JAJSD62C March 2013 – January 2020 OPA188
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
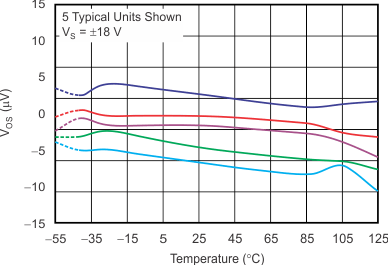
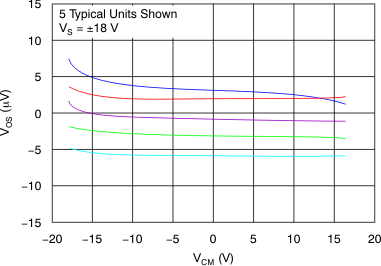
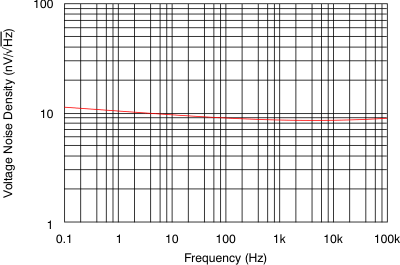
7.8 Typical Characteristics
at VS = ±18 V, VCM = VS / 2, RLOAD = 10 kΩ connected to VS / 2, and CL = 100 pF (unless otherwise noted)



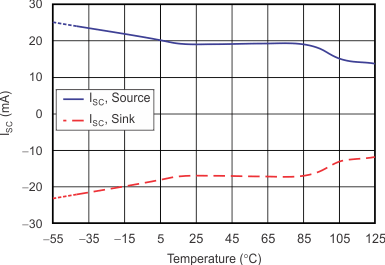
Output Current (Maximum Supply)






Capacitive Load (100-mV Output Step)
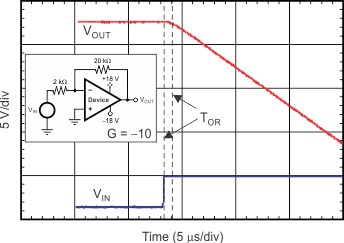
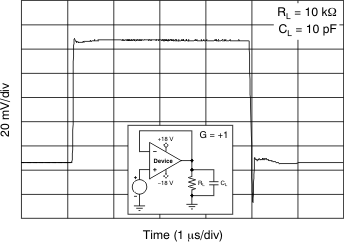
(100 mV)

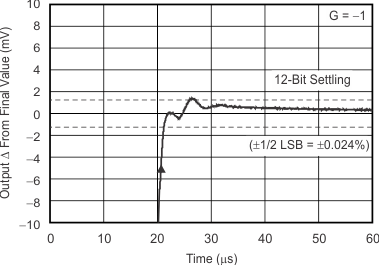
(10-V Positive Step)
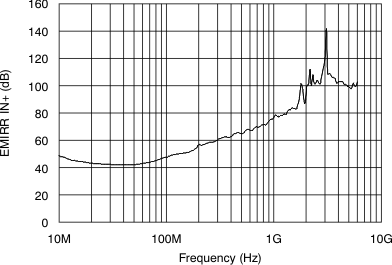
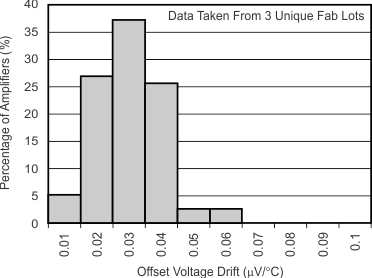





(Referred-to-Input)


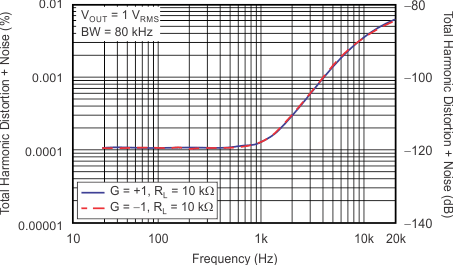



Capacitive Load (100-mV Output Step)



(100 mV)


(10-V Negative Step)