SNVS179F February 2003 – September 2015 LP3995
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
The dynamic performance of the LP3995 is dependant on the layout of the PCB. PCB layout practices that are adequate for typical LDOs may degrade the PSRR, noise, or transient performance of the LP3995. Best performance is achieved by placing CIN and COUT on the same side of the PCB as the LP3995, and as close as is practical to the package. The ground connections for CIN and COUT should be back to the LP3995 ground pin using as wide, and as short, of a copper trace as is practical. Connections using long trace lengths, narrow trace widths, and/or connections through vias should be avoided. These add parasitic inductances and resistance that result in inferior performance especially during transient conditions.
11.2 Layout Examples
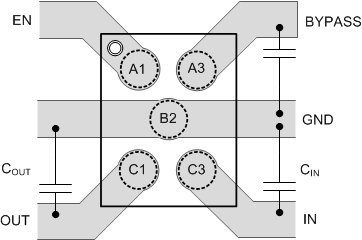 Figure 22. LP3995 DSBGA Layout
Figure 22. LP3995 DSBGA Layout
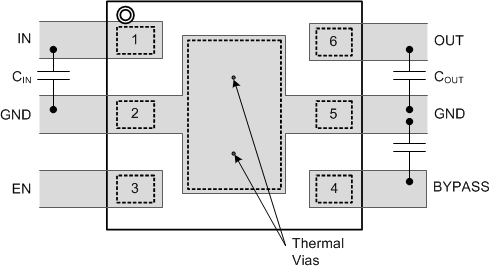 Figure 23. LP3995 WSON Layout
Figure 23. LP3995 WSON Layout
11.3 DSBGA Mounting
The DSBGA package requires specific mounting techniques that are detailed in TI's AN-1112 Application Report (SNVA009). Referring to the section Surface Mount Assembly Considerations, it should be noted that the pad style which must be used with the 5-pin package is NSMD (non-solder mask defined) type.
For best results during assembly, alignment ordinals on the PC board may be used to facilitate placement of the DSBGA device.
11.4 DSBGA Light Sensitivity
Exposing the DSBGA device to direct sunlight may cause mis-operation of the device. Light sources such as halogen lamps can affect electrical performance if they are situated in proximity to the device.
The wavelengths that have the most detrimental effect are reds and infra-reds, which means that the fluorescent lighting used inside most buildings has little effect on performance. Tests carried out on a DSBGA test board showed a negligible effect on the regulated output voltage when brought within 1 cm of a fluorescent lamp. A deviation of less than 0.1% from nominal output voltage was observed.