JAJS280O October 2003 – March 2019 TMS320F2801 , TMS320F28015 , TMS320F28016 , TMS320F2802 , TMS320F2806 , TMS320F2808 , TMS320F2809
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 5.3 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5
Power Consumption Summary
- Table 5-1 TMS320F2809, TMS320F2808 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- Table 5-2 TMS320F2806 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- Table 5-3 TMS320F2802, TMS320F2801 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- Table 5-4 TMS320C2802, TMS320C2801 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- 5.5.1 Reducing Current Consumption
- 5.5.2 Current Consumption Graphs
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F280x 100-Ball GGM Package
- 5.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F280x 100-Pin PZ Package
- 5.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for C280x 100-Ball GGM Package
- 5.10 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for C280x 100-Pin PZ Package
- 5.11 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F2809 100-Ball GGM Package
- 5.12 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F2809 100-Pin PZ Package
- 5.13 Thermal Design Considerations
- 5.14
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.14.1 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 5.14.2 Power Sequencing
- 5.14.3 Clock Requirements and Characteristics
- 5.14.4
Peripherals
- 5.14.4.1 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 5.14.4.2 Enhanced Control Peripherals
- 5.14.4.3 External Interrupt Timing
- 5.14.4.4 I2C Electrical Specification and Timing
- 5.14.4.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- 5.14.5 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the DSP
- 5.14.6 Flash Timing
- 5.15 On-Chip Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 5.16 Migrating From F280x Devices to C280x Devices
- 5.17 ROM Timing (C280x only)
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 6.1.1 C28x CPU
- 6.1.2 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 6.1.3 Peripheral Bus
- 6.1.4 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 6.1.5 Flash
- 6.1.6 ROM
- 6.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 6.1.8 L0, L1, H0 SARAMs
- 6.1.9 Boot ROM
- 6.1.10 Security
- 6.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 6.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1, XINT2, XNMI)
- 6.1.13 Oscillator and PLL
- 6.1.14 Watchdog
- 6.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 6.1.16 Low-Power Modes
- 6.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2 (PFn)
- 6.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 6.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 6.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 6.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 6.2
Peripherals
- 6.2.1 32-Bit CPU-Timers 0/1/2
- 6.2.2 Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM1/2/3/4/5/6)
- 6.2.3 Hi-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 6.2.4 Enhanced CAP Modules (eCAP1/2/3/4)
- 6.2.5 Enhanced QEP Modules (eQEP1/2)
- 6.2.6 Enhanced Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Module
- 6.2.7 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Modules (eCAN-A and eCAN-B)
- 6.2.8 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Modules (SCI-A, SCI-B)
- 6.2.9 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Modules (SPI-A, SPI-B, SPI-C, SPI-D)
- 6.2.10 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 6.2.11 GPIO MUX
- 6.3 Memory Maps
- 6.4 Register Map
- 6.5 Interrupts
- 6.6 System Control
- 6.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 9メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PZ|100
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PZ|100
発注情報
Table 5-14 General-Purpose Input Timing Requirements
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(SP) | Sampling period | QUALPRD = 0 | 1tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| QUALPRD ≠ 0 | 2tc(SCO) * QUALPRD | cycles | |||
| tw(IQSW) | Input qualifier sampling window | tw(SP) * (n(1) – 1) | cycles | ||
| tw(GPI)(2) | Pulse duration, GPIO low/high | Synchronous mode | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| With input qualifier | tw(IQSW) + tw(SP) + 1tc(SCO) | cycles | |||
(1) "n" represents the number of qualification samples as defined by GPxQSELn register.
(2) For tw(GPI), pulse width is measured from VIL to VIL for an active low signal and VIH to VIH for an active high signal.
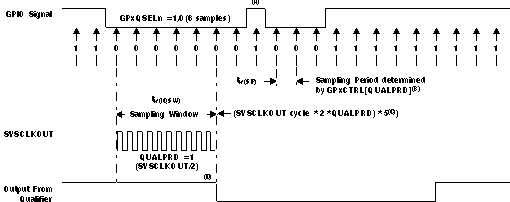
A. This glitch will be ignored by the input qualifier. The QUALPRD bit field specifies the qualification sampling period. It can vary from 00 to 0xFF. If QUALPRD = 00, then the sampling period is 1 SYSCLKOUT cycle. For any other value "n", the qualification sampling period in 2n SYSCLKOUT cycles (that is, at every 2n SYSCLKOUT cycles, the GPIO pin will be sampled).
B. The qualification period selected via the GPxCTRL register applies to groups of 8 GPIO pins.
C. The qualification block can take either three or six samples. The GPxQSELn Register selects which sample mode is used.
D. In the example shown, for the qualifier to detect the change, the input should be stable for 10 SYSCLKOUT cycles or greater. In other words, the inputs should be stable for (5 x QUALPRD x 2) SYSCLKOUT cycles. This would ensure 5 sampling periods for detection to occur. Since external signals are driven asynchronously, an 13-SYSCLKOUT-wide pulse ensures reliable recognition.
Figure 5-11 Sampling Mode