JAJSEA5D December 2017 – October 2019 OPA207
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
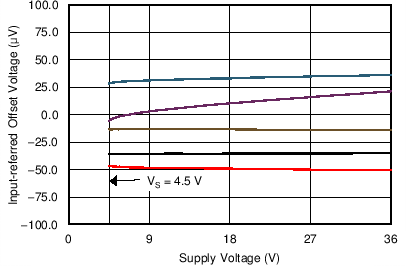
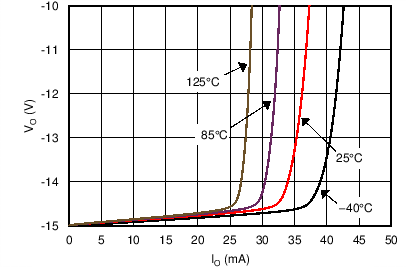
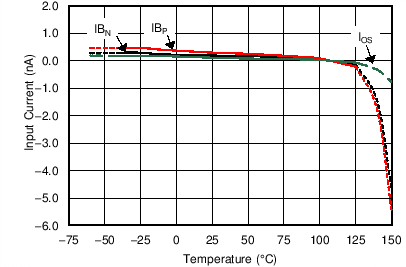
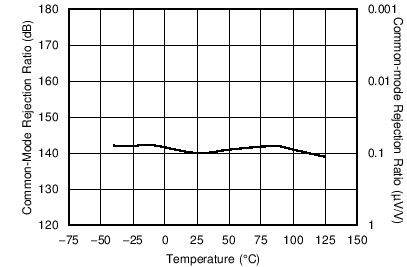
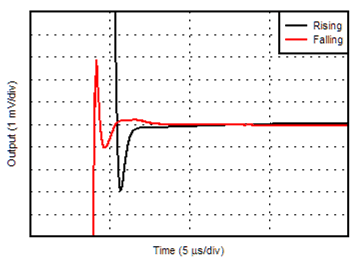
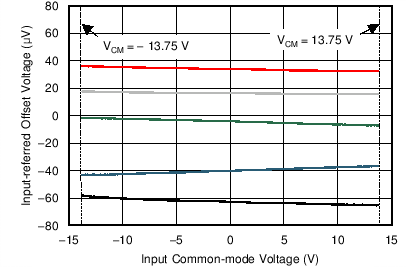
6.6 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±15 V, and RL = 2 kΩ (unless otherwise noted)






| G = +1 V/V | ||
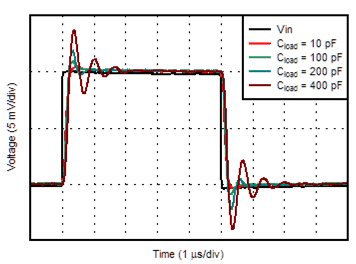
| G = +1 V/V | ||

| G = –1 V/V | ||

| VOUT = 3 VRMS |
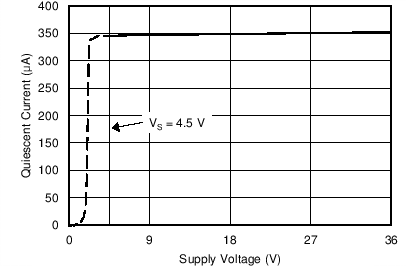
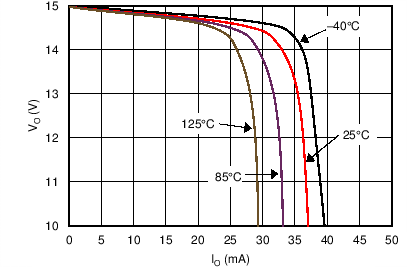

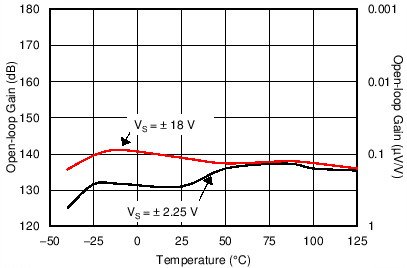




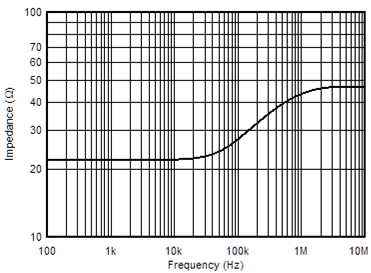
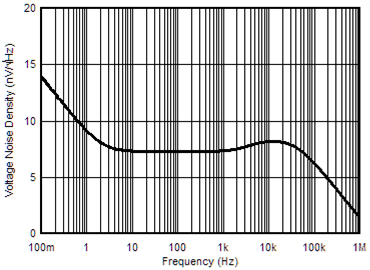


| VOUT = 3 VRMS | ||

| G = –1 V/V |

| G = +1 V/V | ||
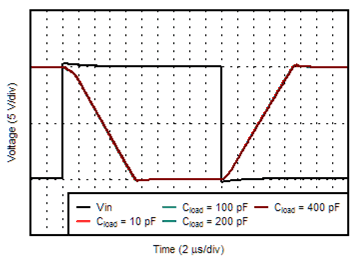
| G = –1 V/V | ||

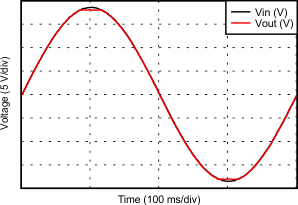
| VOUT = 3 VRMS |