SPNS155I September 2009 – June 2015 SM470R1B1M-HT
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Device Characteristics
- 4 Bare Die
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.5 Thermal Characteristics
- 6.6 ZPLL and Clock Specifications
- 6.7 RST and PORRST Timings
- 6.8 JTAG Scan Interface Timing
- 6.9 Output Timings
- 6.10 Input Timings
- 6.11 Flash Timings
- 6.12 SPIn Master Mode Timing Parameters
- 6.13 SPIn Slave Mode Timing Parameters
- 6.14 SCIN Isosynchronous Mode Timings - Internal Clock
- 6.15 SCIN Isosynchronous Mode Timings - External Clock
- 6.16 I2C Timing
- 6.17 Standard Can Controller (SCC) Mode Timings
- 6.18 Expansion Bus Module Timing
- 6.19 Multi-Buffered A-to-D Converter (MibADC)
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
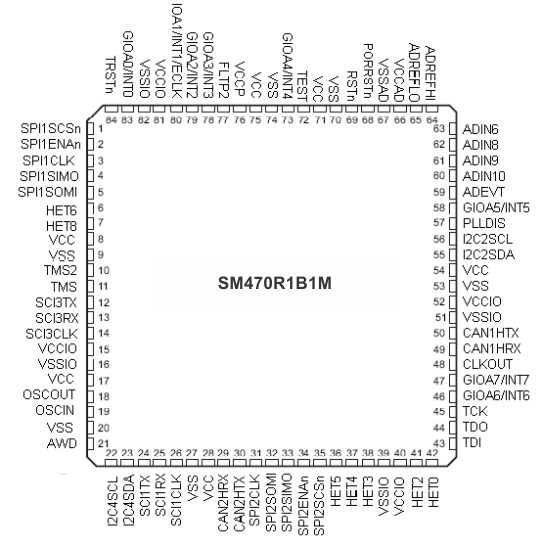 Figure 5-1 SM470R1B1M HFQ/HKP Packages, 84-Pin CQFP Ceramic Quad Flatpack (Top View)
Figure 5-1 SM470R1B1M HFQ/HKP Packages, 84-Pin CQFP Ceramic Quad Flatpack (Top View)
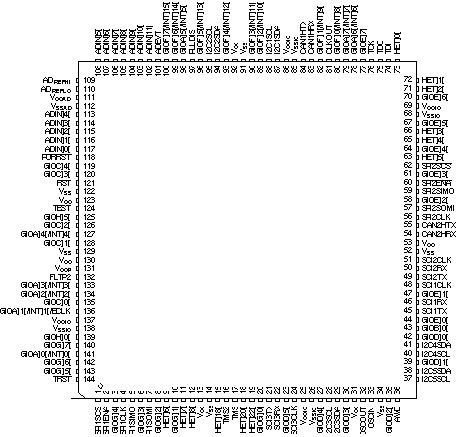 Figure 5-2 SM470R1B1M-HT PGE Package, 144-Pin LQFP Plastic Low-Profile Quad Flatpack Without Expansion Bus (Top View)
Figure 5-2 SM470R1B1M-HT PGE Package, 144-Pin LQFP Plastic Low-Profile Quad Flatpack Without Expansion Bus (Top View)
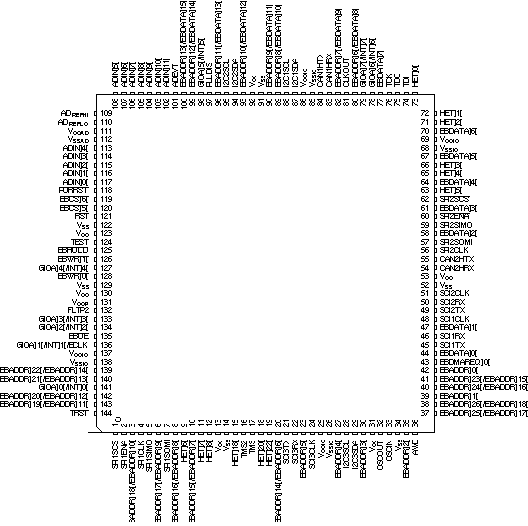 Figure 5-3 SM470R1B1M-HT PGE Package 144-Pin LQFP Plastic Low-Profile Quad Flatpack With Expansion Bus (Top View)
Figure 5-3 SM470R1B1M-HT PGE Package 144-Pin LQFP Plastic Low-Profile Quad Flatpack With Expansion Bus (Top View)
5.1 Features
The reduced pin count version of SM470R1B1M has the following features.
- Communication interfaces
- Two SPIs
- Two SCIs
- Two HECC
- Two I2C modules
- 4-channel, 10-bit MibADC
- High-end timer lite (HET) controlling seven programmable I/O channels
- Eight general-purpose I/Os
5.2 Pin Functions (HFQ/HKP Package)
| PIN | TYPE(2)(3) | CURRENT OUTPUT | INTERNAL PULLUP/ PULLDOWN(4) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | PAD NO. | HFQ/ HKP(1) | ||||
| HIGH-END TIMER (HET) | ||||||
| HET[0] | 76 | 42 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | Timer input capture or output compare. The HET[8:0,18,20,22] applicable pins can be programmed as general-purpose input/output (GIO) pins. All are high-resolution pins. The high-resolution (HR) SHARE feature allows even HR pins to share the next higher odd HR pin structures. This HR sharing is independent of whether or not the odd pin is available externally. If an odd pin is available externally and shared, then the odd pin can only be used as a general-purpose I/O. For more information on HR SHARE, see the TMS470R1x High-End Timer (HET) Reference Guide (SPNU199). |
| HET[1] | 75 | NC | ||||
| HET[2] | 74 | 41 | ||||
| HET[3] | 69 | 38 | ||||
| HET[4] | 68 | 37 | ||||
| HET[5] | 66 | 36 | ||||
| HET[6] | 9 | 6 | ||||
| HET[7] | 11 | NC | ||||
| HET[8] | 13 | 7 | ||||
| HET[18] | 16 | NC | ||||
| HET[20] | 19 | NC | ||||
| HET[22] | 20 | NC | ||||
| HIGH-END CAN CONTROLLER (HECC) | ||||||
| CAN1HRX | 86 | 49 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | HECC1 receive pin or GIO pin | |
| CAN1HTX | 87 | 50 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | HECC1 transmit pin or GIO pin |
| CAN2HRX | 57 | 29 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | HECC2 receive pin or GIO pin | |
| CAN2HTX | 58 | 30 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | HECC2 transmit pin or GIO pin |
| GENERAL-PURPOSE I/O (GIO) | ||||||
| GIOA[0]/INT[0] | 147 | 83 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | General-purpose input/output pins. GIOA[7:0]/INT[7:0] are interrupt-capable pins. GIOA[1]/INT[1]/ECLK pin is multiplexed with the external clock-out function of the external clock prescale (ECP) module. |
|
| GIOA[1]/INT[1]/ECLK | 140 | 80 | ||||
| GIOA[2]/INT[2] | 138 | 79 | ||||
| GIOA[3]/INT[3] | 137 | 78 | ||||
| GIOA[4]/INT[4] | 130 | 73 | ||||
| GIOA[5]/INT[5] | 101 | 58 | ||||
| GIOA[6]/INT[6] | 81 | 46 | ||||
| GIOA[7]/INT[7] | 82 | 47 | ||||
| GIOB[0]/EBDMAREQ0 | 46 | NC | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | GIOB[0], GIOC[4:0], GIOD[5:0], GIOE[7:0:], GIOF[7:0], GIOG[7:0], and GIOH[5,0] are multiplexed with the expansion bus module. See Table 8-3. |
| GIOC[0]/EBOE | 139 | NC | ||||
| GIOC[1]/EBWR[0] | 131 | NC | ||||
| GIOC[2]/EBWR[1] | 129 | NC | ||||
| GIOC[3]/EBCS[5] | 123 | NC | ||||
| GIOC[4]/EBCS[6] | 122 | NC | ||||
| GIOD[0]/EBADDR[0] | 45 | NC | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | GIOB[0], GIOC[4:0], GIOD[5:0], GIOE[7:0:], GIOF[7:0], GIOG[7:0], and GIOH[5,0] are multiplexed with the expansion bus module. GIOF[7:0]/INT[15:8] are interrupt-capable pins. See Table 8-3. |
| GIOD[1]/EBADDR[1] | 42 | NC | ||||
| GIOD[2]/EBADDR[2] | 38 | NC | ||||
| GIOD[3]/EBADDR[3] | 33 | NC | ||||
| GIOD[4]/EBADDR[4] | 30 | NC | ||||
| GIOD[5]/EBADDR[5] | 25 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[0]/EBDATA[0] | 47 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[1]/EBDATA[1] | 50 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[2]/EBDATA[2] | 61 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[3]/EBDATA[3] | 64 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[4]/EBDATA[4] | 67 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[5]/EBDATA[5] | 70 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[6]/EBDATA[6] | 73 | NC | ||||
| GIOE[7]/EBDATA[7] | 80 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[0]/INT[8]/ EBADDR[6]/EBDATA[8] |
83 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[1]/INT[9]/ EBADDR[7]/EBDATA[9] |
85 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[2]/INT[10]/ EBADDR[8]/EBDATA[10] |
92 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[3]/INT[11]/ EBADDR[9]/EBDATA[11] |
93 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[4]/INT[12]/ EBADDR[10]/EBDATA[12] |
96 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[5]/INT[13]/ EBADDR[11]/EBDATA[13] |
99 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[6]/INT[14]/ EBADDR[12]/EBDATA[14] |
102 | NC | ||||
| GIOF[7]/INT[15]/ EBADDR[13]/EBDATA[15] |
103 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[0]/EBADDR[14]/ EBADDR[6] |
21 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[1]/EBADDR[15]/ EBADDR[7] |
10 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[2]/EBADDR[16]/ EBADDR[8] |
8 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[3]/EBADDR[17]/ EBADDR[9] |
6 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[4]/EBADDR[18]/ EBADDR[10] |
3 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[5]/EBADDR[19]/ EBADDR[11] |
150 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[6]/EBADDR[20]/EBADDR[12] | 148 | NC | ||||
| GIOG[7]/EBADDR[21]/ EBADDR[13] |
145 | NC | ||||
| GIOH[0]/EBADDR[22]/ EBADDR[14] |
144 | NC | ||||
| GIOH[5]/EBHOLD | 128 | NC | ||||
| MULTI-BUFFERED ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER (MibADC) | ||||||
| ADEVT | 104 | 59 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | MibADC event input. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| ADIN[0] | 120 | NC | MibADC analog input pins | |||
| ADIN[1] | 119 | NC | ||||
| ADIN[2] | 118 | NC | ||||
| ADIN[3] | 117 | NC | ||||
| ADIN[4] | 116 | NC | ||||
| ADIN[5] | 111 | NC | ||||
| ADIN[6] | 110 | 63 | ||||
| ADIN[7] | 109 | NC | ||||
| ADIN[8] | 108 | 62 | ||||
| ADIN[9] | 107 | 61 | ||||
| ADIN[10] | 106 | 60 | ||||
| ADIN[11] | 105 | NC | ||||
| ADREFHI | 112 | 64 | 3.3 VREF | MibADC module high-voltage reference input | ||
| ADREFLO | 113 | 65 | GND REF | MibADC module low-voltage reference input | ||
| VCCAD | 114 | 66 | 3.3-V PWR | MibADC analog supply voltage | ||
| VSSAD | 115 | 67 | GND | MibADC analog ground reference | ||
| SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE 1 (SPI1) | ||||||
| SPI1CLK | 4 | 3 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SPI1 clock. SPI1CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SPI1ENA | 2 | 2 | SPI1 chip enable. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI1SCS | 1 | 1 | SPI1 slave chip select. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI1SIMO | 5 | 4 | SPI1 data stream. Slave in/master out. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI1SOMI | 7 | 5 | SPI1 data stream. Slave out/master in. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE 2 (SPI2) | ||||||
| SPI2CLK | 59 | 31 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SPI2 clock. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SPI2ENA | 63 | 34 | SPI2 chip enable. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI2SCS | 65 | 35 | SPI2 slave chip select. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI2SIMO | 62 | 33 | SPI2 data stream. Slave in/master out. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI2SOMI | 60 | 32 | SPI2 data stream. Slave out/master in. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 1 (I2C1) | ||||||
| I2C1SDA | 90 | NC | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C1 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C1SCL | 91 | NC | I2C1 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 2 (I2C2) | ||||||
| I2C2SDA | 97 | 55 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C2 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C2SCL | 98 | 56 | I2C2 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 3 (I2C3) | ||||||
| I2C3SDA | 32 | NC | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C3 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C3SCL | 31 | NC | I2C3 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 4 (I2C4) | ||||||
| I2C4SDA | 44 | 23 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C4 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C4SCL | 43 | 22 | I2C4 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 5 (I2C5) | ||||||
| I2C5SDA | 41 | NC | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C5 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C5SCL | 40 | NC | I2C5 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| ZERO-PIN PHASE-LOCKED LOOP (ZPLL) | ||||||
| OSCIN | 36 | 19 | 1.8 V | Crystal connection pin or external clock input | ||
| OSCOUT | 35 | 18 | 2 mA | External crystal connection pin | ||
| PLLDIS | 100 | 57 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Enable/disable the ZPLL. The ZPLL can be bypassed and the oscillator becomes the system clock. If not in bypass mode, TI recommends that this pin be connected to ground or pulled down to ground by an external resistor. | |
| SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE 1 (SCI1) | ||||||
| SCI1CLK | 51 | 26 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | SCI1 clock. SCI1CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SCI1RX | 49 | 25 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SCI1 data receive. SCI1RX can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SCI1TX | 48 | 24 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | SCI1 data transmit. SCI1TX can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE 2 (SCI2) | ||||||
| SCI2CLK | 54 | NC | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | SCI2 clock. SCI2CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SCI2RX | 53 | NC | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SCI2 data receive. SCI2RX can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SCI2TX | 52 | NC | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | SCI2 data transmit. SCI2TX can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE 3 (SCI3) | ||||||
| SCI3CLK | 27 | 14 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | SCI3 clock. SCI3CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SCI3RX | 24 | 13 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SCI3 data receive. SCI3RX can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SCI3TX | 23 | 12 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | SCI3 data transmit. SCI3TX can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SYSTEM MODULE (SYS) | ||||||
| CLKOUT | 84 | 48 | 3.3 V | 8 mA | Bidirectional pin. CLKOUT can be programmed as a GIO pin or the output of SYSCLK, ICLK, or MCLK. | |
| PORRST | 121 | 68 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Input master chip power-up reset. External VCC monitor circuitry must assert a power-on reset. | |
| RST | 124 | 69 | 3.3 V | 4 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Bidirectional reset. The internal circuitry can assert a reset, and an external system reset can assert a device reset. On this pin, the output buffer is implemented as an open drain (drives low only). To ensure an external reset is not arbitrarily generated, TI recommends that an external pullup resistor be connected to this pin. |
| WATCHDOG/REAL-TIME INTERRUPT (WD/RTI) | ||||||
| AWD | 39 | 21 | 3.3 V | 8 mA | Analog watchdog reset. The AWD pin provides a system reset if the WD KEY is not written in time by the system, providing an external RC network circuit is connected. If the user is not using AWD, TI recommends that this pin be connected to ground or pulled down to ground by an external resistor. For more details on the external RC network circuit, see the TMS470R1x System Module Reference Guide (SPNU189). |
|
| TEST/DEBUG (T/D) | ||||||
| TCK | 79 | 45 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Test clock. TCK controls the test hardware (JTAG). | |
| TDI | 77 | 43 | 8 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Test data in. TDI inputs serial data to the test instruction register, test data register, and programmable test address (JTAG). | |
| TDO | 78 | 44 | 8 mA | IPD (20 µA) | Test data out. TDO outputs serial data from the test instruction register, test data register, identification register, and programmable test address (JTAG). | |
| TEST | 127 | 72 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Test enable. Reserved for internal use only. TI recommends that this pin be connected to ground or pulled down to ground by an external resistor. | |
| TMS | 18 | 11 | 8 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Serial input for controlling the state of the CPU test access port (TAP) controller (JTAG). | |
| TMS2 | 17 | 10 | 8 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Serial input for controlling the second TAP. TI recommends that this pin be connected to VCCIO or pulled up to VCCIO by an external resistor. | |
| TRST | 151 | 84 | IPD (20 µA) | Test hardware reset to TAP1 and TAP2. IEEE Standard 1149-1 (JTAG) Boundary-Scan Logic. TI recommends that this pin be pulled down to ground by an external resistor. | ||
| FLASH | ||||||
| FLTP2 | 135 | 77 | NC | NC | Flash test pad 2. For proper operation, this pin must not be connected [no connect (NC)]. | |
| VCCP | 134 | 76 | 3.3-V PWR | Flash external pump voltage (3.3 V) | ||
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE CORE (1.8 V) | ||||||
| VCC | 14 | 8 | 1.8-V PWR | Core logic supply voltage | ||
| 34 | 17 | |||||
| 56 | 28 | |||||
| 95 | 54 | |||||
| 126 | 71 | |||||
| 133 | 75 | |||||
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE DIGITAL I/O (3.3 V) | ||||||
| VCCIO | 28 | 15 | 3.3-V PWR | Digital I/O supply voltage | ||
| 72 | 40 | |||||
| 89 | 52 | |||||
| 141 | 81 | |||||
| SUPPLY GROUND CORE | ||||||
| VSS | 15 | 9 | GND | Core supply ground reference | ||
| 37 | 20 | |||||
| 55 | 27 | |||||
| 94 | 53 | |||||
| 125 | 70 | |||||
| 132 | 74 | |||||
| SUPPLY GROUND DIGITAL I/O | ||||||
| VSSIO | 29 | 16 | GND | Digital I/O supply ground reference | ||
| 71 | 39 | |||||
| 88 | 51 | |||||
| 142 | 82 | |||||
(1) Any pins marked as NC are physically connected to ground internal to the package. Care must be used to keep these pins in a high impedance input state.
(2) PWR = power, GND = ground, REF = reference voltage, NC = no connect
(3) All I/O pins, except RST , are configured as inputs while PORRST is low and immediately after PORRST goes high.
(4) IPD = internal pulldown, IPU = internal pullup (all internal pullups and pulldowns are active on input pins, independent of the PORRST state.)
5.3 Pin Functions (PGE Package)
| PIN | TYPE(1)(2) | CURRENT OUTPUT | INTERNAL PULLUP/ PULLDOWN(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| HIGH-END TIMER (HET) | |||||
| HET[0] | 73 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | Timer input capture or output compare. The HET[8:0,18,20,22] applicable pins can be programmed as general-purpose input/output (GIO) pins. All are high-resolution pins. The high-resolution (HR) SHARE feature allows even HR pins to share the next higher odd HR pin structures. This HR sharing is independent of whether or not the odd pin is available externally. If an odd pin is available externally and shared, then the odd pin can only be used as a general-purpose I/O. For more information on HR SHARE, see the TMS470R1x High-End Timer (HET) Reference Guide (SPNU199). |
| HET[1] | 72 | ||||
| HET[2] | 71 | ||||
| HET[3] | 66 | ||||
| HET[4] | 65 | ||||
| HET[5] | 63 | ||||
| HET[6] | 9 | ||||
| HET[7] | 11 | ||||
| HET[8] | 12 | ||||
| HET[18] | 15 | ||||
| HET[20] | 18 | ||||
| HET[22] | 19 | ||||
| HIGH-END CAN CONTROLLER (HECC) | |||||
| CAN1HRX | 83 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | HECC1 receive pin or GIO pin | |
| CAN1HTX | 84 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | HECC1 transmit pin or GIO pin |
| CAN2HRX | 54 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | HECC2 receive pin or GIO pin | |
| CAN2HTX | 55 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | HECC2 transmit pin or GIO pin |
| STANDARD CAN CONTROLLER (SCC) | |||||
| CANSRX | - | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SCC receive pin. The CANSRX signal is only connected to the pad and not to a package pin. For reduced power consumption in low power mode, CANSRX should be driven output LOW. | |
| CANSTX | - | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | SCC transmit pin. The CANSTX signal is only connected to the pad and not to a package pin. For reduced power consumption in low power mode, CANSTX should be driven output LOW. |
| GENERAL-PURPOSE I/O (GIO) | |||||
| GIOA[0]/INT[0] | 141 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | General-purpose input/output pins. GIOA[7:0]/INT[7:0] are interrupt-capable pins. GIOA[1]/INT[1]/ECLK pin is multiplexed with the external clock-out function of the external clock prescale (ECP) module. |
|
| GIOA[1]/INT[1]/ECLK | 136 | ||||
| GIOA[2]/INT[2] | 134 | ||||
| GIOA[3]/INT[3] | 133 | ||||
| GIOA[4]/INT[4] | 127 | ||||
| GIOA[5]/INT[5] | 98 | ||||
| GIOA[6]/INT[6] | 78 | ||||
| GIOA[7]/INT[7] | 79 | ||||
| GIOB[0]/EBDMAREQ0 | 43 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | GIOB[0], GIOC[4:0], GIOD[5:0], GIOE[7:0:], GIOF[7:0], GIOG[7:0], and GIOH[5,0] are multiplexed with the expansion bus module. See Table 8-3. |
| GIOC[0]/EBOE | 135 | ||||
| GIOC[1]/EBWR[0] | 128 | ||||
| GIOC[2]/EBWR[1] | 126 | ||||
| GIOC[3]/EBCS[5] | 120 | ||||
| GIOC[4]/EBCS[6] | 119 | ||||
| GIOD[0]/EBADDR[0] | 42 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | GIOB[0], GIOC[4:0], GIOD[5:0], GIOE[7:0:], GIOF[7:0], GIOG[7:0], and GIOH[5,0] are multiplexed with the expansion bus module. GIOF[7:0]/INT[15:8] are interrupt-capable pins. See Table 8-3. |
| GIOD[1]/EBADDR[1] | 39 | ||||
| GIOD[2]/EBADDR[2] | 35 | ||||
| GIOD[3]/EBADDR[3] | 30 | ||||
| GIOD[4]/EBADDR[4] | 27 | ||||
| GIOD[5]/EBADDR[5] | 23 | ||||
| GIOE[0]/EBDATA[0] | 44 | ||||
| GIOE[1]/EBDATA[1] | 47 | ||||
| GIOE[2]/EBDATA[2] | 58 | ||||
| GIOE[3]/EBDATA[3] | 61 | ||||
| GIOE[4]/EBDATA[4] | 64 | ||||
| GIOE[5]/EBDATA[5] | 67 | ||||
| GIOE[6]/EBDATA[6] | 70 | ||||
| GIOE[7]/EBDATA[7] | 77 | ||||
| GIOF[0]/INT[8]/ EBADDR[6]/EBDATA[8] |
80 | ||||
| GIOF[1]/INT[9]/ EBADDR[7]/EBDATA[9] |
82 | ||||
| GIOF[2]/INT[10]/ EBADDR[8]/EBDATA[10] |
89 | ||||
| GIOF[3]/INT[11]/ EBADDR[9]/EBDATA[11] |
90 | ||||
| GIOF[4]/INT[12]/ EBADDR[10]/EBDATA[12] |
93 | ||||
| GIOF[5]/INT[13]/ EBADDR[11]/EBDATA[13] |
96 | ||||
| GIOF[6]/INT[14]/ EBADDR[12]/EBDATA[14] |
99 | ||||
| GIOF[7]/INT[15]/ EBADDR[13]/EBDATA[15] |
100 | ||||
| GIOG[0]/EBADDR[14]/ EBADDR[6] |
20 | ||||
| GIOG[1]/EBADDR[15]/ EBADDR[7] |
10 | ||||
| GIOG[2]/EBADDR[16]/ EBADDR[8] |
8 | ||||
| GIOG[3]/EBADDR[17]/ EBADDR[9] |
6 | ||||
| GIOG[4]/EBADDR[18]/ EBADDR[10] |
3 | ||||
| GIOG[5]/EBADDR[19]/ EBADDR[11] |
143 | ||||
| GIOG[6]/EBADDR[20]/EBADDR[12] | 142 | ||||
| GIOG[7]/EBADDR[21]/ EBADDR[13] |
140 | ||||
| GIOH[0]/EBADDR[22]/ EBADDR[14] |
139 | ||||
| GIOH[5]/EBHOLD | 125 | ||||
| MULTI-BUFFERED ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER (MibADC) | |||||
| ADEVT | 101 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | MibADC event input. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| ADIN[0] | 117 | MibADC analog input pins | |||
| ADIN[1] | 116 | ||||
| ADIN[2] | 115 | ||||
| ADIN[3] | 114 | ||||
| ADIN[4] | 113 | ||||
| ADIN[5] | 108 | ||||
| ADIN[6] | 107 | ||||
| ADIN[7] | 106 | ||||
| ADIN[8] | 105 | ||||
| ADIN[9] | 104 | ||||
| ADIN[10] | 103 | ||||
| ADIN[11] | 102 | ||||
| ADREFHI | 109 | 3.3 VREF | MibADC module high-voltage reference input | ||
| ADREFLO | 110 | GND REF | MibADC module low-voltage reference input | ||
| VCCAD | 111 | 3.3-V PWR | MibADC analog supply voltage | ||
| VSSAD | 112 | GND | MibADC analog ground reference | ||
| SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE 1 (SPI1) | |||||
| SPI1CLK | 4 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SPI1 clock. SPI1CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SPI1ENA | 2 | SPI1 chip enable. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI1SCS | 1 | SPI1 slave chip select. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI1SIMO | 5 | SPI1 data stream. Slave in/master out. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI1SOMI | 7 | SPI1 data stream. Slave out/master in. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE 2 (SPI2) | |||||
| SPI2CLK | 56 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SPI2 clock. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SPI2ENA | 60 | SPI2 chip enable. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI2SCS | 62 | SPI2 slave chip select. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI2SIMO | 59 | SPI2 data stream. Slave in/master out. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| SPI2SOMI | 57 | SPI2 data stream. Slave out/master in. Can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 1 (I2C1) | |||||
| I2C1SDA | 87 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C1 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C1SCL | 88 | I2C1 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 2 (I2C2) | |||||
| I2C2SDA | 94 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C2 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C2SCL | 95 | I2C2 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 3 (I2C3) | |||||
| I2C3SDA | 29 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C3 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C3SCL | 28 | I2C3 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 4 (I2C4) | |||||
| I2C4SDA | 41 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C4 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C4SCL | 40 | I2C4 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 5 (I2C5) | |||||
| I2C5SDA | 38 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | I2C5 serial data pin or GIO pin | |
| I2C5SCL | 37 | I2C5 serial clock pin or GIO pin | |||
| ZERO-PIN PHASE-LOCKED LOOP (ZPLL) | |||||
| OSCIN | 33 | 1.8 V | Crystal connection pin or external clock input | ||
| OSCOUT | 32 | 2 mA | External crystal connection pin | ||
| PLLDIS | 97 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Enable/disable the ZPLL. The ZPLL can be bypassed and the oscillator becomes the system clock. If not in bypass mode, TI recommends that this pin be connected to ground or pulled down to ground by an external resistor. | |
| SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE 1 (SCI1) | |||||
| SCI1CLK | 48 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | SCI1 clock. SCI1CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SCI1RX | 46 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SCI1 data receive. SCI1RX can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SCI1TX | 45 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | SCI1 data transmit. SCI1TX can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE 2 (SCI2) | |||||
| SCI2CLK | 51 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | SCI2 clock. SCI2CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SCI2RX | 50 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SCI2 data receive. SCI2RX can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SCI2TX | 49 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | SCI2 data transmit. SCI2TX can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE 3 (SCI3) | |||||
| SCI3CLK | 24 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPD (20 µA) | SCI3 clock. SCI3CLK can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SCI3RX | 22 | 5-V tolerant | 4 mA | SCI3 data receive. SCI3RX can be programmed as a GIO pin. | |
| SCI3TX | 21 | 3.3 V | 2 mA -z | IPU (20 µA) | SCI3 data transmit. SCI3TX can be programmed as a GIO pin. |
| SYSTEM MODULE (SYS) | |||||
| CLKOUT | 81 | 3.3 V | 8 mA | Bidirectional pin. CLKOUT can be programmed as a GIO pin or the output of SYSCLK, ICLK, or MCLK. | |
| PORRST | 118 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Input master chip power-up reset. External VCC monitor circuitry must assert a power-on reset. | |
| RST | 121 | 3.3 V | 4 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Bidirectional reset. The internal circuitry can assert a reset, and an external system reset can assert a device reset. On this pin, the output buffer is implemented as an open drain (drives low only). To ensure an external reset is not arbitrarily generated, TI recommends that an external pullup resistor be connected to this pin. |
| WATCHDOG/REAL-TIME INTERRUPT (WD/RTI) | |||||
| AWD | 36 | 3.3 V | 8 mA | Analog watchdog reset. The AWD pin provides a system reset if the WD KEY is not written in time by the system, providing an external RC network circuit is connected. If the user is not using AWD, TI recommends that this pin be connected to ground or pulled down to ground by an external resistor. For more details on the external RC network circuit, see the TMS470R1x System Module Reference Guide (SPNU189). |
|
| TEST/DEBUG (T/D) | |||||
| TCK | 76 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Test clock. TCK controls the test hardware (JTAG). | |
| TDI | 74 | 8 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Test data in. TDI inputs serial data to the test instruction register, test data register, and programmable test address (JTAG). | |
| TDO | 75 | 8 mA | IPD (20 µA) | Test data out. TDO outputs serial data from the test instruction register, test data register, identification register, and programmable test address (JTAG). | |
| TEST | 124 | 3.3 V | IPD (20 µA) | Test enable. Reserved for internal use only. TI recommends that this pin be connected to ground or pulled down to ground by an external resistor. | |
| TMS | 17 | 8 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Serial input for controlling the state of the CPU test access port (TAP) controller (JTAG). | |
| TMS2 | 16 | 8 mA | IPU (20 µA) | Serial input for controlling the second TAP. TI recommends that this pin be connected to VCCIO or pulled up to VCCIO by an external resistor. | |
| TRST | 144 | IPD (20 µA) | Test hardware reset to TAP1 and TAP2. IEEE Standard 1149-1 (JTAG) Boundary-Scan Logic. TI recommends that this pin be pulled down to ground by an external resistor. | ||
| FLASH | |||||
| FLTP2 | 132 | NC | NC | Flash test pad 2. For proper operation, this pin must not be connected [no connect (NC)]. | |
| VCCP | 131 | 3.3-V PWR | Flash external pump voltage (3.3 V) | ||
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE CORE (1.8 V) | |||||
| VCC | 13 | 1.8-V PWR | Core logic supply voltage | ||
| 31 | |||||
| 53 | |||||
| 92 | |||||
| 123 | |||||
| 130 | |||||
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE DIGITAL I/O (3.3 V) | |||||
| VCCIO | 25 | 3.3-V PWR | Digital I/O supply voltage | ||
| 69 | |||||
| 86 | |||||
| 137 | |||||
| SUPPLY GROUND CORE | |||||
| VSS | 14 | GND | Core supply ground reference | ||
| 34 | |||||
| 52 | |||||
| 91 | |||||
| 122 | |||||
| 129 | |||||
| SUPPLY GROUND DIGITAL I/O | |||||
| VSSIO | 26 | GND | Digital I/O supply ground reference | ||
| 68 | |||||
| 85 | |||||
| 138 | |||||
(1) PWR = power, GND = ground, REF = reference voltage, NC = no connect
(2) All I/O pins, except RST , are configured as inputs while PORRST is low and immediately after PORRST goes high.
(3) IPD = internal pulldown, IPU = internal pullup (all internal pullups and pulldowns are active on input pins, independent of the PORRST state.)