-
SNx5HVD251 Industrial CAN Bus Transceiver SLLS545G November 2002 – October 2015 SN55HVD251 , SN65HVD251
PRODUCTION DATA.
-
SNx5HVD251 Industrial CAN Bus Transceiver
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Supply Current
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Driver
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Receiver
- 6.8 VREF-Pin Characteristics
- 6.9 Power Dissipation Characteristics
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics: Driver
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics: Device
- 6.12 Switching Characteristics: Receiver
- 6.13 Dissipation Ratings
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
SNx5HVD251 Industrial CAN Bus Transceiver
1 Features
- Drop-In Improved Replacement for the PCA82C250 and PCA82C251
- Bus-Fault Protection of ±36 V
- Meets or Exceeds ISO 11898
- Signaling Rates(1) up to 1 Mbps
- High Input Impedance Allows up to 120 Nodes on a Bus
- Bus Pin ESD Protection Exceeds 14 kV HBM
- Unpowered Node Does Not Disturb the Bus
- Low-Current Standby Mode: 200-µA Typical
- Thermal Shutdown Protection
- Glitch-Free Power-Up and Power-Down CAN Bus Protection for Hot-Plugging
- DeviceNet Vendor ID #806 (1)
2 Applications
- CAN Data Buses
- Industrial Automation
- SAE J1939 Standard Data Bus Interface
- NMEA 2000 Standard Data Bus Interface
Block Diagram
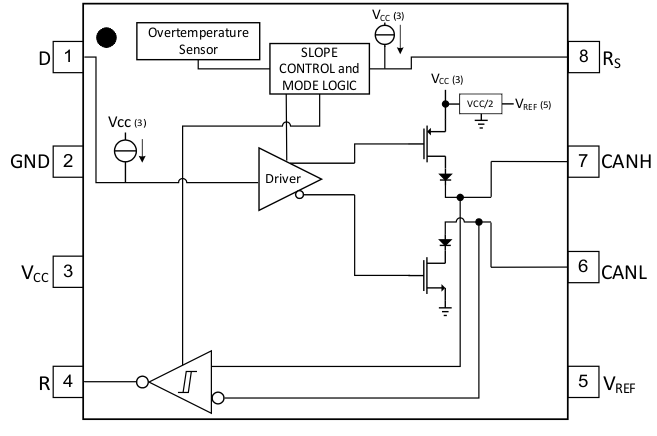
3 Description
The HVD251 is intended for use in applications employing the Controller Area Network (CAN) serial communication physical layer in accordance with the ISO 11898 Standard. The HVD251 provides differential transmit capability to the bus and differential receive capability to a CAN controller at speeds up to 1 megabits per second (Mbps).
Designed for operation in harsh environments, the device features cross-wire, overvoltage and loss of ground protection to ±36 V. Also featured are overtemperature protection as well as –7-V to 12-V common-mode range, and tolerance to transients of ±200 V. The transceiver interfaces the single-ended CAN controller with the differential CAN bus found in industrial, building automation, and automotive applications.
Rs, pin 8, selects one of three different modes of operation: high-speed, slope control, or low-power mode. The high-speed mode of operation is selected by connecting pin 8 to ground, allowing the transmitter output transistors to switch as fast as possible with no limitation on the rise and fall slope. The rise and fall slope can be adjusted by connecting a resistor to ground at pin 8; the slope is proportional to the pin's output current. Slope control with an external resistor value of 10 kΩ gives about 15-V / µs slew rate; 100 kΩ gives about 2-V/µs slew rate.
If a high logic level is applied to the Rs pin 8, the device enters a low-current standby mode where the driver is switched off and the receiver remains active. The local protocol controller returns the device to the normal mode when it transmits to the bus.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| SN55HVD251 | WSON (8) | 4.00 mm × 4.00 mm |
| SN65HVD251 | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| PDIP (8) | 9.81 mm × 6.35 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
4 Revision History
Changes from F Revision (June 2015) to G Revision
- Changed the value of HBM "All pins" From: ±14000 V To: ±6000 V. Changed the value of "CANH, CANL and GND" From: ±6000 V To: ±14000 V in the ESD RatingsGo
Changes from E Revision (March 2010) to F Revision
- Added Pin Configuration and Functions section, ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
- Changed the location of section "6.12 VREF-Pin Characteristics" to section 6.8 Go
Changes from C Revision (September 2005) to D Revision
- Added device SN55HVD251Go
- Added the DRJ Package.Go
- Changed the data sheet title From: CAN TRANSCEIVER To: INDUSTRIAL CAN TRANSCEIVERGo
- Deleted APPLICATIONS bullets: DeviceNet™ Data Buses, Smart Distributed Systems (SDS™), and ISO 11783 Standard Data Bus InterfaceGo
- Deleted last paragraph from the DESCRIPTION - "The HVD251 may be used..."Go
- Added Electrical fast transient/burst to the Abs Max Ratings tableGo
- Deleted the condition - over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted). From the RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS tableGo
- Added SN55HVD251 to the Operating free-air temperature, TA in the ROC tableGo
- Added DRJ to the Junction-to-case thermal resistanceGo
- Added DRJ to the Junction-to-board thermal resistanceGo
- Added the SUPPLY CURRENT tableGo
- Deleted ICC - Supply current from the DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICSGo
- Added T ≥ -40°C to VO(D) Test Conditions in the DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Go
- Added RNODE = 330 Ω to Differential output voltage (Dominant) (second line of Test Conditions) in the DRIVER ELECTRICAL tableGo
- Added a third line of Test Conditions to Differential output voltage (Dominant) in the DRIVER ELECTRICAL tableGo
- Added T ≤ 85°C to VOD®) Test Conditions in the DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Go
- Deleted ICC - Supply current from the RECEIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICSGo
- Added Receiver noise rejection row to the RECEIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC tableGo
- Added TYP values to the Differential output signal rise and fall times in the DRIVER SWITCHING CHARACTERISTIC tableGo
- Changed table title From: ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION RATINGS To: PACKAGE DISSIPATION RATINGSGo
- Added the SON (DRJ) option to the PACKAGE DISSIPATION RATINGS tableGo
- Changed Figure 1 title From: tLOOP1-LOOP TIME To: RECESSIVE-TO-DOMINANT LOOP DELAYGo
- Changed Figure 2 title From: tLOOP2-LOOP TIME To: DOMINANT-TO-RECESSIVE LOOP DELAYGo
- Changed Figure 4 From: DRIVER LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT vs LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE To: DRIVER OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs OUTPUT CURRENTGo
- Changed Figure 5 From: DRIVER HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT vs HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE To: DRIVER DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs OUTPUT CURRENTGo
- Changed Figure 8 title From: DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT FALL TIME To: DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT TRANSITION TIMEGo
- Changed Figure 12 - Driver VOD, label RNODE was 330Ω±1%Go
- Changed Table 1 header From: MEASURED To: DIFFERENTIAL INPUTGo
- Added Note B to Figure 22Go
- Added a row ( X Open) to Table 2 - DriverGo
Changes from B Revision (September 2003) to C Revision
- Changed the front page format.Go
- Changed Junction temperature, TJ - SOIC Package MAX value From 150°C To: 145°CGo
- Changed the THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS table valuesGo
- Changed the ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION RATINGS table valuesGo
Changes from A Revision (September 2003) to B Revision
- Changed the front page format.Go
- Changed DESCRIPTION text From: and tolerance to transients of ±50 V To: and tolerance to transients of ±200 VGo
Changes from * Revision (November 2002) to A Revision
- Changed multiple items within the document.Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| CANH | 7 | I/O | High-level CAN bus line |
| CANL | 6 | I/O | Low-level CAN bus line |
| D | 1 | I | CAN transmit data input (LOW for dominant and HIGH for recessive bus states), also called TXD, driver input |
| GND | 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| R | 4 | O | CAN receive data output (LOW for dominant and HIGH for recessive bus states), also called RXD, receiver output |
| RS | 8 | I | Mode select pin: strong pulldown to GND = high-speed mode, strong pull up to VCC = low-power mode, 10-kΩ to 100-kΩ pulldown to GND = slope control mode |
| VCC | 3 | Supply | Transceiver 5-V supply voltage |
| VREF | 5 | O | Reference output voltage |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)(2)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VCC | –0.3 | 7 | V | ||
| Voltage at any bus pin(CANH or CANL) | –36 | 36 | V | ||
| Transient voltage per ISO 7637, pulse 1, 2, 3a, 3b | CANH, CANL | –200 | 200 | V | |
| Input voltage, VI (D, Rs, or R) | –0.3 | VCC + 0.5 | V | ||
| Receiver output current, IO | –10 | 10 mA | mA | ||
| Electrical fast transient/burst | IEC 61000-4-4, Classification B | CANH, CANL | –3 | 3 | kV |
| Continuous total power dissipation | (see Dissipation Ratings) | ||||
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | All pins | ±6000 | V |
| CANH, CANL and GND | ±14000 | ||||
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | ||||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VCC | 4.5 | 5.5 | V | ||||
| Voltage at any bus terminal (separately or common mode) VI or VIC | –7(1) | 12 | V | ||||
| High-level input voltage, VIH | D input | 0.7 VCC | V | ||||
| Low-level input voltage, VIL | D input | 0.3 VCC | V | ||||
| Differential input voltage, VID | –6 | 6 | V | ||||
| Input voltage to Rs, VI(Rs) | 0 | VCC | V | ||||
| Input voltage at Rs for standby, VI(Rs) | 0.75 VCC | VCC | V | ||||
| Rs wave-shaping resistance | 0 | 100 | kΩ | ||||
| High-level output current, IOH | Driver | –50 | mA | ||||
| Receiver | –4 | ||||||
| Low-level output current, IOL | Driver | 50 | mA | ||||
| Receiver | 4 | ||||||
| Operating free-air temperature, TA | SN65HVD251 | –40 | 125 | °C | |||
| SN55HVD251 | –55 | 125 | |||||
| Junction temperature, TJ | 145 | °C | |||||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN55HVD251 | SN65HVD251 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRJ (SON) | D (SOIC) | P (PDIP) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 52 | 44.6 | 66.6 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 73 | 78.7 | 48.9 | °C/W |
6.5 Supply Current
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP(1) | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | Supply current | Standby | Rs at VCC, D at VCC | 275 | µA | |||
| Dominant | D at 0 V, 60-Ω load, Rs at 0 V | 65 | mA | |||||
| Recessive | D at VCC, no load, Rs at 0 V | 14 | ||||||
6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Driver
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP(1) | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
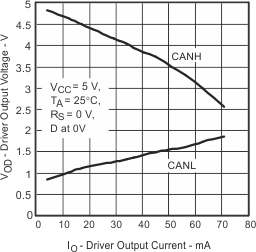
| VO(D) | Bus output voltage (Dominant) | CANH | Figure 10 and Figure 11 , D at 0 V Rs at 0 V, T ≥ –40°C |
2.75 | 3.5 | 4.5 | V | |
| CANL | 0.5 | 2 | ||||||
| VO(R) | Bus output voltage (Recessive) | CANH | Figure 10 and Figure 11 , D at 0.7 VCC, Rs at 0 V |
2 | 2.5 | 3 | ||
| CANL | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | |||||
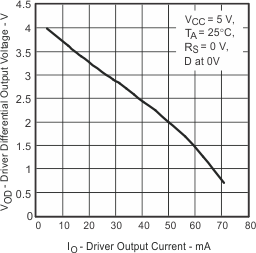
| VOD(D) | Differential output voltage (Dominant) | Figure 10 , D at 0 V, Rs at 0 V | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | V | ||
| Figure 12 , D at 0 V, Rs at 0 V, RNODE = 330 Ω | 1.2 | 2 | 3.1 | V | ||||
| Figure 12 , D at 0 V, Rs at 0 V, RNODE = 165 Ω, VCC ≥ 4.75 V | 1.2 | 2 | 3.1 | V | ||||
| VOD(R) | Differential output voltage (Recessive) | Figure 10 and Figure 11 , D at 0.7 VCC | –120 | 12 | mV | |||
| D at 0.7 VCC, no load, T ≤ 85°C | –0.5 | 0.05 | V | |||||
| VOC(pp) | Peak-to-peak common-mode output voltage | Figure 18, Rs at 0 V | 600 | mV | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current, D Input | D at 0.7 VCC | –40 | 0 | µA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current, D Input | D at 0.3 VCC | –60 | 0 | µA | |||
| IOS(SS) | Short-circuit steady-state output current | Figure 20, VCANH at –7 V, CANL Open | –200 | mA | ||||
| Figure 20, VCANH at 12 V, CANL Open | 2.5 | |||||||
| Figure 20, VCANL at -7 V, CANH Open | –2 | |||||||
| Figure 20, VCANL at 12 V, CANH Open | 200 | |||||||
| CO | Output capacitance | See receiver input capacitance | ||||||
| IOZ | High-impedance output current | See receiver input current | ||||||
| IIRs(s) | Rs input current for standby | Rs at 0.75 VCC | –10 | µA | ||||
| IIRs(f) | Rs input current for full speed operation | Rs at 0 V | –550 | 0 | µA | |||
6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Receiver
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIT+ | Positive-going input threshold voltage | Rs at 0 V, (See Table 1) | 750 | 900 | mV | ||||
| VIT- | Negative-going input threshold voltage | 500 | 650 | ||||||
| Vhys | Hysteresis voltage (VIT+ - VIT-) | 100 | |||||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | Figure 15, IO = –4 mA | 0.8 VCC | V | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | Figure 15, IO = 4 mA | 0.2 VCC | V | |||||
| II | Bus input current | CANH or CANL at 12 V | Other bus pin at 0 V, Rs at 0 V, D at 0.7 VCC | 600 | µA | ||||
| CANH or CANL at 12 V, VCC at 0 V | 715 | ||||||||
| CANH or CANL at -7 V | –460 | ||||||||
| CANH or CANL at -7 V, VCC at 0 V | –340 | ||||||||
| CI | Input capacitance, (CANH or CANL) | Pin-to-ground, VI = 0.4 sin (4E6πt) + 0.5 V, D at 0.7 VCC | 20 | pF | |||||
| CID | Differential input capacitance | Pin-to-pin, VI = 0.4 sin (4E6πt) + 0.5 V, D at 0.7 VCC | 10 | pF | |||||
| RID | Differential input resistance | D at 0.7 VCC, Rs at 0 V | 40 | 100 | kΩ | ||||
| RIN | Input resistance, (CANH or CANL) | D at 0.7 VCC, Rs at 0 V | 20 | 50 | kΩ | ||||
| Receiver noise rejection | See Figure 22 | ||||||||
6.8 VREF-Pin Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VO | Reference output voltage | –5 µA < IO < 5 µA | 0.45 VCC | 0.55 VCC | V | |
| –50 µA < IO < 50 µA | 0.4 VCC | 0.6 VCC | ||||
6.9 Power Dissipation Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Device power dissipation | VCC = 5 V, Tj = 27°C, RL = 60 Ω, RS at 0 V, Input to D a 500-kHz 50% duty cycle square wave |
97.7 | mW | |||
| VCC = 5.5 V, Tj = 130°C, RL = 60 Ω, RS at 0 V, Input to D a 500-kHz 50% duty cycle square wave |
142 | mW | |||||
| TSD | Thermal shutdown junction temperature | 165 | °C | ||||
6.10 Switching Characteristics: Driver
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tpLH | Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output | Figure 13, Rs at 0 V | 40 | 70 | ||
| Figure 13, Rs with 10 kΩ to ground | 90 | 125 | ||||
| Figure 13, Rs with 100 kΩ to ground | 500 | 800 | ||||
| tpHL | Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output | Figure 13, Rs at 0 V | 85 | 125 | ||
| Figure 13, Rs with 10 kΩ to ground | 200 | 260 | ||||
| Figure 13, Rs with 100 kΩ to ground | 1150 | 1450 | ||||
| tsk(p) | Pulse skew (|tpHL - tpLH|) | Figure 13, Rs at 0 V | 45 | 85 | ||
| Figure 13, Rs with 10 kΩ to ground | 110 | 180 | ns | |||
| Figure 13, Rs with 100 kΩ to ground | 650 | 900 | ||||
| tr | Differential output signal rise time | Figure 13, Rs at 0 V | 35 | 80 | 100 | |
| tf | Differential output signal fall time | 35 | 80 | 100 | ||
| tr | Differential output signal rise time | Figure 13, Rs with 10 kΩ to ground | 100 | 150 | 250 | |
| tf | Differential output signal fall time | 100 | 150 | 250 | ||
| tr | Differential output signal rise time | Figure 13, Rs with 100 kΩ to ground | 600 | 950 | 1550 | |
| tf | Differential output signal fall time | 600 | 950 | 1550 | ||
| ten | Enable time from standby to dominant | Figure 17 | 0.5 | µs | ||
6.11 Switching Characteristics: Device
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
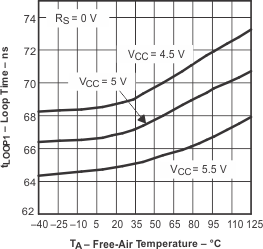
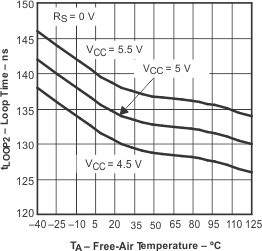
| tloop1 | Total loop delay, driver input to receiver output, recessive to dominant | Figure 19, Rs at 0 V | 60 | 100 | ns | |
| Figure 19, Rs with 10 kΩ to ground | 100 | 150 | ||||
| Figure 19, Rs with 100 kΩ to ground | 440 | 800 | ||||
| tloop2 | Total loop delay, driver input to receiver output, dominant to recessive | Figure 19, Rs at 0 V | 115 | 150 | ns | |
| Figure 19, Rs with 10 kΩ to ground | 235 | 290 | ||||
| Figure 19, Rs with 100 kΩ to ground | 1070 | 1450 | ||||
| tloop2 | Total loop delay, driver input to receiver output, dominant to recessive | Figure 19, Rs at 0 V, VCC from 4.5 V to 5.1 V | 105 | 145 | ns | |
6.12 Switching Characteristics: Receiver
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tpLH | Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output | Figure 15 | 35 | 50 | ||
| tpHL | Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output | 35 | 50 | |||
| tsk(p) | Pulse skew (|tpHL - tpLH|) | 20 | ns | |||
| tr | Output signal rise time | 2 | 4 | |||
| tf | Output signal fall time | 2 | 4 | |||
| tp(sb) | Propagation delay time in standby | Figure 21, Rs at VCC | 500 | |||
6.13 Dissipation Ratings
| PACKAGE | CIRCUIT BOARD MODEL | TA = 25°C POWER RATING |
DERATING FACTOR (1) ABOVE TA = 25°C | TA = 85°C POWER RATING | TA = 125°C POWER RATING |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOIC (D) | Low-K(2) | 576 mW | 4.8 mW/°C | 288 mW | 96 mW |
| High-K(3) | 924 mW | 7.7 mW/°C | 462 mW | 154 mW | |
| PDIP (P) | Low-K(2) | 888 mW | 7.4 mW/°C | 444 mW | 148 mW |
| High-K(3) | 1212 mW | 10.1 mW/°C | 606 mW | 202 mW | |
| WSON (DRJ) | Low-K(2) | 403 mW | 4.03 mW/°C | 262 mW | 100 mW |
| High-K (no Vias)(3) |
1081 mW | 10.8 mW/°C | 703 mW | 270 mW | |
| High-K (with Vias) |
2793 mW | 27.9 mW/°C | 1815 mW | 698 mW |
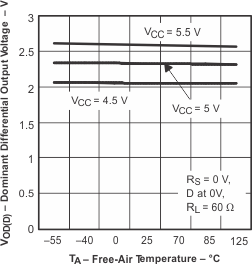
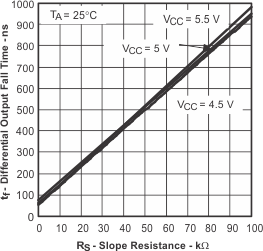
6.14 Typical Characteristics
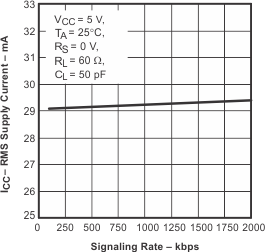 Figure 3. Supply Current (RMS) vs Signaling Rate
Figure 3. Supply Current (RMS) vs Signaling Rate
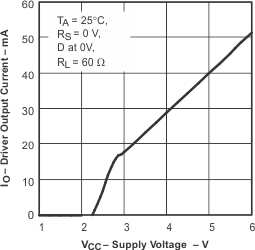 Figure 7. Driver Output Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 7. Driver Output Current vs Supply Voltage
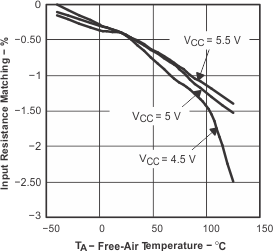 Figure 9. Input Resistance Matching vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 9. Input Resistance Matching vs Free-Air Temperature