SNVS056J May 2000 – June 2015 LP3961 , LP3964
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 External Capacitors
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting a Capacitor
- 8.2.2.3 Capacitor Characteristics
- 8.2.2.4 RFI and EMI Susceptibility
- 8.2.2.5 Output Adjustment
- 8.2.2.6 Turnon Characteristics for Output Voltages Programmed to 2.0 V or Below
- 8.2.2.7 Output Noise
- 8.2.2.8 Shutdown Operation
- 8.2.2.9 Maximum Output Current Capability
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The LP3961/LP3964 are a series of ultra-low dropout linear regulators. Fixed output products have output voltage options from 1.2 V to 5 V, adjustable output voltage is only available for LP3964. These regulators can provide maximum 800-mA load current. The device can operate under extremely low dropout conditions.
The LP3961 has an ERROR flag pin, this pin will go low when the output voltage drops 10% below nominal value. The LP3964 (fixed output products) provides a SENSE pin. The SENSE pin can improve regulation at remote loads. The LP3961, LP3964 also provide short-circuit protection and reverse current path. The devices can be operated with shutdown (SD) pin control.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
 Figure 17. LP3961 Block Diagram
Figure 17. LP3961 Block Diagram
 Figure 18. LP3964 Block Diagram
Figure 18. LP3964 Block Diagram
 Figure 19. LP3964 Adjustable Version Block Diagram
Figure 19. LP3964 Adjustable Version Block Diagram
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Short-Circuit Protection
The LP3961 and LP3964 are short-circuit protected and in the event of a peak overcurrent condition, the short-circuit control loop will rapidly drive the output PMOS pass element off. Once the power pass element shuts down, the control loop will rapidly cycle the output on and off until the average power dissipation causes the thermal shutdown circuit to respond to servo the on/off cycling to a lower frequency. Please refer to the section on thermal information for power dissipation calculations.
7.3.2 ERROR Flag Operation
The LP3961 produces a logic low signal at the ERROR flag pin when the output drops out of regulation due to low input voltage, current limiting, or thermal limiting. This flag has a built-in hysteresis. The timing diagram in Figure 20 shows the relationship between the ERROR pin and the output voltage. In this example, the input voltage is changed to demonstrate the functionality of the ERROR flag.
The internal ERROR flag comparator has an open drain output stage. Hence, the ERROR pin should be pulled high through a pull-up resistor. Although the ERROR pin can sink current of 1 mA, this current is an energy drain from the input supply. Hence, the value of the pull-up resistor should be in the range of 100 kΩ to 1 MΩ. The ERROR pin must be connected to ground if this function is not used. It should also be noted that when the SD pin is pulled low, the ERROR pin is forced to be invalid for reasons of saving power in shutdown mode.
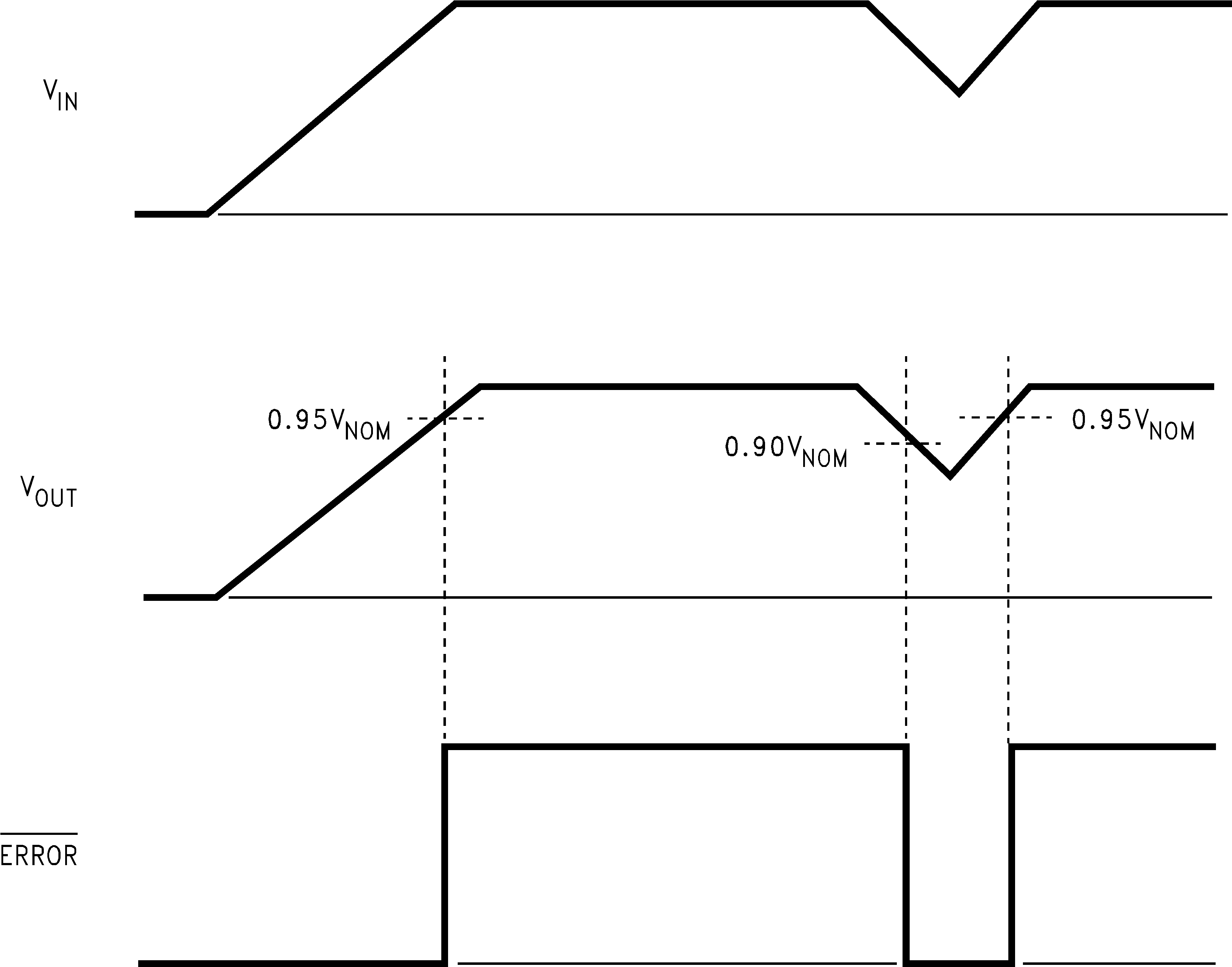 Figure 20. ERROR Flag Operation
Figure 20. ERROR Flag Operation
7.3.3 SENSE Pin
In applications where the regulator output is not very close to the load, LP3964 can provide better remote load regulation using the SENSE pin. Figure 21 depicts the advantage of the SENSE option. LP3961 regulates the voltage at the OUT pin. Hence, the voltage at the remote load will be the regulator output voltage minus the drop across the trace resistance. For example, in the case of a 3.3-V output, if the trace resistance is 100 mΩ, the voltage at the remote load will be 3.22 V with 800 mA of load current, ILOAD. The LP3964 regulates the voltage at the SENSE pin. Connecting the SENSE pin to the remote load will provide regulation at the remote load, as shown in Figure 21. If the sense option pin is not required, the SENSE pin must be connected to the OUT pin.
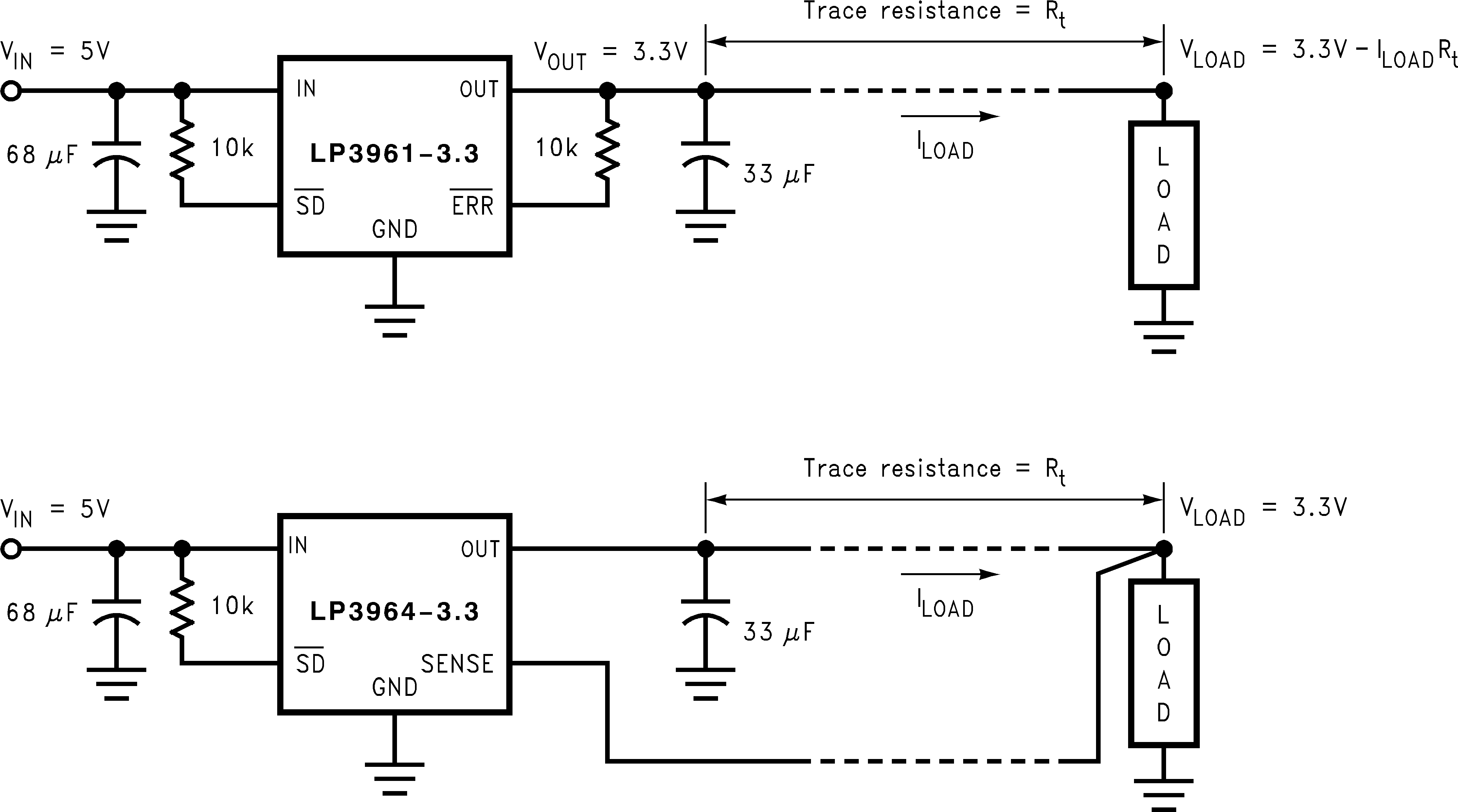 Figure 21. Improving Remote Load Regulation Using LP3964
Figure 21. Improving Remote Load Regulation Using LP3964
7.3.4 Dropout Voltage
The dropout voltage of a regulator is defined as the minimum input-to-output differential required to stay within 2% of the output voltage. The LP3961 and LP3964 use an internal MOSFET with an Rds(on) of 240 mΩ (typically). For CMOS LDOs, the dropout voltage is the product of the load current and the Rds(on) of the internal MOSFET.
7.3.5 Reverse Current Path
The internal MOSFET in LP3961 and LP3964 has an inherent parasitic diode. During normal operation, the input voltage is higher than the output voltage and the parasitic diode is reverse biased. However, if the output is pulled above the input in an application, then current flows from the output to the input as the parasitic diode gets forward biased. The output can be pulled above the input as long as the current in the parasitic diode is limited to 200-mA continuous and 1-A peak.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Operation With VOUT(TARGET) + 0.35 V ≤ VIN ≤ 7 V
For the fixed output voltage products, the devices operate if the input voltage is equal to or exceeds VOUT(TARGET) + 0.35 V. At input voltages below the minimum VIN requirement, the devices do not operate correctly and output voltage may not reach target value.
7.4.2 Operation With Shutdown (SD) Pin Control
A CMOS logic low level signal at the shutdown (SD) pin will turn off the regulator. The SD pin must be actively terminated through a 10-kΩ pullup resistor for a proper operation. This pin must be tied to the IN pin if not used .