SCDS119C january 2003 – December 2015 SN74CB3T3306
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage(2) | –0.5 | 7 | V | |
| VIN | Control input voltage(2)(3) | –0.5 | 7 | V | |
| VI/O | Switch I/O voltage(2)(3)(4) | –0.5 | 7 | V | |
| IIK | Control input clamp current | VIN < 0 | –50 | mA | |
| II/OK | I/O port clamp current | VI/O < 0 | –50 | mA | |
| II/O | ON-state switch current(5) | ±128 | mA | ||
| Continuous current through VCC or GND | ±100 | mA | |||
| TJ | Junction temperature | 150 | °C | ||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are with respect to ground, unless otherwise specified.
(3) The input and output voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output clamp-current ratings are observed.
(4) VI and VO are used to denote specific conditions for VI/O.
(5) II and IO are used to denote specific conditions for II/O.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | +2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | +1000 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 2.3 | 3.6 | V | |
| VIH | High-level control input voltage | VCC = 2.3 V to 2.7 V | 1.7 | 5.5 | V |
| VCC = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 2 | 5.5 | |||
| VIL | Low-level control input voltage | VCC = 2.3 V to 2.7 V | 0 | 0.7 | V |
| VCC = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 0 | 0.8 | |||
| VI/O | Data input and output voltage | 0 | 5.5 | V | |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | |
(1) All unused control inputs of the device must be held at VCC or GND to ensure proper device operation. Refer to the TI application report, Implications of Slow or Floating CMOS Inputs, SCBA004.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN74CB3T3306 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCT (SSOP) | DCU (VSSOP) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 182.6 | 209.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 113.2 | 75.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 95.1 | 88.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 39.2 | 6.4 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 94.1 | 88.3 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP(2) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIK | VCC = 3 V, II = –18 mA (see Figure 9 and Figure 1) |
–1.2 | V | ||||
| VOH | |||||||
| IIN | Control inputs | VCC = 3.6 V, VIN = 3.6 V to 5.5 V or GND | ±10 | µA | |||
| II | VCC = 3.6 V, Switch ON, VIN = VCC or GND |
VI = VCC – 0.7 V to 5.5 V | ±20 | µA | |||
| VI = 0.7 V to VCC – 0.7 V | –40 | ||||||
| VI = 0 to 0.7 V | ±5 | ||||||
| IOZ(3) | VCC = 3.6 V, VO = 0 to 5.5 V, VI = 0, Switch OFF, VIN = VCC or GND | ±10 | µA | ||||
| Ioff | VCC = 0, VO = 0 to 5.5 V, VI = 0 | 10 | µA | ||||
| ICC | VCC = 3.6 V, II/O = 0, Switch ON or OFF, VIN = VCC or GND |
VI = VCC or GND | 20 | µA | |||
| VI = 5.5 V | 20 | ||||||
| ΔICC(4) | Control inputs | VCC = 3 V to 3.6 V, One input at VCC – 0.6 V, Other inputs at VCC or GND |
300 | µA | |||
| Cin | Control inputs | VCC = 3.3 V, VIN = VCC or GND | 3 | pF | |||
| Cio(OFF) | VCC = 3.3 V, VI/O = 5.5 V, 3.3 V, or GND, Switch OFF, VIN = VCC or GND |
4.5 | pF | ||||
| Cio(ON) | VCC = 3.3 V, Switch ON, VIN = VCC or GND |
VI/O = 5.5 V or 3.3 V | 4 | pF | |||
| VI/O = GND | 15 | ||||||
| ron(5) | VCC = 2.3 V, TYP at VCC = 2.5 V, VI = 0 |
IO = 24 mA | 5 | 8 | Ω | ||
| IO = 16 mA | 5 | 8 | |||||
| VCC = 3 V, VI = 0 | IO = 64 mA | 5 | 7 | ||||
| IO = 32 mA | 5 | 7 | |||||
(1) VIN and IIN refer to control inputs. VI, VO, II, and IO refer to data pins.
(2) All typical values are at VCC = 3.3 V (unless otherwise noted), TA = 25°C.
(3) For I/O ports, the parameter IOZ includes the input leakage current.
(4) This is the increase in supply current for each input that is at the specified TTL voltage level, rather than VCC or GND.
(5) Measured by the voltage drop between A and B terminals at the indicated current through the switch. ON-state resistance is determined by the lower of the voltages of the two (A or B) terminals.
6.6 Switching Characteristics
over recommended operating free-air temperature range unless otherwise noted (see Figure 4)| PARAMETER | FROM (INPUT) |
TO (OUTPUT) |
TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tpd(1) | A or B | B or A | VCC = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V | 0.15 | ns | ||
| VCC = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V |
0.25 | ns | |||||
| ten | OE | A or B | VCC = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V | 1 | 8.5 | ns | |
| VCC = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V |
1 | 6.5 | ns | ||||
| tdis | OE | A or B | VCC = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V | 1 | 9 | ns | |
| VCC = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V |
|||||||
(1) The propagation delay is the calculated RC time constant of the typical ON-state resistance of the switch and the specified load capacitance, when driven by an ideal voltage source (zero output impedance).
6.7 Typical Characteristics
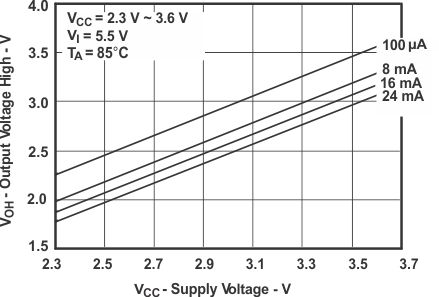 Figure 1. VOH vs Supply Voltage
Figure 1. VOH vs Supply Voltage
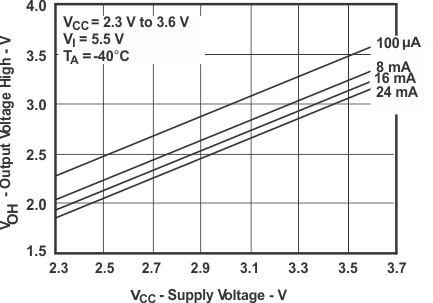 Figure 3. VOH vs Supply Voltage
Figure 3. VOH vs Supply Voltage
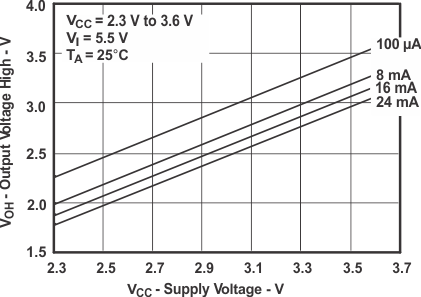 Figure 2. VOH vs Supply Voltage
Figure 2. VOH vs Supply Voltage