SLASF36A January 2024 – December 2024 TAC5311-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Timing Requirements: I2C Interface
- 5.7 Switching Characteristics: I2C Interface
- 5.8 Timing Requirements: SPI Interface
- 5.9 Switching Characteristics: SPI Interface
- 5.10 Timing Requirements: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 5.11 Switching Characteristics: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 5.12 Timing Requirements: PDM Digital Microphone Interface
- 5.13 Switching Characteristics: PDM Digial Microphone Interface
- 5.14 Timing Diagrams
- 5.15 Typical Charactaristics
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Serial Interfaces
- 6.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 6.3.3 Input Channel Configuration
- 6.3.4 Reference Voltage
- 6.3.5 Microphone Bias
- 6.3.6 Digital PDM Microphone Record Channel
- 6.3.7
Signal-Chain Processing
- 6.3.7.1
ADC Signal-Chain
- 6.3.7.1.1 Programmable Channel Gain and Digital Volume Control
- 6.3.7.1.2 Programmable Channel Gain Calibration
- 6.3.7.1.3 Programmable Channel Phase Calibration
- 6.3.7.1.4 Programmable Digital High-Pass Filter
- 6.3.7.1.5 Programmable Digital Biquad Filters
- 6.3.7.1.6 Programmable Channel Summer and Digital Mixer
- 6.3.7.1.7
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 6.3.7.1.7.1
Linear-phase filters
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8kHz or 7.35kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16kHz or 14.7kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24kHz or 22.05kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32kHz or 29.4kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48kHz or 44.1kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96kHz or 88.2kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192kHz or 176.4kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.8 Sampling Rate: 384kHz or 352.8kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.1.9 Sampling Rate: 768kHz or 705.6kHz
- 6.3.7.1.7.2 Low-latency Filters
- 6.3.7.1.7.3 Ultra-Low-Latency Filters
- 6.3.7.1.7.1
Linear-phase filters
- 6.3.7.2
DAC Signal-Chain
- 6.3.7.2.1 Programmable Channel Gain and Digital Volume Control
- 6.3.7.2.2 Programmable Channel Gain Calibration
- 6.3.7.2.3 Programmable Digital High-Pass Filter
- 6.3.7.2.4 Programmable Digital Biquad Filters
- 6.3.7.2.5 Programmable Digital Mixer
- 6.3.7.2.6
Configurable Digital Interpolation Filters
- 6.3.7.2.6.1
Linear-phase filters
- 6.3.7.2.6.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8kHz or 7.35kHz
- 6.3.7.2.6.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16kHz or 14.7kHz
- 6.3.7.2.6.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24kHz or 22.05kHz
- 6.3.7.2.6.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32kHz or 29.4kHz
- 6.3.7.2.6.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48kHz or 44.1kHz
- 6.3.7.2.6.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96kHz or 88.2kHz
- 6.3.7.2.6.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192kHz or 176.4kHz
- 6.3.7.2.6.2 Low-latency Filters
- 6.3.7.2.6.1
Linear-phase filters
- 6.3.7.1
ADC Signal-Chain
- 6.3.8 Interrupts, Status, and Digital I/O Pin Multiplexing
- 6.3.9 Input DC Fault Diagnostics
- 6.3.10 Power Tune Mode
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
-
7 Register Maps
- 7.1 Device Configuration Registers
- 7.2
Programmable Coefficienct Registers
- 7.2.1 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 8
- 7.2.2 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 9
- 7.2.3 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 10
- 7.2.4 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 11
- 7.2.5 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 15
- 7.2.6 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 16
- 7.2.7 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 17
- 7.2.8 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 18
- 7.2.9 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 19
- 7.2.10 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 25
- 7.2.11 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 26
- 7.2.12 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 27
- 7.2.13 Programmable Coefficient Registers: Page 28
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTV|32
発注情報
6.3.6 Digital PDM Microphone Record Channel
In addition to supporting analog microphones, the TAC5311-Q1 also interfaces to digital pulse-density-modulation (PDM) microphones and uses high-order and high-performance decimation filters to generate pulse code modulation (PCM) output data that can be transmitted on the audio serial interface to the host. The device supports up to four digital microphone recording channels (when the analog channels are not used). The device can also support simultaneous recording on one analog and three digital microphone channels.
The GPIO1, GPIxA and GPO1A pins can be configured for the PDM data lines (PDMDINx) and PDM Clock (PDMCLK) functions as per the Table 6-57 for the digital PDM microphone recording.
The device internally generates PDMCLK with a programmable frequency of either 6.144MHz, 3.072MHz, 1.536MHz, or 768kHz (for output data sample rates in multiples or submultiples of 48kHz) or 5.6448MHz, 2.8224MHz, 1.4112MHz, or 705.6kHz (for output data sample rates in multiples or submultiples of 44.1kHz) using the PDM_CLK_CFG[1:0] (P0_R53_D[7:6]) register bits. PDMCLK can be routed on the GPIO1 and GPO1A pins using the respective configuration registers: GPIO1_CFG (P0_R10[7:4]) and GPO1A_CFG (P0_R12[7:4]). This clock can be connected to the external digital microphone device. Figure 6-19 shows a connection diagram of the digital PDM microphones.
 Figure 6-19 Digital
PDM Microphones Connection Diagram for the TAC5311-Q1
Figure 6-19 Digital
PDM Microphones Connection Diagram for the TAC5311-Q1The single-bit output of the external digital microphone device can be connected to the GPIxA or GPIO1 pin. The device supports two PDM data lines: PDMDIN1 and PDMDIN2 set through the registers PDM_DIN1_SEL (P0_R19_D[3:2]) and PDM_DIN2_SEL (P0_R19_D[1:0]). When using GPIxA, make sure that the GPI function is enabled using the GPI_CFG (P0_R13[1]). This single data line can be shared by two digital microphones to place their data on the opposite edge of PDMCLK. Internally, the device latches the steady value of the data on either the rising or falling edge of PDMCLK based on the configuration register bits set in PDMDIN1_EDGE (P0_R19_D[4]) and PDMDIN2_EDGE (P0_R19_D[5]). Figure 6-20shows the digital PDM microphone interface timing diagram.
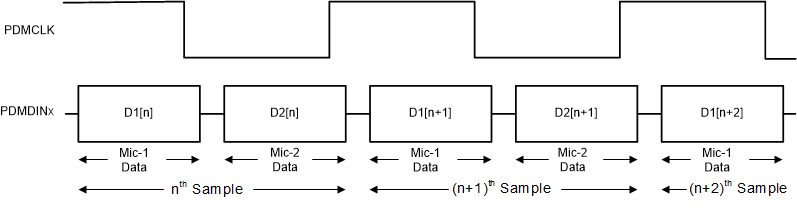 Figure 6-20 Digital
PDM Microphone Protocol Timing Diagram
Figure 6-20 Digital
PDM Microphone Protocol Timing DiagramWhen the digital microphone is used for recording, the analog blocks of the respective ADC channel are powered down and bypassed for power efficiency. Channel 3 and channel 4 support only the digital microphone interface. Use the PDM_CH1_SEL[1:0] (P0_R19_D[7]) and PDM_CH2_SEL[1:0] (P0_R19_D[6]) register bits to select the analog microphone or digital microphone for channel 1 to channel 2 respectively.