SLVSCG3F January 2014 – July 2017 TPS22968
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DPU|14
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DPU|14
発注情報
10.2.2.2 Inrush Current
To determine how much inrush current is caused by the CL capacitor, use Equation 3.
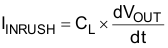
where
- IINRUSH is the amount of inrush caused by CL
- CL is the capacitance on VOUT
- dt is the time it takes for change in VOUT during the ramp up of VOUT when the device is enabled
- dVOUT is the change in VOUT during the ramp up of VOUT when the device is enabled
The device offers adjustable rise time for VOUT. This feature allows the user to control the inrush current during turnon through the CTx pins. The appropriate rise time can be calculated using the design requirements and the inrush current equation ( Equation 3). See Equation 4 and Equation 5.
To ensure an inrush current of less than 330 mA, choose a CT based on Table 1 or Equation 1 value that yields a rise time of more than 220 µs. See the oscilloscope captures in the Application Curves for an example of how the CT capacitor can be used to reduce inrush current. See Table 1 for correlation between rise times and CT values.
An appropriate CL value must be placed on VOUT such that the IMAX and IPLS specifications of the device are not violated.