JAJSIK2B february 2020 – december 2020 ISOW7841A-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description Continued
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Ratings
- 7.6 Insulation Specifications
- 7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 7.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics—5-V Input, 5-V Output
- 7.10 Supply Current Characteristics—5-V Input, 5-V Output
- 7.11 Electrical Characteristics—3.3-V Input, 5-V Output
- 7.12 Supply Current Characteristics—3.3-V Input, 5-V Output
- 7.13 Electrical Characteristics—5-V Input, 3.3-V Output
- 7.14 Supply Current Characteristics—5-V Input, 3.3-V Output
- 7.15 Electrical Characteristics—3.3-V Input, 3.3-V Output
- 7.16 Supply Current Characteristics—3.3-V Input, 3.3-V Output
- 7.17 Switching Characteristics—5-V Input, 5-V Output
- 7.18 Switching Characteristics—3.3-V Input, 5-V Output
- 7.19 Switching Characteristics—5-V Input, 3.3-V Output
- 7.20 Switching Characteristics—3.3-V Input, 3.3-V Output
- 7.21 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 7.22 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.22 Typical Characteristics

| VISO = 3.3 V | TA = 25°C |

| TA = 25°C |

| TA = 25°C |
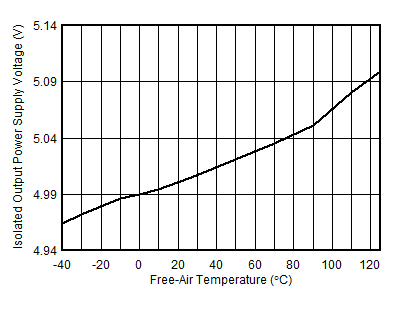
| No IISO load | VCC = 5 V | VISO = 5 V |

| CL = 15 pF | TA = 25°C | No IISO load |


| TA = 25°C |

| VCC = 5 V | VISO = 3.3 V | |
| Negligible undershoot and overshoot because of load transient | ||

| VCC = 5 V | VISO = 3.3 V | |
| Input current spike is because of charging the input supply decoupling capacitor | ||

| VCC = 5 V | VISO = 5 V | |
| Input current spike is because of charging the input supply decoupling capacitor | ||

| VCC = 5 V | VISO = 3.3 V |

| VISO = 5 V | TA = 25°C |

| TA = 25°C |

| No IISO load | VCC = 5 V | VISO = 3.3 V |

| VISO shorted to GND2 | TA = 25°C |

| CL = no load | TA = 25°C | No IISO load |


| TA = 25°C |

| VCC = 5 V | VISO = 3.3 V | |
| Current spike is because of charging the input supply capacitor | ||

| VCC = 5 V | VISO = 5 V | |
| Input current spike is because of charging the input supply decoupling capacitor | ||

| VCC = 5 V | VISO = 5 V | |