-
LMK5B12204 2 つの周波数ドメインに対応した超低ジッタ・ネットワーク・シンクロナイザ・クロック
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 概要 (続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Oscillator Input (XO_P/N)
- 9.3.2 Reference Inputs (PRIREF_P/N and SECREF_P/N)
- 9.3.3 Clock Input Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.4 Reference Input Mux Selection
- 9.3.5 Hitless Switching
- 9.3.6 Gapped Clock Support on Reference Inputs
- 9.3.7 Input Clock and PLL Monitoring, Status, and Interrupts
- 9.3.8
PLL Relationships
- 9.3.8.1 PLL Frequency Relationships
- 9.3.8.2 Analog PLLs (APLL1, APLL2)
- 9.3.8.3 APLL Reference Paths
- 9.3.8.4 APLL Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) and Charge Pump
- 9.3.8.5 APLL Feedback Divider Paths
- 9.3.8.6 APLL Loop Filters (LF1, LF2)
- 9.3.8.7 APLL Voltage Controlled Oscillators (VCO1, VCO2)
- 9.3.8.8 APLL VCO Clock Distribution Paths (P1, P2)
- 9.3.8.9 DPLL Reference (R) Divider Paths
- 9.3.8.10 DPLL Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)
- 9.3.8.11 DPLL Loop Filter (DLF)
- 9.3.8.12 DPLL Feedback (FB) Divider Path
- 9.3.9 Output Clock Distribution
- 9.3.10 Output Channel Muxes
- 9.3.11 Output Dividers (OD)
- 9.3.12 Clock Outputs (OUTx_P/N)
- 9.3.13 Glitchless Output Clock Start-Up
- 9.3.14 Clock Output Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.15 Output Synchronization (SYNC)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- 重要なお知らせ
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGZ|48
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGZ|48
発注情報
DATA SHEET
LMK5B12204 2 つの周波数ドメインに対応した超低ジッタ・ネットワーク・シンクロナイザ・クロック
このリソースの元の言語は英語です。 翻訳は概要を便宜的に提供するもので、自動化ツール (機械翻訳) を使用していることがあり、TI では翻訳の正確性および妥当性につきましては一切保証いたしません。 実際の設計などの前には、ti.com で必ず最新の英語版をご参照くださいますようお願いいたします。
1 特長
- デジタル・フェーズ・ロック・ループ (DPLL) ×1:
- ヒットレス・スイッチング:± 50ps の位相過渡応答
- プログラミング可能な Fastlock によるループ帯域幅
- 低コストの TCXO/OCXO を使用する規格準拠の同期およびホールドオーバー
- 業界をリードするジッタ性能を備えたアナログ・フェーズ・ロック・ループ (APLL) ×2:
- 312.5MHz で 50fs の RMS ジッタ (APLL1)
- 155.52MHz で 125fs の RMS ジッタ (APLL2)
- 基準クロック入力 ×2
- 優先度に基づく入力選択
- 基準喪失時のデジタル・ホールドオーバー
- とプログラマブル・ドライバ付きの 4 つのクロック出力
- 最大 4 種類の出力周波数
- AC-LVDS、AC-CML、AC-LVPECL、HCSL、および 1.8V の LVCMOS 出力フォーマット
- 起動時のカスタム・クロック用 EEPROM/ROM
- 柔軟な構成オプション
- 入力 で 1Hz (1PPS)~800MHz
- XO/TCXO/OCXO 入力: 10~100MHz
- DCO モード:0.001ppb/ステップ未満で高精度のクロック・ステアリングを実現 (IEEE 1588 PTP スレーブ)
- 高度なクロック監視およびステータス
- I2Cまたは SPI インターフェイス
- PSNR:–83dBc (3.3V 電源で 50mVpp のノイズ)
- 3.3V 電源、1.8V、2.5V、または3.3V 出力
- 産業用温度範囲:-40℃~+85℃
2 アプリケーション
- SyncE (G.8262)、SONET/SDH (Stratum 3/3E、G.813、GR-1244、GR-253)、IEEE 1588 PTP スレーブ・クロック、または光伝送ネットワーク(G.709)
- イーサネット・スイッチおよびルーター用 400G ライン・カード、ファブリック・カード
- 無線基地局 (BTS)、ワイヤレス・バックホール
- 試験および測定機器、医用画像処理
- 56G/112G PAM-4 PHY、ASIC、FPGA、SoC、プロセッサにおけるジッタ・クリーニング、ワンダ減衰、基準クロック生成
3 概要
LMK5B12204 は高性能のネットワーク・シンクロナイザ・クロックであり、ジッタ・クリーニング、クロック生成、高度なクロック監視、優れたヒットレス・スイッチング性能により、通信インフラおよび産業機器の厳しいタイミング要件を満たすことができます。超低ジッタ・高PSNR (電源ノイズ除去性能) により、高速シリアル・リンクにおけるビット誤り率 (BER) を低減します。
TI 独自のバルク弾性波 (BAW) VCO テクノロジー により、XO および基準入力のジッタおよび周波数に関係なく、50fs の RMS ジッタで出力クロックを生成できます。
製品情報
| 部品番号 | パッケージ (1) | 本体サイズ (公称) |
|---|---|---|
| LMK5B12204 | VQFN (48) | 7.00mm × 7.00mm |
(1) 利用可能なすべてのパッケージについては、このデータシートの末尾にある注文情報を参照してください。
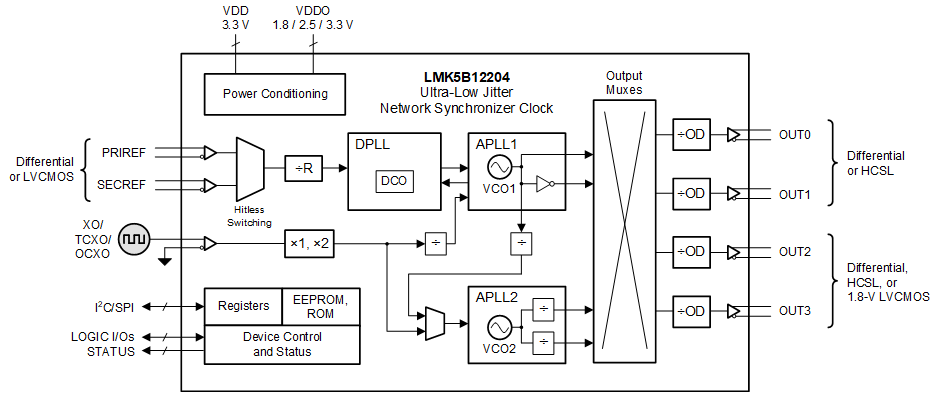 ブロック概略図
ブロック概略図