SNVS469F October 2006 – December 2015 LP5952
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Quiescent Currents
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Shutdown Currents
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: Enable Control
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics: Thermal Protection
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics: Transient Characteristics
- 6.11 Input and Output Capacitors (Recommended)
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)(3)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN, BATT pins: Voltage to GND, VIN ≤ VBATT | –0.2 | V | ||
| BATT pin to IN pin | 0.2 | V | ||
| EN pin, voltage to GND | –0.2 | V | ||
| Continuous power dissipation(4) | Internally limited | |||
| Junction Temperature (TJ-MAX ) | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(3) If Military or Aerospace specified devices are required, contact Texas Instruments Sales Office or Distributors for availability and specifications.
(4) Internal thermal shutdown circuitry protects the device from permanent damage. Thermal shutdown engages at TJ = 165°C (typical) and disengages at TJ = 145°C (typical).
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Machine model | ±200 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage, VIN | 0.7 | 4.5 | V | |
| Input voltage, VBATT | 2.5 | 5.5 | V | |
| Input voltage, VEN | 0 | VBATT | V | |
| Recommended load current | 0 | 350 | mA | |
| Junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| Ambient temperature, TA(1) | –40 | 85 | °C | |
(1) In applications where high power dissipation and/or poor package thermal resistance is present, the maximum ambient temperature may have to be derated. Maximum ambient temperature (TA-MAX) is dependent on the maximum operating junction temperature (TJ-MAX-OP = 125°C), the maximum power dissipation of the device in the application (PD-MAX), and the junction-to ambient thermal resistance of the part/package in the application (RθJA), as given by: TA-MAX = TJ-MAX-OP – (RθJA × PD-MAX).
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LP5952 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZR (DSBGA) | NKH (USON) | |||
| 5 PINS | 6 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance(2) | 181.0 | 181.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 0.9 | 93.1 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 110.3 | 116.7 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 7.4 | 8.0 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 110.3 | 116.7 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
(2) Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance is highly application and board-layout dependent. In applications where high maximum power dissipation exists, special attention must be paid to thermal dissipation issues in board design.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, typical values are for TA = 25°C, and minimum and maximum limits apply over the full operating temperature range: –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C; specifications apply to the Typical Application Circuit with VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V (whichever is higher), IOUT = 1 mA, CVIN = 1 µF, COUT = 2.2 µF, VEN = VBATT.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔVOUT / VOUT | Output voltage tolerance | VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V, TA = 25°C | –1.5 | 1.5 | |||
| VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V | 2 | 2 | |||||
| ΔVOUT / ΔVIN | Line regulation error | VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V to 4.5 V, VBATT = 4.5 V | 1 | 0.3 | 1 | mV/V | |
| ΔVOUT / ΔVBATT | VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V (≥ 2.5 V) to 5.5 V | 2.2 | 0.5 | 2.2 | |||
| ΔVOUT / ΔmA | Load regulation error | IOUT = 1 mA to 350 mA | DSBGA package | 30 | 15 | 30 | µV/mA |
| IOUT = 1 mA to 350 mA | USON package | 60 | 43 | 60 | µV/mA | ||
| ISC | Output current (short circuit) | VOUT = 0 V, VEN = VIN = VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V | 350 | 500 | mA | ||
| VDO_VBATT
(4) |
Output voltage dropout VBATT(5) | IOUT = 350 mA, VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V | DSBGA package | 1.07 | 1.5 | V | |
| IOUT = 350 mA VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V |
USON package | 1.08 | 1.5 | V | |||
| IOUT = 150 mA VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V |
DSBGA package | 0.96 | 1.3 | V | |||
| IOUT = 150 mA VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V |
USON package | 0.97 | 1.3 | V | |||
| VDO_VIN | Output voltage dropout VIN | IOUT = 350 mA VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V |
DSBGA package | 88 | 200 | mV | |
| IOUT = 350 mA VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V |
USON package | 128 | 250 | mV | |||
| EN | Output noise | 10 Hz to 100 kHz | 100 | µVRMS | |||
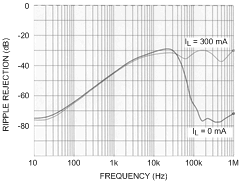
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | Sine modulated VBATT, ƒ = 10 Hz | 70 | dB | |||
| Sine modulated VBATT, ƒ = 100 Hz | 65 | ||||||
| Sine modulated VBATT, ƒ = 1 kHz | 45 | ||||||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | Sine modulated VIN, ƒ = 10 Hz | 80 | dB | |||
| Sine modulated VIN, ƒ = 100 Hz | 90 | ||||||
| Sine modulated VIN, ƒ = 1 kHz | 95 | ||||||
| Sine modulated VIN, ƒ = 10 kHz | 85 | ||||||
| Sine modulated VIN, ƒ = 100 kHz | 64 | ||||||
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not ensured, but do represent the most likely norm. Unless otherwise specified, conditions for typical specifications are: VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V, whichever is higher, TA = 25°C.
(3) VOUT(NOM) is the stated output voltage option
(4) This specification does not apply if the battery voltage VBATT needs to be decreased below the minimum operating limit of 2.5 V during this test.
(5) Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output voltage differential at which the output voltage falls to 100mV below the nominal output voltage.
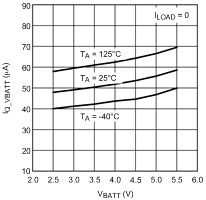
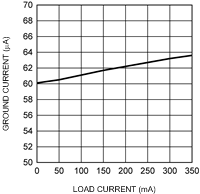
6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Quiescent Currents
Unless otherwise noted, typical values are for TA = 25°C, and minimum and maximum limits apply over the full operating temperature range: –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQ_VBATT | Current into VBATT | ILOAD = 0 mA to 350mA | 50 | 100 | µA | |
| IQ_VIN | Current into VIN | ILOAD = 0 | 11 | 28 | µA | |
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not ensured, but do represent the most likely norm. Unless otherwise specified, conditions for typical specifications are: VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V, whichever is higher, TA = 25°C.
(3) VOUT(NOM) is the stated output voltage option
6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Shutdown Currents
Unless otherwise noted, typical values are for TA = 25°C, and minimum and maximum limits apply over the full operating temperature range: –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQ_VBATT | Current into VBATT | VEN = 0 V | 0.1 | 1 | µA | |
| IQ_VIN | Current into VIN | VEN = 0 V | 0.1 | 1 | µA | |
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not ensured, but do represent the most likely norm. Unless otherwise specified, conditions for typical specifications are: VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V, whichever is higher, TA = 25°C.
(3) VOUT(NOM) is the stated output voltage option.
6.8 Electrical Characteristics: Enable Control
Unless otherwise noted, typical values are for TA = 25°C, and minimum and maximum limits apply over the full operating temperature range: –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEN | Maximum input current at EN input | 0.01 | 1 | µA | ||
| VIL | Low input threshold (shutdown) | 0.4 | V | |||
| VIH | High input threshold (enable) | 1 | V | |||
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not ensured, but do represent the most likely norm. Unless otherwise specified, conditions for typical specifications are: VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V, whichever is higher, TA = 25°C.
(3) VOUT(NOM) is the stated output voltage option.
6.9 Electrical Characteristics: Thermal Protection
Typical values are for TA = 25°C.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSHDN | Thermal-shutdown temperature | 165 | °C | |||
| ΔTSHDN | Thermal-shutdown hysteresis | 20 | °C | |||
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not ensured, but do represent the most likely norm. Unless otherwise specified, conditions for typical specifications are: VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V, whichever is higher, TA = 25°C.
(3) VOUT(NOM) is the stated output voltage option.
6.10 Electrical Characteristics: Transient Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, typical values are for TA = 25°C, and minimum and maximum limits apply over the full operating temperature range: –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔVOUT | Dynamic line transient response VIN | VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V to VOUT(NOM) + 0.9 V; tr, tf = 10 µs |
±1 | mV | |||
| ΔVOUT | Dynamic line transient response VBATT | VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V to VOUT(NOM) + 2.1 V; tr, tf = 10 µs |
±15 | mV | |||
| ΔVOUT | Dynamic load transient response | Pulsed load 0 ...300 mA, di/dt = 300 mA/1 µs |
DSBGA package | ±15 | mV | ||
| Pulsed load 0 ...300mA, di/dt = 300 mA/1 µs |
USON package | –35/+15 | mV | ||||
| TSTARTUP | Start-up time | EN to 0.95 × VOUT | 70 | 150 | µs | ||
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not ensured, but do represent the most likely norm. Unless otherwise specified, conditions for typical specifications are: VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V, whichever is higher, TA = 25°C.
(3) VOUT(NOM) is the stated output voltage option.
6.11 Input and Output Capacitors (Recommended)
All values are for TA = 25°C.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COUT | Output capacitance | Capacitance(4) | 1.5 | 2.2 | 10 | µF |
| ESR | 3 | 300 | mΩ | |||
| CVIN | Input capacitance at VIN | Capacitance(4), not needed in typical post-regulation application (see Figure 18) | 0.47 | 1 | µF | |
| ESR | 3 | 300 | mΩ | |||
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not ensured, but do represent the most likely norm. Unless otherwise specified, conditions for typical specifications are: VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT= VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V or 2.5 V, whichever is higher, TA = 25°C.
(3) VOUT(NOM) is the stated output voltage option.
(4) The capacitor tolerance should be 30% or better over temperature. The full operating conditions for the application should be considered when selecting a suitable capacitor to ensure that the minimum value of capacitance is always met. Recommended capacitor type is X7R. However, dependent on application, X5R, Y5V, and Z5U can also be used. The shown minimum limit represents real minimum capacitance, including all tolerances and must be maintained over temperature and DC bias voltage (See Detailed Design Procedure in Application and Implementation.)
6.12 Typical Characteristics
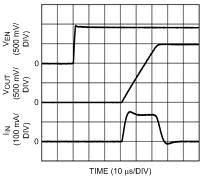
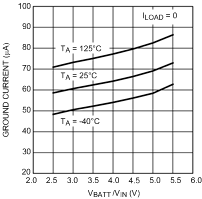
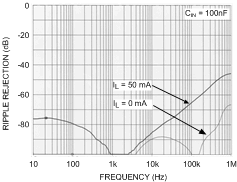
Unless otherwise specified, TA = 25°C, CIN = 1-µF ceramic, COUT = 2.2-µF ceramic, VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 1 V, VBATT = VOUT(NOM) + 1.5 V, EN pin is tied to VBATT (DSBGA package).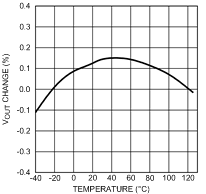
| 1.5-V Option | ||
| 1.5-V Option |
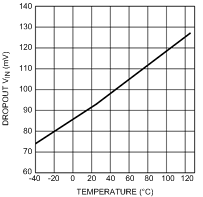
| ILOAD = 350 mA |
| 1.5-V Option |