SPNS155I September 2009 – June 2015 SM470R1B1M-HT
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Device Characteristics
- 4 Bare Die
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.5 Thermal Characteristics
- 6.6 ZPLL and Clock Specifications
- 6.7 RST and PORRST Timings
- 6.8 JTAG Scan Interface Timing
- 6.9 Output Timings
- 6.10 Input Timings
- 6.11 Flash Timings
- 6.12 SPIn Master Mode Timing Parameters
- 6.13 SPIn Slave Mode Timing Parameters
- 6.14 SCIN Isosynchronous Mode Timings - Internal Clock
- 6.15 SCIN Isosynchronous Mode Timings - External Clock
- 6.16 I2C Timing
- 6.17 Standard Can Controller (SCC) Mode Timings
- 6.18 Expansion Bus Module Timing
- 6.19 Multi-Buffered A-to-D Converter (MibADC)
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
9 Device and Documentation Support
9.1 Device Support
9.1.1 Device Identification Code Register
The device identification code register identifies the silicon version, the technology family (TF), a ROM or flash device, and an assigned device-specific part number (see Table 9-1). The B1M device identification code register value is 0xnA5F.
| 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 |
| Reserved | |||||||||||||||
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| VERSION | TF | R/F | PART NUMBER | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| R-K | R-K | R-K | R-K | R-1 | R-1 | R-1 | |||||||||
| LEGEND: For bits 3-15: R = Read only, -K = Value constant after RESET. For bits 0-2: R = Read only, -1 = Value after RESET. |
Table 9-1 SM470 Device ID Bit Allocation Register Field Descriptions
| BIT | FIELD | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31-16 | Reserved | Reads are undefined and writes have no effect. | |
| 15-12 | VERSION | Silicon version (revision) bits These bits identify the silicon version of the device. |
|
| 11 | TF | Technology family bit This bit distinguishes the technology family core power supply: |
|
| 0 | 3.3 V for F10/C10 devices | ||
| 1 | 1.8 V for F05/C05 devices | ||
| 10 | R/F | ROM/flash bit This bit distinguishes between ROM and flash devices: |
|
| 0 | Flash device | ||
| 1 | ROM device | ||
| 9-3 | PART NUMBER | Device-specific part number bits These bits identify the assigned device-specific part number. The assigned device-specific part number for the B1M device is 1001011. |
|
| 2-0 | 1 | Mandatory High Bits 2, 1, and 0 are tied high by default. |
9.1.2 Timing Parameter Symbology
Timing parameter symbols have been created in accordance with JEDEC Standard 100. To shorten the symbols, some of the pin names and other related terminology have been abbreviated as follows:
| CM | Compaction, CMPCT | RD | Read |
| CO | CLKOUT | RST | Reset, RST |
| ER | Erase | RX | SCInRX |
| ICLK | Interface clock | S | Slave mode |
| M | Master mode | SCC | SCInCLK |
| OSC, OSCI | OSCIN | SIMO | SPInSIMO |
| OSCO | OSCOUT | SOMI | SPInSOMI |
| P | Program, PROG | SPC | SPInCLK |
| R | Ready | SYS | System clock |
| R0 | Read margin 0, RDMRGN0 | TX | SCInTX |
| R1 | Read margin 1, RDMRGN1 |
Lowercase subscripts and their meanings are:
| a | access time | r | rise time |
| c | cycle time (period) | su | setup time |
| d | delay time | t | transition time |
| f | fall time | v | valid time |
| h | hold time | w | pulse duration (width) |
The following additional letters are used with these meanings:
| H | High | X | Unknown, changing, or don't care level |
| L | Low | Z | High impedance |
| V | Valid |
9.2 Development Support
TI offers an extensive line of development tools, including tools to evaluate the performance of the processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully integrate and debug software and hardware modules. The tool's support documentation is electronically available within the Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
The following products support development of the SM470R1B1M-HT device applications:
Software Development Tools: Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE): including Editor C/C++/Assembly Code Generation, and Debug plus additional development tools Scalable, Real-Time Foundation Software (DSP/BIOS™), which provides the basic run-time target software needed to support any SM470R1B1M-HT device application.
Hardware Development Tools: Extended Development System (XDS™) Emulator
For a complete listing of development-support tools for the SM470R1B1M-HT platform, visit the Texas Instruments website at www.ti.com. For information on pricing and availability, contact the nearest TI field sales office or authorized distributor.
9.3 Device Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all DSP devices and support tools. Each DSP commercial family member has one of three prefixes: TMX, TMP, or TMS (for example, TMS470R1B1M). Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (TMX/TMDX) through fully qualified production devices/tools (TMS/TMDS).
Device development evolutionary flow:
-
TMXExperimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device's electrical specifications
-
TMP Final silicon die that conforms to the device's electrical specifications but has not completed quality and reliability verification
-
SM Fully qualified production device
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
-
TMDX Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal qualification testing.
-
TMDS Fully qualified development-support product
TMX and TMP devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped against the following disclaimer:
"Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes."
TMS devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (TMX or TMP) have a greater failure rate than the standard production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used.
Figure 9-2 illustrates the numbering and symbol nomenclature for the SM470R1x family.
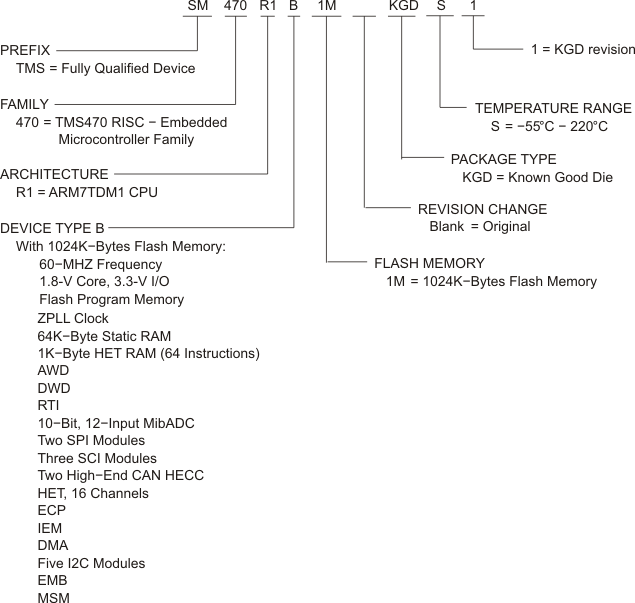 Figure 9-2 SM470R1x Family Nomenclature
Figure 9-2 SM470R1x Family Nomenclature
9.4 Documentation Support
Extensive documentation supports all of the SM470 microcontroller family generation of devices. The types of documentation available include data sheets with design specifications; complete user's guides for all devices and development support tools; and hardware and software applications. Useful reference documentation includes:
- Bulletin
- TMS470 Microcontroller Family Product Bulletin (SPNB086)
- User's Guides
- TMS470R1x System Module Reference Guide (SPNU189)
- TMS470R1x General Purpose Input/Output (GIO) Reference Guide (SPNU192)
- TMS470R1x Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller Reference Guide (SPNU194)
- TMS470R1x Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller Reference Guide (SPNU194)
- TMS470R1x Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Reference Guide (SPNU195)
- TMS470R1x Serial Communication Interface (SCI) Reference Guide (SPNU196)
- TMS470R1x Controller Area Network (CAN) Reference Guide (SPNU197)
- TMS470R1x High End Timer (HET) Reference Guide (SPNU199)
- TMS470R1x External Clock Prescale (ECP) Reference Guide (SPNU202)
- TMS470R1x MultiBuffered Analog to Digital (MibADC) Reference Guide (SPNU206)
- TMS470R1x Zero Pin Phase Locked Loop (ZPLL) Clock Module Reference Guide (SPNU212)
- TMS470R1x Digital Watchdog Timer Reference Guide (SPNU244)
- TMS470R1x Interrupt Expansion Module (IEM) Reference Guide (SPNU211)
- TMS470R1x Class II Serial Interface B (C2SIb) Reference Guide (SPNU214)
- TMS470R1x Class II Serial Interface A (C2SIa) Reference Guide (SPNU218)
- TMS470R1x Expansion Bus Module (EBM) Reference Guide (SPNU222)
- TMS470R1x Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Reference Guide (SPNU223)
- TMS470R1x JTAG Security Module (JSM) Reference Guide (SPNU245)
- TMS470R1x Memory Security Module (MSM) Reference Guide (SPNU246)
- TMS470 Peripherals Overview Reference Guide (SPNU248)
- Errata Sheet
- TMS470R1B1M TMS470 Microcontrollers Silicon Errata (SPNZ139)
9.5 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
TI Embedded Processors Wiki Texas Instruments Embedded Processors Wiki. Established to help developers get started with Embedded Processors from Texas Instruments and to foster innovation and growth of general knowledge about the hardware and software surrounding these devices.
9.6 Trademarks
E2E is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
ARM7TDMI is a trademark of Advanced RISC Machines Limited (ARM).
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
9.7 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
9.8 Glossary
SLYZ022 — TI Glossary.
This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.