JAJSPU8F june 2004 – february 2023 SN65HVD485E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: Driver
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Receiver
- 7.7 Power Dissipation Characteristics
- 7.8 Supply Current
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics: Driver
- 7.10 Switching Characteristics: Receiver
- 7.11 Dissipation Ratings
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
9.1 Application Information
The SN65HVD485E device is a half-duplex RS-485 transceiver commonly used for asynchronous data transmissions. The driver and receiver enable pins allow for configuration of different operating modes.
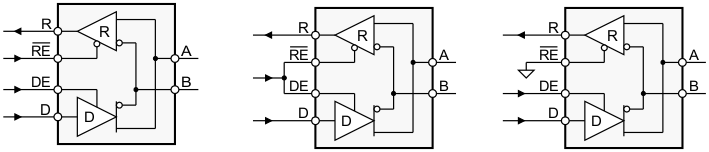 Figure 9-1 Half-Duplex Transceiver Configurations
Figure 9-1 Half-Duplex Transceiver ConfigurationsUsing independent enable lines provides the most flexible control as it allows for the driver and the receiver to be turned on and off individually. While this configuration requires two control lines, it allows for selective listening into the bus traffic whether the driver is transmitting data or not.
Combining the enable signals simplifies the interface to the controller by forming a single direction-control signal. In this configuration, the transceiver operates as a driver when the direction-control line is high and as a receiver when the direction-control line is low.
Additionally, only one line is required when connecting the receiver-enable input to ground and controlling only the driver-enable input. In this configuration, a node receives the data from the bus, receives the data it sends, and can verify that the correct data has been transmitted.