SNAS322C February 2006 – January 2016 LMX2487
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 R0 Register
- 8.6.2 R1 Register
- 8.6.3 R2 Register
- 8.6.4 R3 Register
- 8.6.5
R4 Register
- 8.6.5.1 MUX[3:0] Frequency Out & Lock Detect MUX
- 8.6.5.2 IF_P - IF Prescaler
- 8.6.5.3 RF_CPP - RF PLL Charge Pump Polarity
- 8.6.5.4 IF_CPP - IF PLL Charge Pump Polarity
- 8.6.5.5 OSC_OUT Oscillator Output Buffer Enable
- 8.6.5.6 OSC2X - Oscillator Doubler Enable
- 8.6.5.7 FM[1:0] - Fractional Mode
- 8.6.5.8 DITH[1:0] - Dithering Control
- 8.6.5.9 ATPU - PLL Automatic Power Up
- 8.6.6 R5 Register
- 8.6.7 R6 Register
- 8.6.8 R7 Register
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTW|24
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTW|24
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
See (1).| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply voltage | –0.3 | 4.25 | V |
| Vi | Voltage on any pin with GND = 0 V | –0.3 | VCC + 0.3 | V |
| TL | Lead temperature (solder 4 seconds) | 260 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(1) | Human-body model (HBM) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM) | ±750 | |||
| Machine model (MM) | ±200 | |||
(1) This is a high performance RF device is ESD-sensitive. Handling and assembly of this device should be done at an ESD free workstation.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply voltage(1) | 2.5 | 3 | 3.6 | V |
| TA | Operating temperature | –40 | 25 | 85 | °C |
(1) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Recommended Operating Conditions indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits. For ensured specifications and test conditions, see Electrical Characteristics. The ensured specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. The voltage at all the power supply pins of VddRF1, VddRF2, VddRF3, VddRF4, VddRF5, VddIF1 and VddIF2 must be the same. VCC will be used to refer to the voltage at these pins and ICC will be used to refer to the sum of all currents through all these power pins.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LMX2485, LMX2485E | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RTW (WQFN) | |||
| 24 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 47.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 43 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 24 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.8 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 24 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 7 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
(VCC = 3.0 V; –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C unless otherwise specified)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC PARAMETERS | ||||||||
| ICCRF | Power supply current, RF synthesizer | IF PLL OFF RF PLL ON Charge Pump TRI-STATE |
5.7 | mA | ||||
| ICCIF | Power supply current, IF synthesizer | IF PLL ON RF PLL OFF Charge Pump TRI-STATE |
2.5 | mA | ||||
| ICCTOTAL | Power supply current, entire synthesizer | IF PLL ON RF PLL ON Charge Pump TRI-STATE |
8.5 | mA | ||||
| ICCPD | Power-down current | CE = ENOSC = 0 V CLK, DATA, LE = 0 V |
< 1 | µA | ||||
| RF SYNTHESIZER PARAMETERS | ||||||||
| fFinRF | Operating frequency | LMX2487 | RF_P = 16 | 1000 | 4000 | MHz | ||
| RF_P = 32 | 1000 | 6000 | ||||||
| pFinRF | Input sensitivity | –10 | 0 | dBm | ||||
| fCOMP | Phase detector frequency(1) | 50 | MHz | |||||
| ICPoutRFSRCE | RF charge pump source current(2) | RF_CPG = 0 VCPoutRF = VCC/2 |
95 | µA | ||||
| RF_CPG = 1 VCPoutRF = VCC/2 |
190 | µA | ||||||
| ... | ... | µA | ||||||
| RF_CPG = 15 VCPoutRF = VCC/2 |
1520 | µA | ||||||
| ICPoutRFSINK | RF charge pump sink current(2) | RF_CPG = 0 VCPoutRF = VCC/2 |
–95 | µA | ||||
| RF_CPG = 1 VCPoutRF = VCC/2 |
–190 | µA | ||||||
| ... | ... | µA | ||||||
| RF_CPG = 15 VCPoutRF = VCC/2 |
–1520 | µA | ||||||
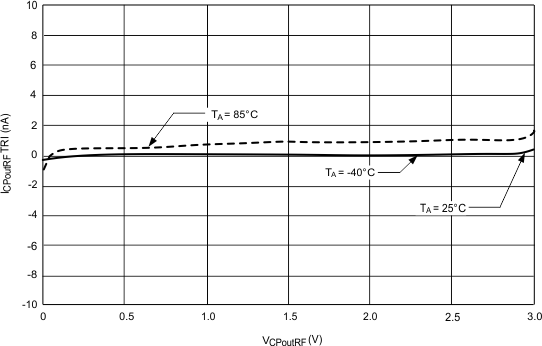
| ICPoutRFTRI | RF charge pump TRI-STATE current magnitude | 0.5 ≤ VCPoutRF ≤ VCC -0.5 | 2 | 10 | nA | |||
| | ICPoutRF%MIS | | Magnitude of RF CP sink vs CP source mismatch | VCPoutRF = VCC/2 TA = 25°C |
RF_CPG > 2 | 3% | 10% | |||
| RF_CPG ≤ 2 | 3% | 13% | ||||||
| | ICPoutRF%V | | Magnitude of RF CP current vs CP voltage | 0.5 ≤ VCPoutRF ≤ VCC -0.5 TA = 25°C |
2% | 8% | ||||
| | ICPoutRF%T | | Magnitude of RF CP current vs temperature | VCPoutRF = VCC/2 | 4% | |||||
| IF SYNTHESIZER PARAMETERS | ||||||||
| fFinIF | Operating frequency | IF_P = 8 | 250 | 2000 | MHz | |||
| IF_P = 16 | 250 | 3000 | ||||||
| pFinIF | IF input sensitivity | –10 | 5 | dBm | ||||
| fCOMP | Phase detector frequency | 10 | MHz | |||||
| ICPoutIFSRCE | IF charge pump source current | VCPoutIF = VCC/2 | 3.5 | mA | ||||
| ICPoutIFSINK | IF charge pump sink current | VCPoutIF = VCC/2 | –3.5 | mA | ||||
| ICPoutIFTRI | IF charge pump TRI-STATE current magnitude | 0.5 ≤ VCPoutIF ≤ VCC RF -0.5 | 2 | 10 | nA | |||
| | ICPoutIF%MIS | | Magnitude of IF CP sink vs CP source mismatch | VCPoutIF = VCC/2 TA = 25°C |
1% | 8% | ||||
| | ICPoutIF%V | | Magnitude of IF CP current vs CP voltage | 0.5 ≤ VCPoutIF ≤ VCC -0.5 TA = 25°C |
4% | 10% | ||||
| | ICPoutIF%TEMP | Magnitude of IF CP current vs temperature | VCPoutIF = VCC/2 | 4% | |||||
| OSCILLATOR PARAMETERS | ||||||||
| fOSCin | Oscillator operating frequency | OSC2X = 0 | 5 | 110 | MHz | |||
| OSC2X = 1 | 5 | 20 | MHz | |||||
| vOSCin | Oscillator input sensitivity | 0.5 | VCC | VP-P | ||||
| IOSCin | Oscillator input current | –100 | 100 | µA | ||||
| SPURS | ||||||||
| Spurs in band(3) | –55 | dBc | ||||||
| PHASE NOISE | ||||||||
| LF1HzRF | RF synthesizer normalized phase noise contribution(4) | RF_CPG = 0 | –202 | dBc/Hz | ||||
| RF_CPG = 1 | –204 | |||||||
| RF_CPG = 3 | –206 | |||||||
| RF_CPG = 7 | –210 | |||||||
| RF_CPG = 15 | –210 | |||||||
| LF1HzIF | IF synthesizer normalized phase noise contribution | –209 | dBc/Hz | |||||
| DIGITAL INTERFACE (DATA, CLK, LE, ENOSC, CE, Ftest/LD, FLoutRF) | ||||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 1.6 | VCC | V | ||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.4 | V | |||||
| IIH | High-level input current | VIH = VCC | –1 | 1 | µA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current | VIL = 0 V | –1 | 1 | µA | |||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –500 µA | VCC – 0.4 | V | ||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 500 µA | 0.4 | V | ||||
(1) For Phase Detector Frequencies above 20 MHz, Cycle Slip Reduction (CSR) may be required. Legal divide ratios are also required.
(2) Refer to the table in RF_CPG – RF PLL Charge Pump Gain for a complete listing of charge pump currents.
(3) In order to measure the in-band spur, the fractional word is chosen such that when reduced to lowest terms, the fractional numerator is one. The spur offset frequency is chosen to be the comparison frequency divided by the reduced fractional denominator. The loop bandwidth must be sufficiently wide to negate the impact of the loop filter. Measurement conditions are: Spur Offset Frequency = 10 kHz, Loop Bandwidth = 100 kHz, Fraction = 1/2000, Comparison Frequency = 20 MHz, RF_CPG = 7, DITH = 0, VCO Frequency = 3 GHz, and a 4th Order Modulator (FM = 0). These are relatively consistent over tuning range.
(4) Normalized Phase Noise Contribution is defined as: LN(f) = L(f) – 20log(N) – 10log(fCOMP) where L(f) is defined as the single side band phase noise measured at an offset frequency, f, in a 1 Hz Bandwidth. The offset frequency, f, must be chosen sufficiently smaller than the PLL loop bandwidth, yet large enough to avoid substantial phase noise contribution from the reference source. Measurement conditions are: Offset Frequency = 11 kHz, Loop Bandwidth = 100 kHz for RF_CPG = 7, Fraction = 1/2000, Comparison Frequency = 20 MHz, FM = 0, DITH = 0, VCO Frequency = 3 GHz.
6.6 Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MICROWIRE INTERFACE TIMING | ||||||
| tCS | Data to clock set-up time | See Figure 1 | 25 | ns | ||
| tCH | Data to clock hold time | See Figure 1 | 8 | ns | ||
| tCWH | Clock pulse width high | See Figure 1 | 25 | ns | ||
| tCWL | Clock pulse width low | See Figure 1 | 25 | ns | ||
| tES | Clock to load enable set-up time | See Figure 1 | 25 | ns | ||
| tEW | Load enable pulse width | See Figure 1 | 25 | ns | ||
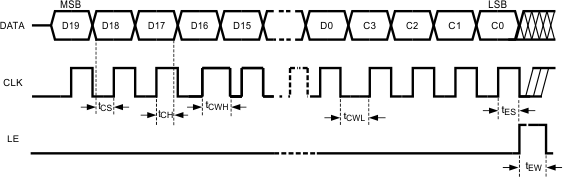 Figure 1. MICROWIRE Input Timing Diagram
Figure 1. MICROWIRE Input Timing Diagram
6.7 Typical Characteristics
6.7.1 Sensitivity
Typical characteristics do not imply any sort of ensured specification. Ensured specifications are in Electrical Characteristics.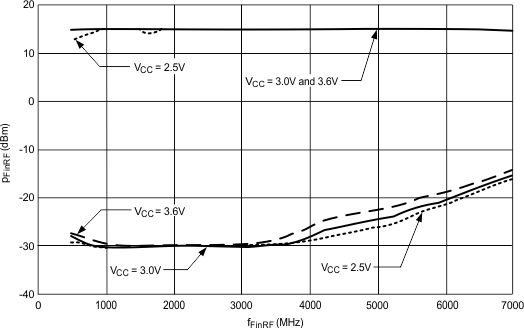
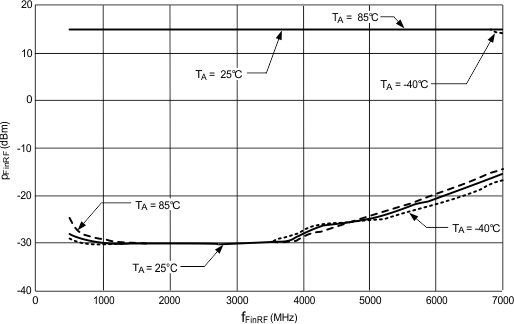
TA = 25°C, RF_P = 32
Figure 2. RF PLL Fin Sensitivity
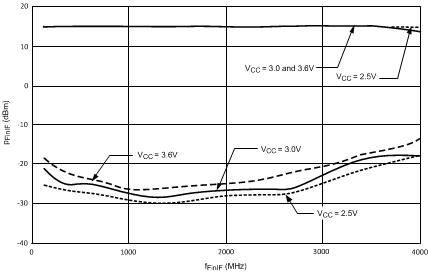
TA = 25°C, IF_P = 16
Figure 4. IF PLL Fin Sensitivity
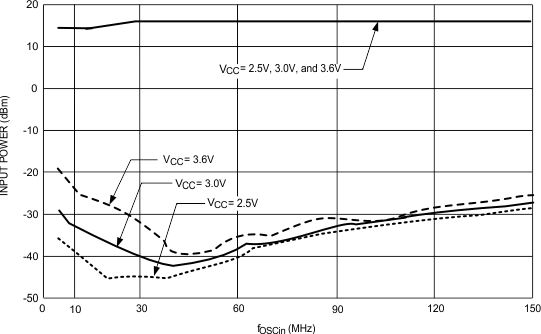
| TA = 25°C, OSC_2X = 0 |
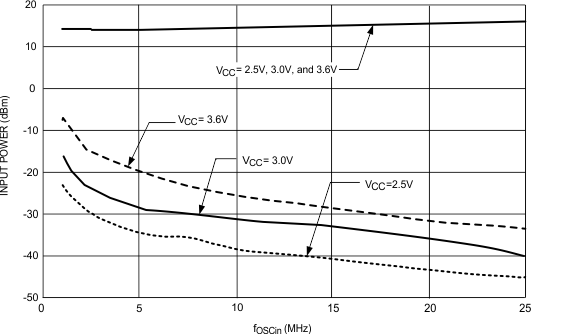
TA = 25°C, OSC_2X =1
Figure 8. OSCin Sensitivity
VCC = 3.0 V, RF_P = 32
Figure 3. RF PLL Fin Sensitivity
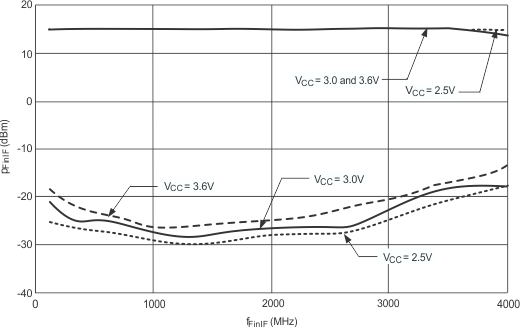
| VCC = 3.0 V, IF_P = 16 |
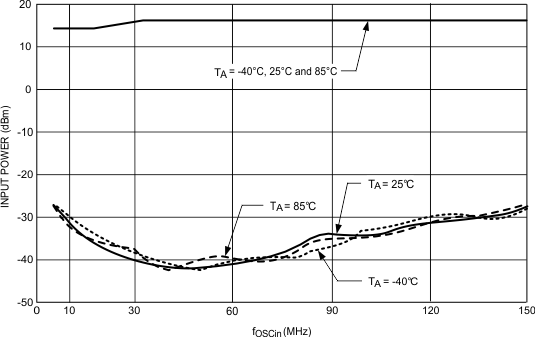
VCC = 3.0 V, OSC_2X = 0
Figure 7. OSCin Sensitivity
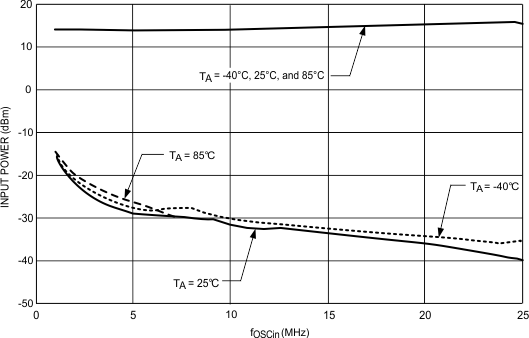
VCC = 3.0 V, OSC_2X = 1
Figure 9. OSCin Sensitivity
6.7.2 FinRF Input Impedance
Typical characteristics do not imply any sort of ensured specification. Ensured specifications are in Electrical Characteristics.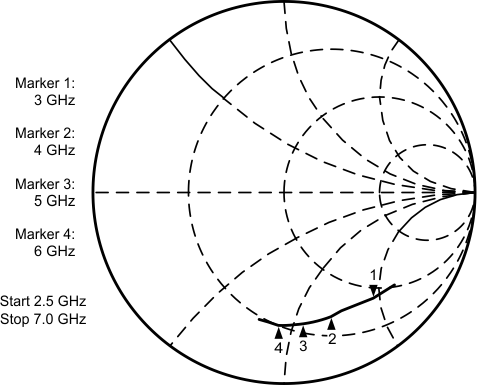 Figure 10. FinRF Input Impedance
Figure 10. FinRF Input Impedance
Table 1. FinRF Input Impedance
| FinRF INPUT IMPEDANCE | ||
|---|---|---|
| FREQUENCY (MHz) | REAL (Ω) | IMAGINARY (Ω) |
| 3000 | 39 | –94 |
| 3200 | 37 | –86 |
| 3400 | 33 | –78 |
| 3600 | 30 | –72 |
| 3800 | 28 | –69 |
| 4000 | 26 | –66 |
| 4250 | 24 | –63 |
| 4500 | 23 | –60 |
| 4750 | 22 | –57 |
| 5000 | 20 | –54 |
| 5250 | 19 | –50 |
| 5500 | 18 | –49 |
| 5750 | 17 | –47 |
| 6000 | 17 | –45 |
| 6250 | 16 | –44 |
| 6500 | 16 | –42 |
| 6750 | 16 | –40 |
| 7000 | 16 | –39 |
6.7.3 FinIF Input Impedance
Typical characteristics do not imply any sort of ensured specification. Ensured specifications are in Electrical Characteristics.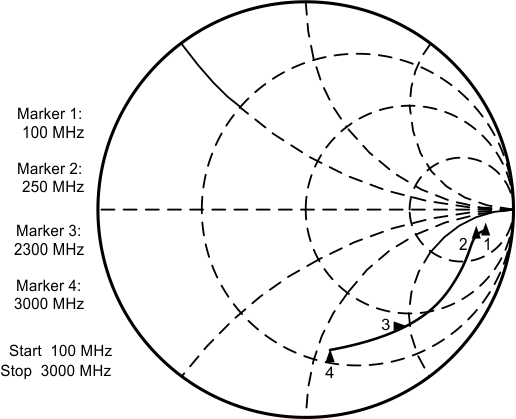 Figure 11. FinIF Input Impedance
Figure 11. FinIF Input Impedance
Table 2. FinIF Input Impedance
| FinIF INPUT IMPEDANCE | ||
|---|---|---|
| FREQUENCY (MHz) | REAL (Ω) | IMAGINARY (Ω) |
| 100 | 508 | –233 |
| 150 | 456 | –215 |
| 200 | 420 | –206 |
| 250 | 403 | –205 |
| 300 | 370 | –207 |
| 400 | 344 | –215 |
| 500 | 207 | –223 |
| 600 | 274 | –225 |
| 700 | 242 | –225 |
| 800 | 242 | –225 |
| 900 | 214 | –222 |
| 1000 | 171 | –208 |
| 1200 | 137 | –191 |
| 1400 | 112 | –176 |
| 1600 | 91 | –158 |
| 1800 | 76 | –139 |
| 2000 | 62 | –122 |
| 2200 | 51 | –105 |
| 2300 | 46 | –96 |
| 2400 | 42 | –88 |
| 2600 | 37 | –74 |
| 2800 | 29 | –63 |
| 3000 | 25 | –54 |
6.7.4 OSCin Input Impedance
Typical characteristics do not imply any sort of ensured specification. Ensured specifications are in Electrical Characteristics.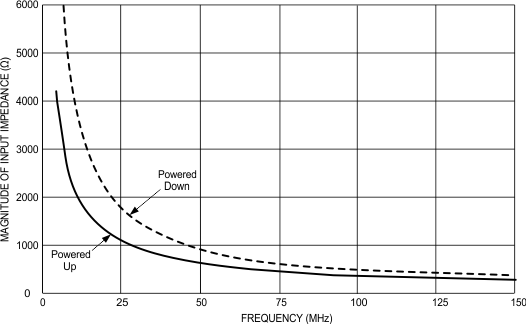 Figure 12. OSCin Input Impedance
Figure 12. OSCin Input Impedance
Table 3. OSCin Input Impedance
| FREQUENCY (MHz) | POWERED UP | POWERED DOWN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REAL | IMAGINARY | MAGNITUDE | REAL | IMAGINARY | MAGNITUDE | |
| 5 | 1730 | –3779 | 4157 | 392 | –8137 | 8146 |
| 10 | 846 | –2236 | 2391 | 155 | –4487 | 4490 |
| 20 | 466 | –1196 | 1284 | 107 | –2215 | 2217 |
| 30 | 351 | –863 | 932 | 166 | –1495 | –1504 |
| 40 | 316 | –672 | 742 | 182 | –1144 | 1158 |
| 50 | 278 | –566 | 631 | 155 | –912 | 925 |
| 60 | 261 | –481 | 547 | 153 | –758 | 774 |
| 70 | 252 | –425 | 494 | 154 | –652 | 669 |
| 80 | 239 | –388 | 456 | 147 | –576 | 595 |
| 90 | 234 | –358 | 428 | 145 | –518 | 538 |
| 100 | 230 | –337 | 407 | 140 | –471 | 492 |
| 110 | 225 | –321 | 392 | 138 | –436 | 458 |
| 120 | 219 | –309 | 379 | 133 | –402 | 123 |
| 130 | 214 | –295 | 364 | 133 | –374 | 397 |
| 140 | 208 | –285 | 353 | 132 | –349 | 373 |
| 150 | 207 | –279 | 348 | 133 | –329 | 355 |
6.7.5 Currents
Typical characteristics do not imply any sort of ensured specification. Ensured specifications are in Electrical Characteristics.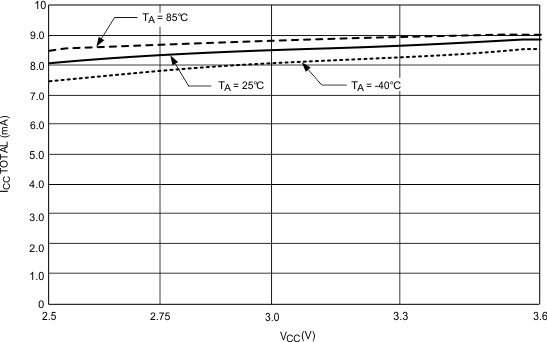
| CE = High | ||
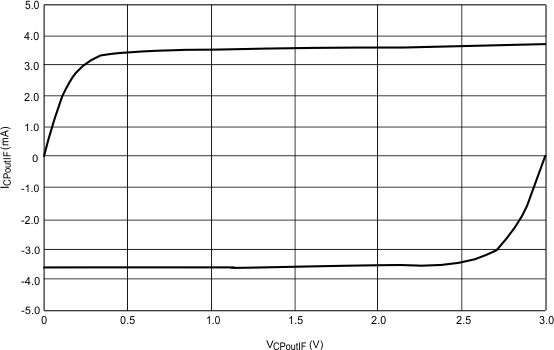
| VCC = 3 V |
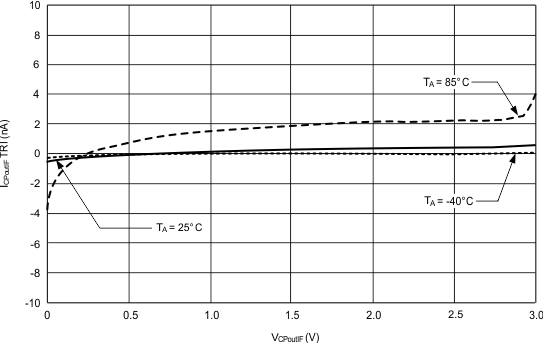
| VCC = 3 V |
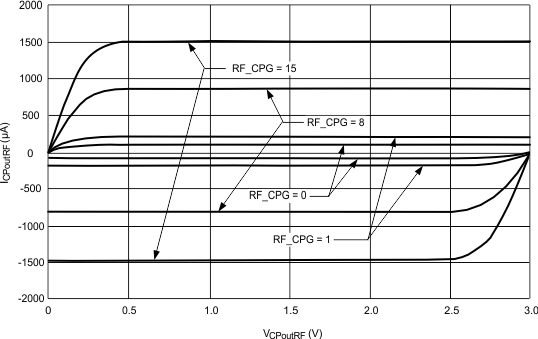
| VCC = 3 V |
| VCC = 3 V | ||