SNAS633A March 2014 – September 2014 LMP93601
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Thermopile Array System Diagram
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Data Format
- 8.3.2 Transfer Function
- 8.3.3 Input Routing Mux
- 8.3.4 Programmable Gain Amplifier
- 8.3.5 PGA Bypass Mode
- 8.3.6 Over-Range Detection
- 8.3.7 Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 8.3.8 Programmable Digital Filters
- 8.3.9 Common Mode Voltage Generator
- 8.3.10 Low Drop-Out Regulator (LDO)
- 8.3.11 External Clock
- 8.3.12 Operating Modes
- 8.3.13 Data Ready Function (DRDYB)
- 8.3.14 Synchronous Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 8.3.15 Power Management Mode; Standby, Conversion and Shutdown
- 8.3.16 Power-On Sequence and Reset (POR) Function
- 8.3.17 Brown-Out Detection Function
- 8.3.18 Reset Function
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 8.7 Multi Byte Access (Auto Increment) Mode
- 8.8 Multi-Channel Data Read
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Supply Voltage, AVDD | -0.3 | 6.0 | V | |
| Digital Supply Range, IOVDD; ( IOVDD must always be lower than or equal to AVDD supply) | -0.3 | 6.0 | V | |
| Voltage between any two analog pins | 6.0 | V | ||
| Voltage between any two digital pins | 6.0 | V | ||
| Voltage between XCAP2 and any GND (A, D or IO) | 2.2 | V | ||
| Input current at any pin | -5.0 | +5.0 | mA | |
| Junction Temperature | 125 | °C | ||
(1) The input negative-voltage and output voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output current ratings are observed.
Handling Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | 150 | °C | ||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | 2000 K | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | 500 | ||||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 2000 -V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 500-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Supply Voltage, AVDD | 2.7 | 5.5 | V | |
| Fclk | 3.6 | 4.4 | MHz | |
| Digital Supply Voltage, IOVDD | 2.7 | AVDD | V | |
| Supply Ground | AGND = DGND = IOGND | |||
| Temperature range | -25 | 85 | °C | |
7.3 Thermal Information
| SYMBOL | THERMAL METRIC | WQFN 24 PINS |
UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|
| ΘJA | Thermal resistance, junction to ambient | 37.9 | °C/W |
| ΘJC | Thermal resistance, junction to case | 4.8 | °C/W |
| ΨJB | Thermal resistance, junction to board | 19.4 | °C/W |
7.4 Electrical Characteristics
Typical conditions: TA=+25⁰C, AVDD=IOVDD=3.3 V, INP1/INN1 enabled with VICM=AVDD/3. PGA gain=64, PGA over-range masked, digital gain=1. SPS select=1057 SPS. fXCLK=4.00 MHz. Conversion power mode. XCAP1=1 uF. XCAP2=0.1 uF.| SYMBOL | PARAMETER | TEST CONDITION | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUTS | ||||||
| XTLK | Crosstalk across input channels | Channel1 enabled with a 100 kΩ resistor as input, channel 2 disabled with 1 V peak-peak , 100 Hz signal as input. | 80 | dB | ||
| Zin | Differential input impedance | 10//7 | MΩ//pF (4) | |||
| Common mode input impedance | 100//4.5 | MΩ//pF(4) | ||||
| IB | Input bias current | -1.3 | nA | |||
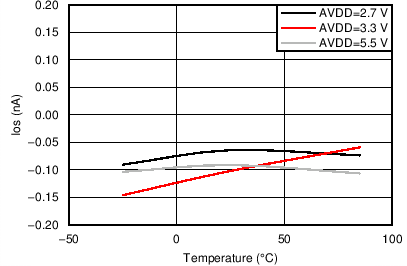
| Ios | Input offset current on differential channels | Maximum of INP1-INN1, .., INP3-INN3 | -200 | pA | ||
| TCIos | Input offset current drift on differential channels | Maximum of INP1-INN1, .., INP3-INN3 | -0.5 | pA/⁰C | ||
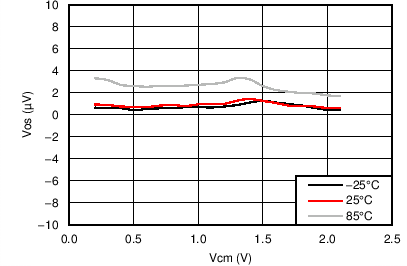
| Vos | Input referred offset voltage | Input short on chip, PGA 64 DG =1, CH1 | -15 | 1 | +15 | uV(5) |
| TCVos | Input referred offset drift with temperature | Input short on chip | 50 | nV/⁰C | ||
| Vdiff | Input differential range for AVDD≥3V | Programmable gain settings =16; ± 3% | -64 | +64 | mV | |
| Programmable gain settings =32; ± 3% | -32 | +32 | ||||
| Programmable gain settings =64; ± 3% | -16 | +16 | ||||
| Programmable gain settings = 128; ± 3% | ± 8 | |||||
| PGA bypass | ±1 | V | ||||
| VICM | Input common mode range. | PGA = 64 V/V; CMRR ≥ 80 dB | 0.3 | AVDD-1.4 | V(2) | |
| PGA = 64 V/V ; CMRR ≥ 72 dB -25 C to 85 C |
0.4 | AVDD-1.45 | ||||
| BW | Channel bandwidth | See Figure 16 | Hz | |||
| ODR | Output data rate | 265 | SPS | |||
| 530 | ||||||
| 1057 | ||||||
| 1326 | ||||||
| PGA | Programmable gain settings | 16, 32 , 64 and 128 | V/V | |||
| Bypass mode | 1 | V/V | ||||
| Digital Gain | Programmable gain settings | 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 | V/V | |||
| Total AFE Gain | Programmable gain settings (analog and digital) | 16 - 4096 | V/V | |||
| Gain steps | 2 x | |||||
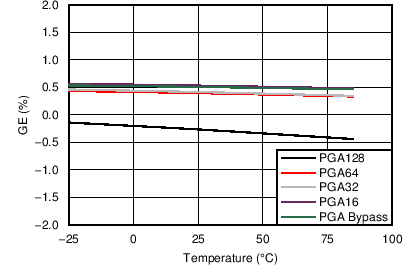
| GE | Gain error | 0.3 % | ||||
| PGA bypassed | -0.3 % | |||||
| GE drift with temperature | -9 | ppm/⁰C | ||||
| ENOB(1) | Effective number of bits | 15.3 | Bits | |||
| THD | Total harmonic distortion (Linearity) | 100 Hz, 50 mVpp differential input, PGA 16 V/V | 91 | dB | ||
| Noise | RMS noise in a 1 kHz BW | PGA = 64 V/V | 0.67(6) | uVrms | ||
| 1/ƒ noise corner | 1 | Hz | ||||
| CMRR | Common mode rejection ratio (at DC) | VICM = 0.3 to AVDD-1.4 V | 80 | 127 | dB(2) | |
| VICM = 0.4 to AVDD-1.45 V, over operating temperature range -25 C to 85 C |
72 | 127 | ||||
| PSRR | Power supply rejection ratio (at DC) | Supply ; 2.7 to 5.5 V | 80 | 120 | dB(2) | |
| Supply ; 2.7 to 5.5 V, over operating temperature range -25 C to 85 C |
72 | 120 | ||||
| EMIRR | EMI rejection ratio | VRF = 100 mVPP | dB | |||
| f=400 MHz | 86 | |||||
| f=900 MHz | 87 | |||||
| f=1800 MHz | 85 | |||||
| f=2400 MHz | 84 | |||||
| VCM | ||||||
| V VCM | Output voltage | AVDD/3 | V | |||
| Tstrp VCM | Startup time | To within 90% of final value | 10 | ms | ||
| Acc VCM | Accuracy | 0.2 | % | |||
| TC VCM | Drift over temperature | 0.5 | ppm/⁰C | |||
| I VCM | Output current | 0.5 | mA | |||
| Load regulation | 0 to 200uA | 4 | 15 | mV | ||
| Zload VCM | Load range | 2.2//100 | MΩ//nF | |||
| SLAVE SPI INTERFACE | ||||||
| Clock frequency | 1 | 20 | MHz | |||
| DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VIH | Logical “1” Input Voltage | 0.7x IOVDD |
V | |||
| VIL | Logical “0” Input Voltage | 0.3x IOVDD |
V | |||
| VOH | Isource=300uA | IOVDD- 0.150 |
||||
| VOL | Isink=300uA | IOGND +0.150 |
||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| AVDD | Analog supply voltage range | 2.7 | 5.5 | V | ||
| IOVDD | Digital supply voltage range | AVDD ≥ IOVDD | AVDD | V(3) | ||
| SUPPLY CURRENT | ||||||
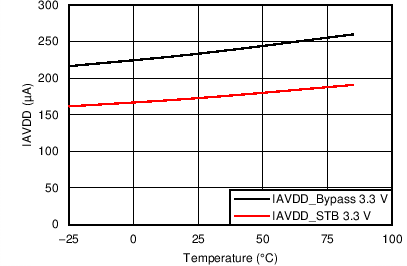
| IIOVDD | Digital on AFE | Shutdown Mode, XCLK off | 0.1 | 1 | µA | |
| Standby Mode | 1.9 | 25 | µA | |||
| Conversion Power Mode | 2.7 | 25 | µA | |||
| Conversion Power Mode, PGA bypassed |
3 | µA | ||||
| IAVDD | Analog on AFE | Shutdown Mode, XCLK off | 0.1 | 1 | µA | |
| Standby Mode | 175 | 250 | µA | |||
| Conversion Power Mode | 1.1 | 1.6 | mA | |||
| Conversion Power Mode, 230 μA PGA bypassed | 230 | µA | ||||
| TEMPERATURE RANGE | ||||||
| Operating | –25 | 85 | °C | |||
(1) ENOB is a DC ENOB spec, not the dynamic ENOB that is measured using FFT and SINAD:
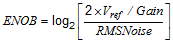
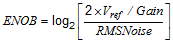
(2) Temperature limits are ensured by statistical analysis or design
(3) IOVDD always ≤ AVDD and IOVDD minimum is 2.7 V
(4) Value from simulation
(5) The input referred offset is measure by an on-chip short.
(6) See Table 1 for detailed noise performance
7.5 Timing Requirements
Under typical conditions with maximum total load capacitance 10 pF.| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPH | High Period, SCLK | 25 | ns | ||
| tPL | Low Period, SCLK | 25 | ns | ||
| tSU | SDI input setup time | 10 | ns | ||
| tH | SDI input hold time | 10 | ns | ||
| tOD | SDO output hold time | 13.5 | ns | ||
| tCSS | CSB setup time | 25 | ns | ||
| tCSH | CSB hold time | 25 | ns | ||
| tIAG | CSB high time | 50 | ns |
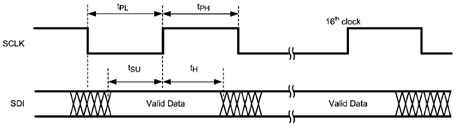 Figure 1. SPI Write Timing Diagram
Figure 1. SPI Write Timing Diagram
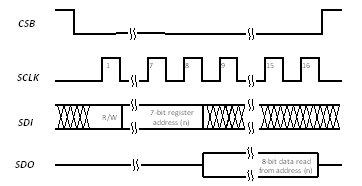 Figure 2. SPI Read Timing Diagram
Figure 2. SPI Read Timing Diagram
7.6 Noise Performance
Table 1. Noise In µVRMS at AVDD= 3.3 V, AGND = 0 V, and Internal Reference = 2.4 VRMS
| ODR (SPS) | PGA Gain (V/V) | D-Gain (V/V) | Vn (uVrms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 265 | 16 | 1 | Below the resolution of the 16 bit SDM. |
| 2 | Below the resolution of the 16 bit SDM. |
||
| 4 | 0.661 | ||
| 8 | 0.597 | ||
| 16 | 0.578 | ||
| 32 | 0.574 | ||
| 32 | 1 | Below the resolution of the 16 bit SDM. |
|
| 2 | 0.516 | ||
| 4 | 0.396 | ||
| 8 | 0.368 | ||
| 16 | 0.361 | ||
| 32 | 0.362 | ||
| 64 | 1 | 0.556 | |
| 2 | 0.321 | ||
| 4 | 0.287 | ||
| 8 | 0.281 | ||
| 16 | 0.275 | ||
| 32 | 0.277 | ||
| 128 | 1 | 0.298 | |
| 2 | 0.254 | ||
| 4 | 0.247 | ||
| 8 | 0.242 | ||
| 16 | 0.242 | ||
| 32 | 0.240 | ||
| 530 | 16 | 1 | Below the resolution of the 16 bit SDM. |
| 2 | 0.944 | ||
| 4 | 0.888 | ||
| 8 | 0.831 | ||
| 16 | 0.810 | ||
| 32 | 0.816 | ||
| 32 | 1 | 0.509 | |
| 2 | 0.609 | ||
| 4 | 0.543 | ||
| 8 | 0.517 | ||
| 16 | 0.521 | ||
| 32 | 0.511 | ||
| 64 | 1 | 0.569 | |
| 2 | 0.421 | ||
| 4 | 0.397 | ||
| 8 | 0.396 | ||
| 16 | 0.397 | ||
| 32 | 0.395 | ||
| 128 | 1 | 0.377 | |
| 2 | 0.348 | ||
| 4 | 0.340 | ||
| 8 | 0.341 | ||
| 16 | 0.340 | ||
| 32 | 0.339 | ||
| 1057 | 16 | 1 | 1.565 |
| 2 | 1.517 | ||
| 4 | 1.410 | ||
| 8 | 1.409 | ||
| 16 | 1.398 | ||
| 32 | 1.401 | ||
| 32 | 1 | 0.932 | |
| 2 | 0.903 | ||
| 4 | 0.834 | ||
| 8 | 0.839 | ||
| 16 | 0.829 | ||
| 32 | 0.824 | ||
| 64 | 1 | 0.667 | |
| 2 | 0.596 | ||
| 4 | 0.580 | ||
| 8 | 0.580 | ||
| 16 | 0.579 | ||
| 32 | 0.574 | ||
| 128 | 1 | 0.501 | |
| 2 | 0.481 | ||
| 4 | 0.476 | ||
| 8 | 0.476 | ||
| 16 | 0.473 | ||
| 32 | 0.470 | ||
| 1326 | 16 | 1 | 2.331 |
| 2 | 1.743 | ||
| 4 | 1.743 | ||
| 8 | 1.665 | ||
| 16 | 1.648 | ||
| 32 | 1.681 | ||
| 32 | 1 | 1.189 | |
| 2 | 0.975 | ||
| 4 | 0.981 | ||
| 8 | 0.954 | ||
| 16 | 0.941 | ||
| 32 | 0.937 | ||
| 64 | 1 | 0.733 | |
| 2 | 0.677 | ||
| 4 | 0.670 | ||
| 8 | 0.667 | ||
| 16 | 0.660 | ||
| 32 | 0.663 | ||
| 128 | 1 | 0.575 | |
| 2 | 0.546 | ||
| 4 | 0.541 | ||
| 8 | 0.537 | ||
| 16 | 0.540 | ||
| 32 | 0.538 |
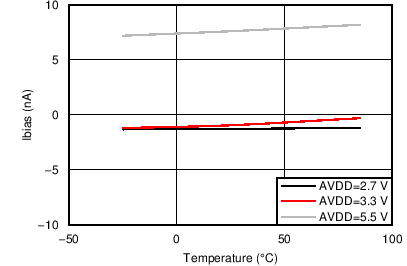
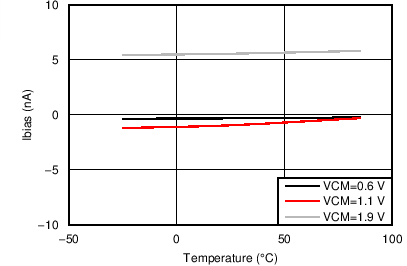
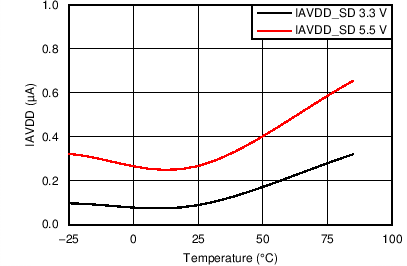
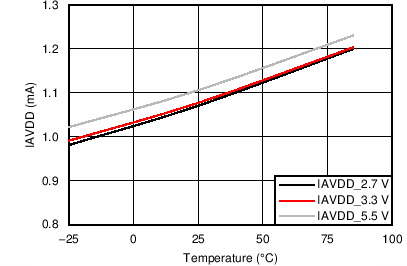
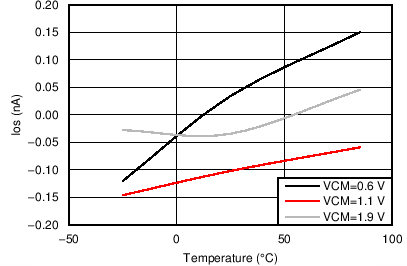
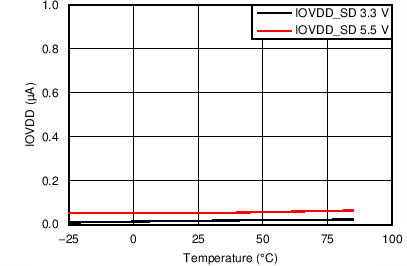
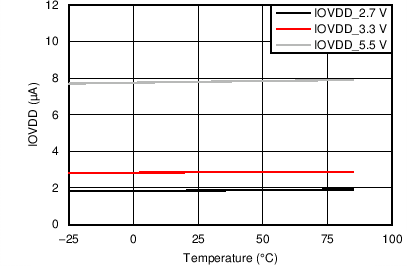
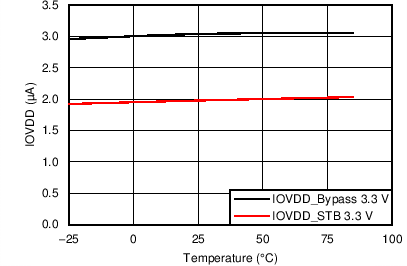
7.7 Typical Characteristics