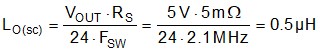JAJSJI6B December 2020 – January 2023 LM25149-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 概要 (続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 8.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, VCCX, VDDA)
- 8.3.3 Precision Enable (EN)
- 8.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PG)
- 8.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 8.3.6 Active EMI Filter
- 8.3.7 Dual Random Spread Spectrum (DRSS)
- 8.3.8 Soft Start
- 8.3.9 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB)
- 8.3.10 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 8.3.11 Error Amplifier and PWM Comparator (FB, EXTCOMP)
- 8.3.12 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.13 Inductor Current Sense (ISNS+, VOUT)
- 8.3.14 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting
- 8.3.15 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO, LO)
- 8.3.16 Output Configurations (CNFG)
- 8.3.17 Single-Output Dual-Phase Operation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Design 1 – High-Efficiency 2.1-MHz Synchronous
Buck Regulator
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.1.2.2 Custom Design With Excel Quickstart Tool
- 9.2.1.2.3 Buck Inductor
- 9.2.1.2.4 Current-Sense Resistance
- 9.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitors
- 9.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitors
- 9.2.1.2.7 Frequency Set Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.8 Feedback Resistors
- 9.2.1.2.9 Compensation Components
- 9.2.1.2.10 Active EMI Components
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2 Design 2 – High Efficiency 440-kHz Synchronous Buck Regulator
- 9.2.3 Design 3 – Dual-Phase 400-kHz 20-A Synchronous Buck Regulator
- 9.2.1
Design 1 – High-Efficiency 2.1-MHz Synchronous
Buck Regulator
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGY|24
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGY|24
発注情報
9.2.1.2.3 Buck Inductor
- Use Equation 34 to calculate the required buck inductance based on a 30% inductor ripple current at
nominal input voltages. Equation 34.
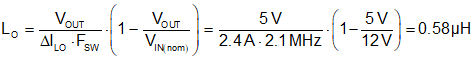
- Select a standard inductor value of 0.56 µH or
use a 0.68 µH to account for effective inductance derating with current of molded
inductors. Use Equation 35 to calculate the peak inductor current at maximum steady-state input voltage.
Subharmonic oscillation occurs with a duty cycle greater than 50% for peak current-mode
control. For design simplification, the LM25149-Q1 has an internal slope compensation ramp proportional to the switching
frequency that is added to the current sense signal to damp any tendency toward
subharmonic oscillation. Equation 35.
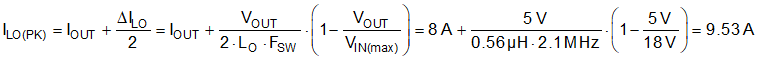
- Based on Equation 9, use Equation 36 to cross-check the inductance to set a slope compensation close to the ideal one times
the inductor current downslope.Equation 36.