SLVSBH4F June 2012 – July 2016 TPS22966
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DPU|14
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DPU|14
発注情報
8 Detailed Description
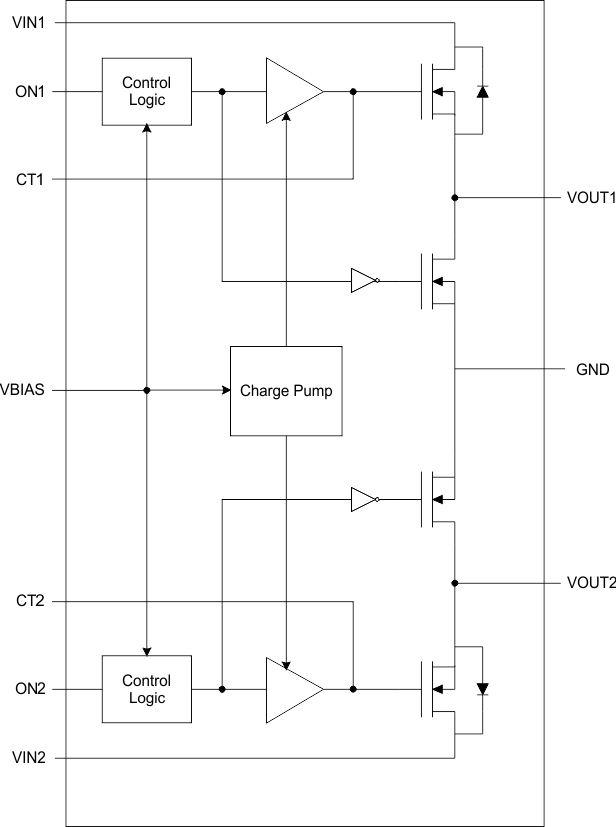
8.1 Overview
The TPS22966 device is a dual-channel, 6-A load switch in a 14-terminal SON package. To reduce the voltage drop in high current rails, the device implements an low resistance N-channel MOSFET. The device has a programmable slew rate for applications that require specific rise-time.
The device has very low leakage current during off state. This prevents downstream circuits from pulling high standby current from the supply. Integrated control logic, driver, power supply, and output discharge FET eliminates the need for any external components, which reduces solution size and bill of materials (BOM) count.
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 ON and OFF Control
The ON pins control the state of the switch. Asserting ON high enables the switch. ON is active high and has a low threshold, making it capable of interfacing with low-voltage signals. The ON pin is compatible with standard GPIO logic threshold. It can be used with any microcontroller with 1.2-V or higher GPIO voltage. This pin cannot be left floating and must be tied either high or low for proper functionality.
8.3.2 Input Capacitor (Optional)
To limit the voltage drop on the input supply caused by transient inrush currents when the switch turns on into a discharged load capacitor, a capacitor needs to be placed between VIN and GND. A 1-µF ceramic capacitor, CIN, placed close to the pins, is usually sufficient. Higher values of CIN can be used to further reduce the voltage drop during high-current application. When switching heavy loads, it is recommended to have an input capacitor about 10 times higher than the output capacitor to avoid excessive voltage drop.
8.3.3 Output Capacitor (Optional)
Due to the integrated body diode in the NMOS switch, a CIN greater than CL is highly recommended. A CL greater than CIN can cause VOUT to exceed VIN when the system supply is removed. This could result in current flow through the body diode from VOUT to VIN. A CIN to CL ratio of 10 to 1 is recommended for minimizing VIN dip caused by inrush currents during startup, however a 10 to 1 ratio for capacitance is not required for proper functionality of the device. A ratio smaller than 10 to 1 (such as 1 to 1) could cause slightly more VIN dip upon turn-on due to inrush currents. This can be mitigated by increasing the capacitance on the CT pin for a longer rise time (see Figure 4).
8.3.4 VIN and VBIAS Voltage Range
For optimal RON performance, make sure VIN ≤ VBIAS. The device is still functional if VIN > VBIAS but it exhibits RON greater than what is listed in the Electrical Characteristics table. See Figure 32 for an example of a typical device. Notice the increasing RON as VIN exceeds VBIAS voltage. Make sure to never exceed the maximum voltage rating for VIN and VBIAS.
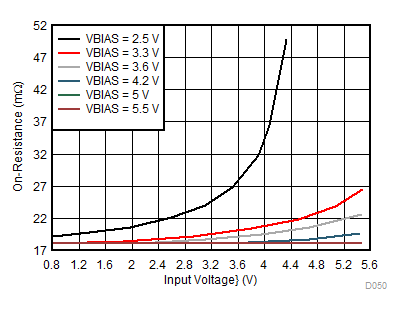
| VIN > VBIAS | IOUT= –200 mA | |
Single Channel
8.4 Device Functional Modes
Table 1 lists the TPS22966 functions.
Table 1. Functions Table
| ONx | VINx to VOUTx | VOUTx to GND |
|---|---|---|
| L | Off | On |
| H | On | Off |