JAJSKI5 February 2021 OPA859-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.5 Current Noise
The input impedance of CMOS and JFET input amplifiers at low frequencies exceed several GΩs. However, at higher frequencies, the transistors parasitic capacitance to the drain, source, and substrate reduces the impedance. The high impedance at low frequencies eliminates any bias current and the associated shot noise. At higher frequencies, the input current noise increases (see Figure 8-8) as a result of capacitive coupling between the CMOS gate oxide and the underlying transistor channel. This phenomenon is a natural artifact of the construction of the transistor and is unavoidable.
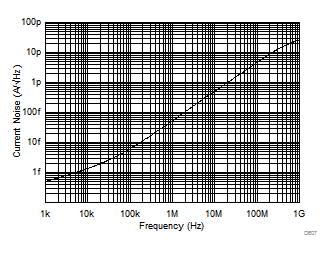 Figure 8-8 Input Current Noise (IBN and IBI) vs Frequency
Figure 8-8 Input Current Noise (IBN and IBI) vs Frequency