JAJSSO6 December 2023 PCM6140-Q1
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Timing Requirements: I2C Interface
- 6.7 Switching Characteristics: I2C Interface
- 6.8 Timing Requirements: SPI Interface
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics: SPI Interface
- 6.10 Timing Requirements: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 6.12 Timing Requirements: PDM Digital Microphone Interface
- 6.13 Switching Characteristics: PDM Digial Microphone Interface
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Serial Interfaces
- 7.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 7.3.3 Input Channel Configurations
- 7.3.4 Reference Voltage
- 7.3.5 Programmable Microphone Bias
- 7.3.6
Signal-Chain Processing
- 7.3.6.1 Programmable Channel Gain and Digital Volume Control
- 7.3.6.2 Programmable Channel Gain Calibration
- 7.3.6.3 Programmable Channel Phase Calibration
- 7.3.6.4 Programmable Digital High-Pass Filter
- 7.3.6.5 Programmable Digital Biquad Filters
- 7.3.6.6 Programmable Channel Summer and Digital Mixer
- 7.3.6.7
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 7.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.6.7.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8 kHz or 7.35 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.8 Sampling Rate: 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.9 Sampling Rate 768 kHz or 705.6 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.2 Low-Latency Filters
- 7.3.6.7.3
Ultra-Low-Latency Filters
- 7.3.6.7.3.1 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.2 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.3 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.4 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.5 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.6 Sampling Rate 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.7 Sampling Rate 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.7 Dynamic Range Enhancer (DRE)
- 7.3.8 Automatic Gain Controller (AGC)
- 7.3.9 Digital PDM Microphone Record Channel
- 7.3.10 Interrupts, Status, and Digital I/O Pin Multiplexing
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 7.6.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 7.6.1.1.1 PAGE_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x00) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.2 SW_RESET Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x01) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.3 SLEEP_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x02) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.4 SHDN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x05) [reset = 5h]
- 7.6.1.1.5 ASI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x07) [reset = 30h]
- 7.6.1.1.6 ASI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x08) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.7 ASI_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x09) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.8 ASI_CH1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.9 ASI_CH2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0C) [reset = 1h]
- 7.6.1.1.10 ASI_CH3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0D) [reset = 2h]
- 7.6.1.1.11 ASI_CH4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0E) [reset = 3h]
- 7.6.1.1.12 ASI_CH5 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0F) [reset = 4h]
- 7.6.1.1.13 ASI_CH6 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x10) [reset = 5h]
- 7.6.1.1.14 ASI_CH7 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x11) [reset = 6h]
- 7.6.1.1.15 ASI_CH8 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x12) [reset = 7h]
- 7.6.1.1.16 MST_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x13) [reset = 2h]
- 7.6.1.1.17 MST_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x14) [reset = 48h]
- 7.6.1.1.18 ASI_STS Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x15) [reset = FFh]
- 7.6.1.1.19 CLK_SRC Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x16) [reset = 10h]
- 7.6.1.1.20 PDMCLK_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x1F) [reset = 40h]
- 7.6.1.1.21 PDMIN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x20) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.22 GPIO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x21) [reset = 22h]
- 7.6.1.1.23 GPO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x22) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.24 GPO_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x23) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.25 GPO_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x24) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.26 GPO_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x25) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.27 GPO_VAL Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x29) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.28 GPIO_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2A) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.29 GPI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.30 GPI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2C) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.31 GPI_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2F) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.32 INT_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x32) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.33 INT_MASK0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x33) [reset = FFh]
- 7.6.1.1.34 INT_LTCH0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x36) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.35 BIAS_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.36 CH1_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3C) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.37 CH1_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3D) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.38 CH1_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3E) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.39 CH1_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3F) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.40 CH1_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x40) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.41 CH2_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x41) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.42 CH2_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x42) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.43 CH2_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x43) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.44 CH2_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x44) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.45 CH2_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x45) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.46 CH3_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x46) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.47 CH3_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x47) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.48 CH3_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x48) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.49 CH3_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x49) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.50 CH3_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4A) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.51 CH4_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.52 CH4_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4C) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.53 CH4_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4D) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.54 CH4_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4E) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.55 CH4_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4F) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.56 CH5_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x52) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.57 CH5_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x53) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.58 CH5_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x54) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.59 CH6_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x57) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.60 CH6_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x58) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.61 CH6_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x59) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.62 CH7_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5C) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.63 CH7_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5D) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.64 CH7_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5E) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.65 CH8_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x61) [reset = C9h]
- 7.6.1.1.66 CH8_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x62) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.67 CH8_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x63) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.68 DSP_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6B) [reset = 1h]
- 7.6.1.1.69 DSP_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6C) [reset = 40h]
- 7.6.1.1.70 DRE_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6D) [reset = 7Bh]
- 7.6.1.1.71 AGC_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x70) [reset = E7h]
- 7.6.1.1.72 IN_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x73) [reset = F0h]
- 7.6.1.1.73 ASI_OUT_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x74) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.74 PWR_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x75) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.75 DEV_STS0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x76) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1.76 DEV_STS1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x77) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.1.77 I2C_CKSUM Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x7E) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 7.6.2 Programmable Coefficient Registers
- 7.6.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.8 Automatic Gain Controller (AGC)
The device includes an automatic gain controller (AGC) for ADC recording. As shown in Figure 7-63, the AGC can be used to maintain a nominally constant output level when recording speech. Instead of manually setting the channel gain in AGC mode, the circuitry automatically adjusts the channel gain when the input signal becomes overly loud or very weak, such as when a person speaking into a microphone moves closer to or farther from the microphone. The AGC algorithm has several programmable parameters, including target level, maximum gain allowed, attack and release (or decay) time constants, and noise thresholds that allow the algorithm to be fine-tuned for any particular application.
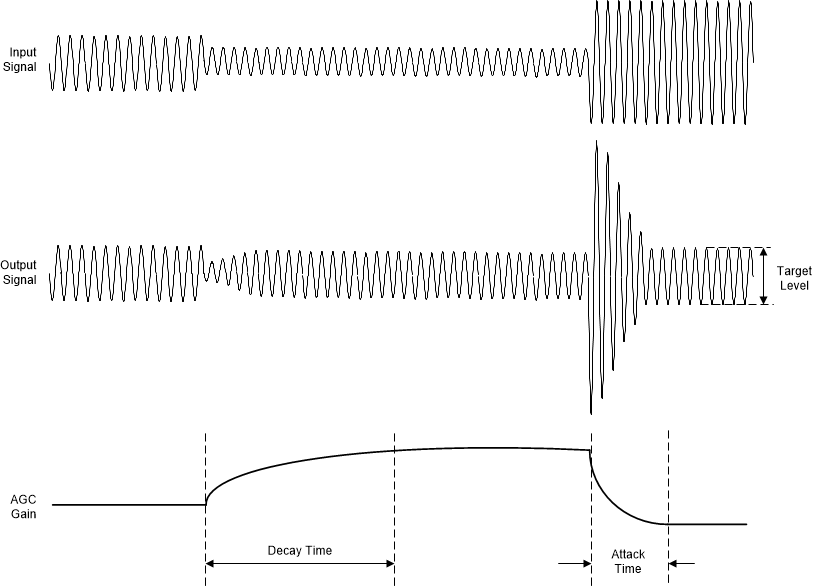 Figure 7-63 AGC Characteristics
Figure 7-63 AGC CharacteristicsThe target level (AGC_LVL) represents the nominal approximate output level at which the AGC attempts to hold the ADC output signal level. The PCM6140-Q1 allows programming of different target levels, which can be programmed from –6 dB to –36 dB relative to a full-scale signal, and the AGC_LVL default value is set to –34 dB. The target level is recommended to be set with enough margin to prevent clipping when loud sounds occur. Table 7-47 lists the AGC target level configuration settings.
| P0_R112_D[7:4] : AGC_LVL[3:0] | AGC TARGET LEVEL FOR OUTPUT |
|---|---|
| 0000 | The AGC target level is the –6-dB output signal level |
| 0001 | The AGC target level is the –8-dB output signal level |
| 0010 | The AGC target level is the –10-dB output signal level |
| … | … |
| 1110 (default) | The AGC target level is the –34-dB output signal level |
| 1111 | The AGC target level is the –36-dB output signal level |
The maximum gain allowed (AGC_MAXGAIN) gives flexibility to the designer to restrict the maximum gain applied by the AGC. This feature limits the channel gain in situations where environmental noise is greater than the programmed noise threshold. The AGC_MAXGAIN can be programmed from 3 dB to 42 dB with steps of 3 dB and the default value is set to 24 dB. Table 7-48 lists the AGC_MAXGAIN configuration settings.
| P0_R112_D[3:0] : AGC_MAXGAIN[3:0] | AGC MAXIMUM GAIN ALLOWED |
|---|---|
| 0000 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 3 dB |
| 0001 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 6 dB |
| 0010 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 9 dB |
| … | … |
| 0111 (default) | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 24 dB |
| … | … |
| 1110 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 39 dB |
| 1111 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 42 dB |
For further details on the AGC various configurable parameter and application use, see the Using the Automatic Gain Controller (AGC) in TLV320ADCx140 application report.