SNVSAG4B November 2015 – December 2024 LMR14020-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Control
- 6.3.2 Slope Compensation
- 6.3.3 Sleep Mode
- 6.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 6.3.5 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 6.3.6 Enable and Adjustable Undervoltage Lockout
- 6.3.7 External Soft-start
- 6.3.8 Switching Frequency and Synchronization (RT/SYNC)
- 6.3.9 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 6.3.10 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 6.3.11 Overvoltage Protection
- 6.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DDA|8
発注情報
6.3.6 Enable and Adjustable Undervoltage Lockout
The LMR14020-Q1 is enabled when the VIN pin voltage rises above 3.7 V (typical) and the EN pin voltage exceeds the enable threshold of 1.2 V (typical). The LMR14020-Q1 is disabled when the VIN pin voltage falls below 3.42 V (typical) or when the EN pin voltage is below 1.2 V. The EN pin has an internal pullup current source (typically IEN = 1 μA) that enables operation of the LMR14020-Q1 when the EN pin is floating.
Many applications benefit from the employment of an enable divider RENT and RENB in Figure 6-3 to establish a precision system UVLO level for the stage. System UVLO can be used for supplies operating from utility power as well as battery power. System UVLO can be used for sequencing, making sure of reliable operation, or supply protection, such as a battery. An external logic signal can also be used to drive EN input for system sequencing and protection.
When EN terminal voltage exceeds 1.2 V, an additional hysteresis current (typically IHYS = 3.6 μA) is sourced out of EN terminal. When the EN terminal is pulled below 1.2 V, IHYS current is removed. This additional current facilitates adjustable input voltage UVLO hysteresis. Use Equation 2 and Equation 3 to calculate RENT and RENB for desired UVLO hysteresis voltage.
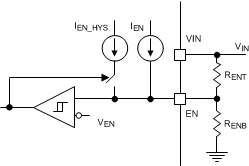 Figure 6-3 System UVLO By Enable Dividers
Figure 6-3 System UVLO By Enable Dividers
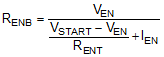
where VSTART is the desired voltage threshold to enable LMR14020-Q1, VSTOP is the desired voltage threshold to disable device.