SNAS888A September 2024 – November 2024 LMK1D2102L , LMK1D2106L
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RHA|40
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
7 Parameter Measurement Information
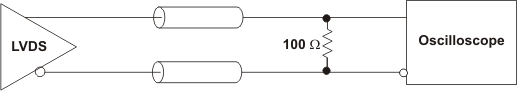 Figure 7-1 LVDS Output DC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 7-1 LVDS Output DC Configuration During Device Test Figure 7-2 LVDS Output AC
Configuration During Device Test
Figure 7-2 LVDS Output AC
Configuration During Device Test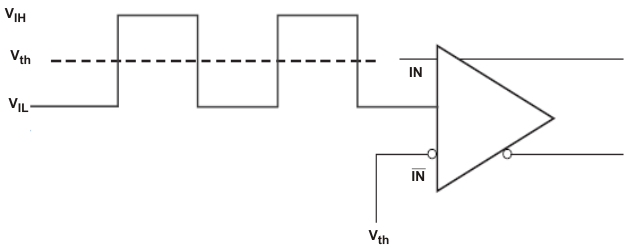 Figure 7-3 DC-Coupled LVCMOS Input During Device Test
Figure 7-3 DC-Coupled LVCMOS Input During Device Test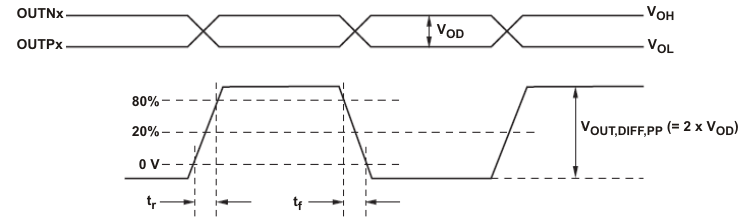 Figure 7-4 Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
Figure 7-4 Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
A. Output skew is calculated as the greater
of the following: the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPLHn or
the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPHLn (n = 0, 1, 2,
..N)
B. Part-to-part skew is calculated as the
greater of the following: the difference between the fastest and the slowest
tPLHn or the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPHLn
across multiple devices (n = 0, 1, 2, ..N)
Figure 7-5 Output Skew and
Part-to-Part Skew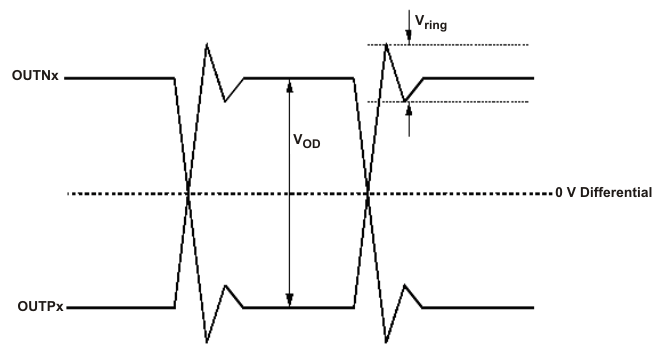 Figure 7-6 Output Overshoot and Undershoot
Figure 7-6 Output Overshoot and Undershoot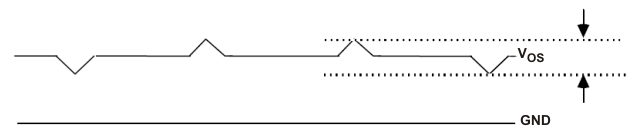 Figure 7-7 Output AC Common Mode
Figure 7-7 Output AC Common Mode