JAJSP54D February 2011 – September 2022 SN74GTL2003
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RKS|20
発注情報
9.2.1 Bidirectional Translation
For the bidirectional clamping configuration (higher voltage to lower voltage or lower voltage to higher voltage), the GREF input must be connected to DREF and both pins pulled to HIGH-side VCC through a pullup resistor (typically 200 kΩ). TI recommends a filter capacitor on DREF. The processor output can be totem pole or open drain (pullup resistors) and the chipset output can be totem pole or open drain (pullup resistors are required to pull the Dn outputs to VCC). However, if either output is totem pole, data must be unidirectional or the outputs must be 3-statable, and the outputs must be controlled by some direction-control mechanism to prevent HIGH-to-LOW contentions in either direction. If both outputs are open drain, no direction control is needed. The opposite side of the reference transistor (SREF) is connected to the processor core power-supply voltage. When DREF is connected through a 200-kΩ resistor to a 3.3-V to 5.5-V VCC supply and SREF is set from 1 V to VCC 1.5 V, the output of each Sn has a maximum output voltage equal to SREF, and the output of each Dn has a maximum output voltage equal to VCC.
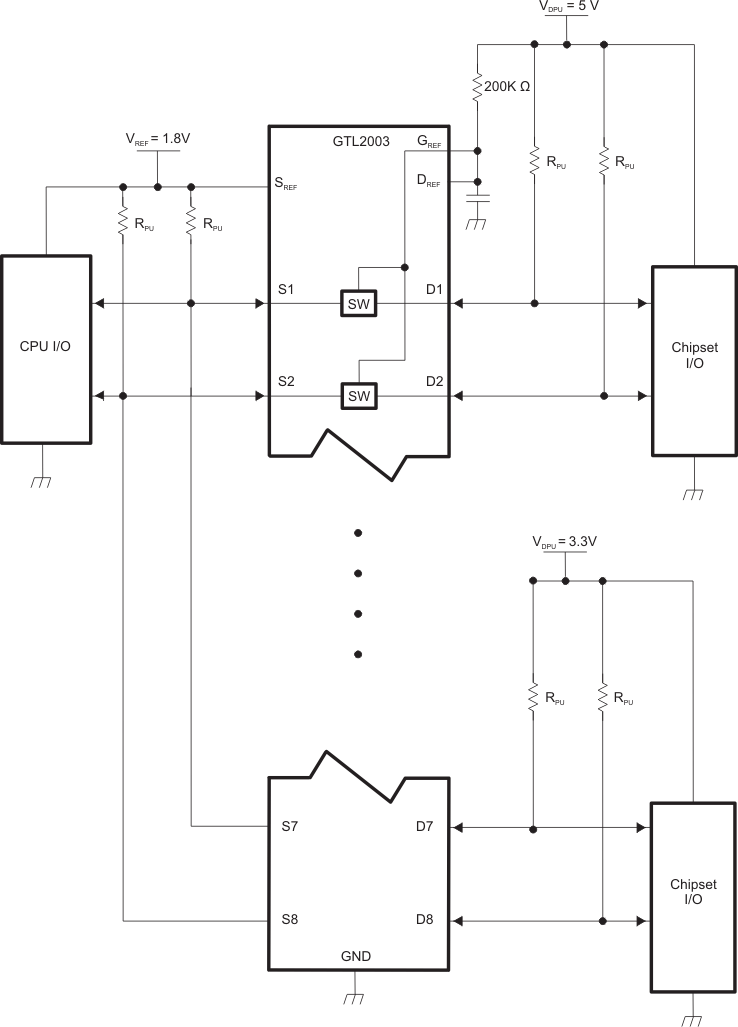 Figure 9-1 Bidirectional Translation to Multiple Higher Voltage Levels
Figure 9-1 Bidirectional Translation to Multiple Higher Voltage Levels (Such as an I2C or SMBus Applications)