JAJSJG0A May 2020 – January 2021 LMK5B12204
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 概要 (続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Oscillator Input (XO_P/N)
- 9.3.2 Reference Inputs (PRIREF_P/N and SECREF_P/N)
- 9.3.3 Clock Input Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.4 Reference Input Mux Selection
- 9.3.5 Hitless Switching
- 9.3.6 Gapped Clock Support on Reference Inputs
- 9.3.7 Input Clock and PLL Monitoring, Status, and Interrupts
- 9.3.8
PLL Relationships
- 9.3.8.1 PLL Frequency Relationships
- 9.3.8.2 Analog PLLs (APLL1, APLL2)
- 9.3.8.3 APLL Reference Paths
- 9.3.8.4 APLL Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) and Charge Pump
- 9.3.8.5 APLL Feedback Divider Paths
- 9.3.8.6 APLL Loop Filters (LF1, LF2)
- 9.3.8.7 APLL Voltage Controlled Oscillators (VCO1, VCO2)
- 9.3.8.8 APLL VCO Clock Distribution Paths (P1, P2)
- 9.3.8.9 DPLL Reference (R) Divider Paths
- 9.3.8.10 DPLL Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)
- 9.3.8.11 DPLL Loop Filter (DLF)
- 9.3.8.12 DPLL Feedback (FB) Divider Path
- 9.3.9 Output Clock Distribution
- 9.3.10 Output Channel Muxes
- 9.3.11 Output Dividers (OD)
- 9.3.12 Clock Outputs (OUTx_P/N)
- 9.3.13 Glitchless Output Clock Start-Up
- 9.3.14 Clock Output Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.15 Output Synchronization (SYNC)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGZ|48
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGZ|48
発注情報
9.5.3 SPI Serial Interface
When started in SPI mode (HW_SW_CTRL = Float or VIM), the device uses a 4-wire SPI interface with SDI, SCK, SDO, and SCS signals. The host device must present data to the device MSB first. A message includes a transfer direction bit ( W/R), a 15-bit address field (A14 to A0), and a 8-bit data field (D7 to D0) as shown in Figure 9-38. The W/R bit is 0 for a SPI write and 1 for a SPI read.
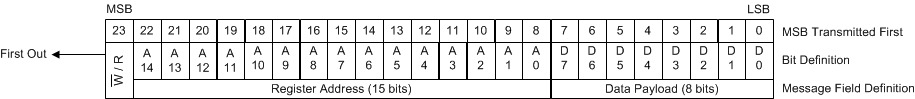 Figure 9-38 SPI Message Format
Figure 9-38 SPI Message FormatA message frame is initiated by asserting SCS low. The frame ends when SCS is deasserted high. The first bit transferred is the W/R bit. The next 15 bits are the register address, and the remaining eight bits are data. On write transfers, data is committed in bytes as the final data bit (D0) is clocked in on the rising edge of SCK. If the write access is not an even multiple of eight clocks, the trailing data bits are not committed. On read transfers, data bits are clocked out from the SDO pin on the falling edges of SCK.