JAJSDG8F July 2011 – March 2018 LM25118
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 R7 = RT
- 8.2.2.3 Inductor Selection – L1
- 8.2.2.4 R13 = RSENSE
- 8.2.2.5 C15 = CRAMP
- 8.2.2.6 Inductor Current Limit Calculation
- 8.2.2.7 C9 - C12 = Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.8 D1
- 8.2.2.9 D4
- 8.2.2.10 C1 – C5 = Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 C20
- 8.2.2.12 C8
- 8.2.2.13 C16 = CSS
- 8.2.2.14 R8, R9
- 8.2.2.15 R1, R3, C21
- 8.2.2.16 R2
- 8.2.2.17 Snubber
- 8.2.2.18 Error Amplifier Configuration
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|20
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|20
発注情報
8.2.2.7 C9 - C12 = Output Capacitors
In buck-boost mode, the output capacitors C9 – C12 must supply the entire output current during the switch on-time. For this reason, the output capacitors are chosen for operation in buck-boost mode, the demands being much less in buck operation. Both bulk capacitance and ESR must be considered to ensure a given output ripple voltage. Buck-boost mode capacitance can be estimated from:
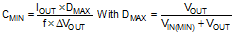
ESR requirements can be estimated from:
For this example, with a ΔVOUT (output ripple) of 50 mV:
If hold-up times are a consideration, the values of input and output capacitors must be increased appropriately. Note that it is usually advantageous to use multiple capacitors in parallel to achieve the ESR value required. Also, it is good practice to put a 0.1-µF to 0.47-µF ceramic capacitor directly on the output pins of the supply to reduce high-frequency noise. Ceramic capacitors have good ESR characteristics, and are a good choice for input and output capacitors. Note that the effective capacitance of ceramic capacitors decreases with DC bias. For larger bulk values of capacitance, a low-ESR electrolytic is usually used. However, electrolytic capacitors have poor tolerance, especially over temperature, and the selected value should be selected larger than the calculated value to allow for temperature variation. Allowing for component tolerances, the following values of Cout were chosen for this design example:
Two 180-µF Oscon electrolytic capacitors for bulk capacitance
Two 47-µF ceramic capacitors to reduce ESR
Two 0.47-µF ceramic capacitors to reduce spikes at the output