 0 V at INx or ENx | –10 | μA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | VI = VCCI or 0 V, VCM = 1500 V; see Figure 16 | 100 | kV/μs | |||
(1) VCCI = Input-side VCC; VCCO = Output-side VCC.
6.12 Supply Current Characteristics—3.3-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 3.3 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | SUPPLY CURRENT | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply current - disable | EN1 = EN2 = 0 V, VI = 0 V (Devices with suffix F), VI = VCCI (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 1 | 1.6 | mA | ||
| ICC2 | 0.8 | 1.3 | |||||
| EN1 = EN2 = 0 V, VI = VCCI (Devices with suffix F), VI = 0 V (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 3.3 | 4.8 | ||||
| ICC2 | 1.9 | 2.9 | |||||
| Supply current - DC signal | VI = 0 V (Devices with suffix F), VI = VCCI (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 1.4 | 2.3 | |||
| ICC2 | 1.7 | 2.6 | |||||
| VI = VCCI (Devices with suffix F), VI = 0 V (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 3.8 | 5.6 | ||||
| ICC2 | 2.9 | 4.3 | |||||
| Supply current - AC signal | All channels switching with square wave clock input; CL = 15 pF |
1 Mbps | ICC1 | 2.6 | 4 | ||
| ICC2 | 2.4 | 3.5 | |||||
| 10 Mbps | ICC1 | 3 | 4.3 | ||||
| ICC2 | 3.1 | 4.3 | |||||
| 100 Mbps | ICC1 | 6.9 | 8.3 | ||||
| ICC2 | 10.1 | 12.2 | |||||
6.13 Electrical Characteristics—2.5-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 2.5 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –1 mA; see Figure 13 | VCCO(1) – 0.4 | VCCO – 0.2 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 1 mA; see Figure 13 | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | ||
| VI(HYS) | Input threshold voltage hysteresis | 0.1 × VCCI(1) | V | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current | VIH = VCCI at INx or ENx | 10 | μA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current | VIL = 0 V at INx or ENx | –10 | μA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | VI = VCCI or 0 V, VCM = 1500 V; see Figure 16 | 100 | kV/μs | |||
(1) VCCI = Input-side VCC; VCCO = Output-side VCC.
6.14 Supply Current Characteristics—2.5-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 2.5 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | SUPPLY CURRENT | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply current - disable | EN1 = EN2 = 0 V, VI = 0 V (Devices with suffix F), VI = VCCI (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 0.9 | 1.6 | mA | ||
| ICC2 | 0.8 | 1.3 | |||||
| EN1 = EN2 = 0 V, VI = VCCI (Devices with suffix F), VI = 0 V (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 3.3 | 4.8 | ||||
| ICC2 | 1.9 | 2.9 | |||||
| Supply current - DC signal | VI = 0 V (Devices with suffix F), VI = VCCI (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 1.4 | 2.3 | |||
| ICC2 | 1.7 | 2.6 | |||||
| VI = VCCI (Devices with suffix F), VI = 0 V (Devices without suffix F) |
ICC1 | 3.8 | 5.6 | ||||
| ICC2 | 2.9 | 4.3 | |||||
| Supply current - AC signal | All channels switching with square wave clock input; CL = 15 pF |
1 Mbps | ICC1 | 2.6 | 4 | ||
| ICC2 | 2.3 | 3.5 | |||||
| 10 Mbps | ICC1 | 2.9 | 4.3 | ||||
| ICC2 | 2.9 | 4.1 | |||||
| 100 Mbps | ICC1 | 5.8 | 7.2 | ||||
| ICC2 | 8.2 | 10 | |||||
6.15 Switching Characteristics—5-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 5 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH, tPHL | Propagation delay time | See Figure 13 | 6 | 11 | 16 | ns | |
| PWD | Pulse width distortion(1) |tPHL – tPLH| | 0.55 | 4.1 | ns | |||
| tsk(o) | Channel-to-channel output skew time(2) | Same-direction channels | 2.5 | ns | |||
| tsk(pp) | Part-to-part skew time(3) | 4.5 | ns | ||||
| tr | Output signal rise time | See Figure 13 | 1.7 | 3.9 | ns | ||
| tf | Output signal fall time | 1.9 | 3.9 | ns | |||
| tPHZ | Disable propagation delay, high-to-high impedance output | See Figure 14 | 12 | 20 | ns | ||
| tPLZ | Disable propagation delay, low-to-high impedance output | 12 | 20 | ns | |||
| tPZH | Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-high output for ISO7831 | 10 | 20 | ns | |||
| Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-high output for ISO7831F | 2 | 2.5 | μs | ||||
| tPZL | Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-low output for ISO7831 | 2 | 2.5 | μs | |||
| Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-low output for ISO7831F | 10 | 20 | ns | ||||
| tDO | Default output delay time from input power loss | Measured from the time VCC goes below 1.7 V. See Figure 15 | 0.2 | 9 | μs | ||
| tie | Time interval error | 216 – 1 PRBS data at 100 Mbps | 0.90 | ns | |||
(1) Also known as pulse skew.
(2) tsk(o) is the skew between outputs of a single device with all driving inputs connected together and the outputs switching in the same direction while driving identical loads.
(3) tsk(pp) is the magnitude of the difference in propagation delay times between any terminals of different devices switching in the same direction while operating at identical supply voltages, temperature, input signals and loads.
6.16 Switching Characteristics—3.3-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 3.3 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH, tPHL | Propagation delay time | See Figure 13 | 6 | 10.8 | 16 | ns | |
| PWD | Pulse width distortion(1) |tPHL – tPLH| | 0.7 | 4.2 | ns | |||
| tsk(o) | Channel-to-channel output skew time(2) | Same-direction channels | 2.2 | ns | |||
| tsk(pp) | Part-to-part skew time(3) | 4.5 | ns | ||||
| tr | Output signal rise time | See Figure 13 | 0.8 | 3 | ns | ||
| tf | Output signal fall time | 0.8 | 3 | ns | |||
| tPHZ | Disable propagation delay, high-to-high impedance output | See Figure 14 | 17 | 32 | ns | ||
| tPLZ | Disable propagation delay, low-to-high impedance output | 17 | 32 | ns | |||
| tPZH | Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-high output for ISO7831 | 17 | 32 | ns | |||
| Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-high output for ISO7831F | 2 | 2.5 | μs | ||||
| tPZL | Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-low output for ISO7831 | 2 | 2.5 | μs | |||
| Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-low output for ISO7831F | 17 | 32 | ns | ||||
| tDO | Default output delay time from input power loss | Measured from the time VCC goes below 1.7 V. See Figure 15 | 0.2 | 9 | μs | ||
| tie | Time interval error | 216 – 1 PRBS data at 100 Mbps | 0.91 | ns | |||
(1) Also known as pulse skew.
(2) tsk(o) is the skew between outputs of a single device with all driving inputs connected together and the outputs switching in the same direction while driving identical loads.
(3) tsk(pp) is the magnitude of the difference in propagation delay times between any terminals of different devices switching in the same direction while operating at identical supply voltages, temperature, input signals and loads.
6.17 Switching Characteristics—2.5-V Supply
VCC1 = VCC2 = 2.5 V ±10% (over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH, tPHL | Propagation delay time | See Figure 13 | 7.5 | 11.7 | 17.5 | ns |
| PWD | Pulse width distortion(1) |tPHL – tPLH| | 0.66 | 4.2 | ns | ||
| tsk(o) | Channel-to-channel output skew time(2) | Same-direction Channels | 2.2 | ns | ||
| tsk(pp) | Part-to-part skew time(3) | 4.5 | ns | |||
| tr | Output signal rise time | See Figure 13 | 1 | 3.5 | ns | |
| tf | Output signal fall time | 1.2 | 3.5 | ns | ||
| tPHZ | Disable propagation delay, high-to-high impedance output | See Figure 14 | 22 | 45 | ns | |
| tPLZ | Disable propagation delay, low-to-high impedance output | 22 | 45 | ns | ||
| tPZH | Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-high output for ISO7831 | 18 | 45 | ns | ||
| Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-high output for ISO7831F | 2 | 2.5 | μs | |||
| tPZL | Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-low output for ISO7831 | 2 | 2.5 | μs | ||
| Enable propagation delay, high impedance-to-low output for ISO7831F | 18 | 45 | ns | |||
| tDO | Default output delay time from input power loss | Measured from the time VCC goes below 1.7 V. See Figure 15 | 0.2 | 9 | μs | |
| tie | Time interval error | 216 – 1 PRBS data at 100 Mbps | 0.91 | ns | ||
(1) Also known as pulse skew.
(2) tsk(o) is the skew between outputs of a single device with all driving inputs connected together and the outputs switching in the same direction while driving identical loads.
(3) tsk(pp) is the magnitude of the difference in propagation delay times between any terminals of different devices switching in the same direction while operating at identical supply voltages, temperature, input signals and loads.
6.18 Insulation Characteristics Curves

| TA upto 150°C | Operating lifetime = 135 years | |
| Stress-voltage frequency = 60 Hz | ||
| Isolation working voltage = 1500 VRMS | ||
 Figure 5. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Power for DW Package
Figure 5. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Power for DW Package

| TA upto 150°C | Operating lifetime = 34 years | |
| Stress-voltage frequency = 60 Hz | ||
| Isolation working voltage = 2000 VRMS | ||
 Figure 4. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Current for DWW Package
Figure 4. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Current for DWW Package
 Figure 6. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Power for DWW Package
Figure 6. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Power for DWW Package
6.19 Typical Characteristics
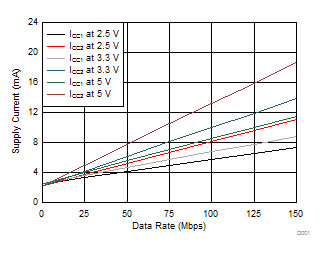
| TA = 25°C | CL = 15 pF |

| TA = 25°C |


| TA = 25°C | CL = No Load |

| TA = 25°C |

