JAJSGP1 December 2018 TLV1805
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要 (続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.2 Typical Applications
Comparators are used to differentiate between two different signal levels. For example, a comparator differentiates between an over-temperature and normal-temperature condition. However, noise or signal variation at the comparison threshold causes multiple transitions. This application example sets upper and lower hysteresis thresholds to eliminate the multiple transitions caused by noise.
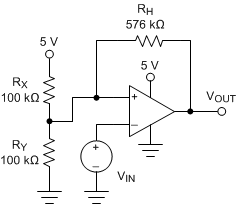 Figure 66. Comparator with Hysteresis
Figure 66. Comparator with Hysteresis