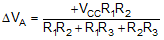JAJSF92O September 2000 – April 2018 LMV7235 , LMV7239
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
7.4.3.1 Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis
The inverting comparator with hysteresis requires a three resistor network that is referenced to the supply voltage V+ of the comparator as shown in Figure 19. When VIN at the inverting input is less than VA, the voltage at the noninverting node of the comparator (VIN< VA), the output voltage is high (for simplicity assume VO switches as high as V+). The three network resistors can be represented as R1//R3 in series with R2.
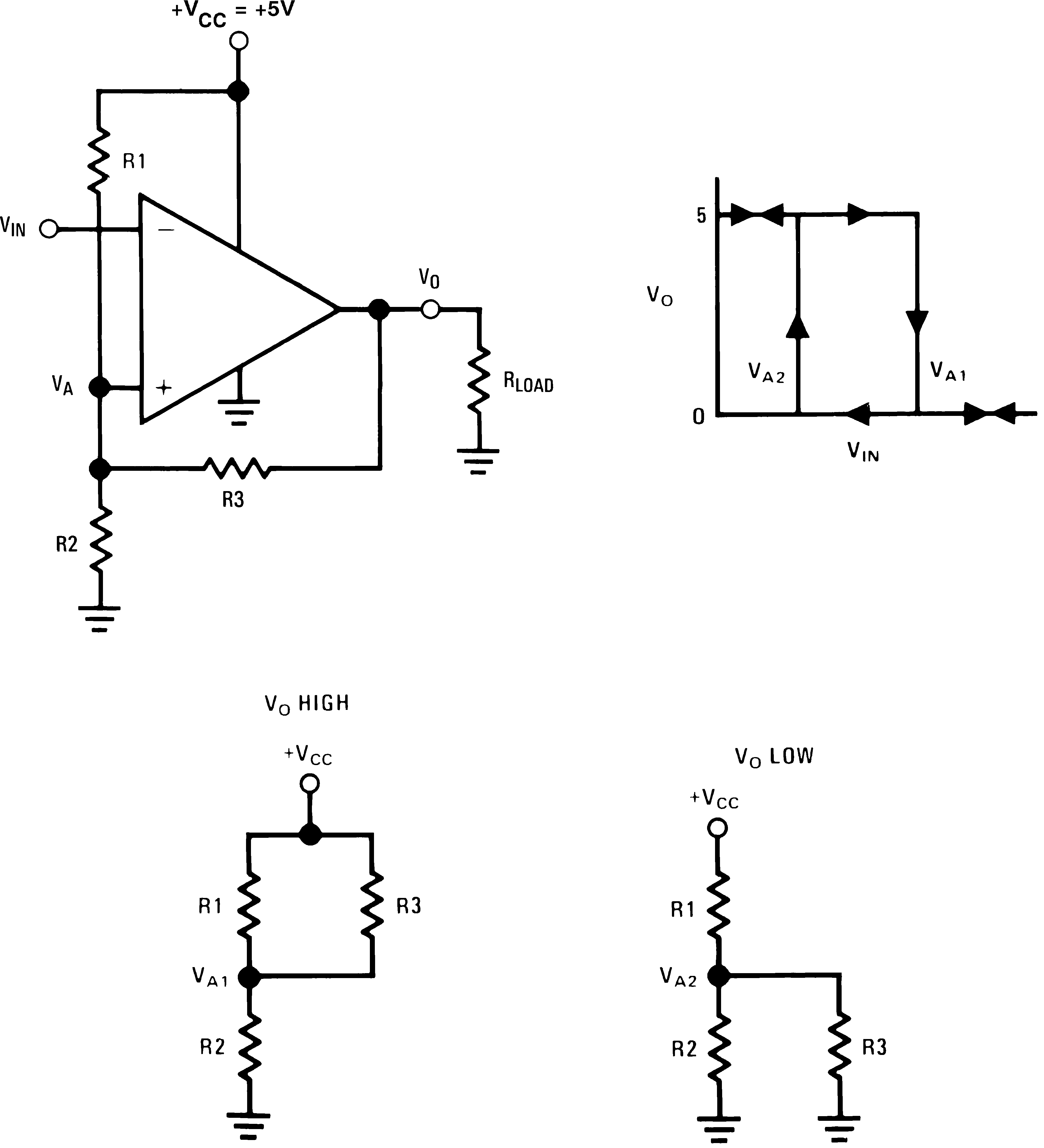 Figure 19. Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis
Figure 19. Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis
The lower input trip voltage VA1 is defined as:
When VIN is greater than VA, the output voltage is low or very close to ground. In this case the three network resistors can be presented as R2 // R3 in series with R1.
The upper trip voltage VA2 is defined as:
The total hysteresis provided by the network is defined as ΔVA = VA1 - VA2.