SLVSCJ7B March 2014 – July 2015 TPS22969
PRODUCTION DATA.
8 Applications and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
This section will highlight some of the design considerations when implementing this device in various applications. A PSPICE model for this device is also available in the product page of this device.
8.2 Typical Application
This application demonstrates how the TPS22969 can be used to power downstream modules with large capacitances. The example below is powering a 100-µF capacitive output load.
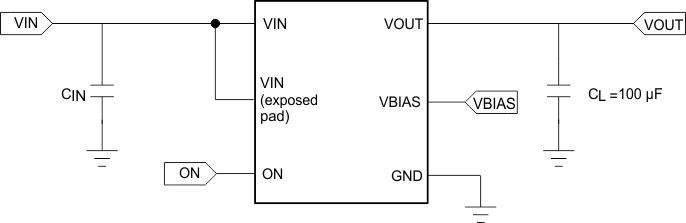 Figure 27. Typical Application Schematic for Powering a Downstream Module
Figure 27. Typical Application Schematic for Powering a Downstream Module
8.2.1 Design Requirements
For this design example, use Table 1 as the input parameters.
Table 1. Design Parameters
| DESIGN PARAMETER | EXAMPLE VALUE |
|---|---|
| VIN | 1.05 V |
| VBIAS | 5.0 V |
| Load current | 6 A |
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
To begin the design process, the designer needs to know the following:
- VIN voltage
- VBIAS voltage
- Load current
8.2.2.1 VIN to VOUT Voltage Drop
The VIN to VOUT voltage drop in the device is determined by the RON of the device and the load current. The RON of the device depends upon the VIN and VBIAS conditions of the device. Refer to the RON specification of the device in the Electrical Characteristics, VBIAS = 5.0 V tables of this datasheet. Once the RON of the device is determined based upon the VIN and VBIAS conditions, use Equation 1 to calculate the VIN to VOUT voltage drop:

where
- ΔV = voltage drop from VIN to VOUT
- ILOAD = load current
- RON = on-resistance of the device for a specific VIN and VBIAS combination
An appropriate ILOAD must be chosen such that the IMAX specification of the device is not violated.
8.2.2.2 Inrush Current
To determine how much inrush current will be caused by the CL capacitor, use Equation 2:
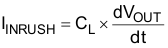
where
- IINRUSH = amount of inrush caused by CL
- CL = capacitance on VOUT
- dt = time it takes for change in VOUT during the ramp up of VOUT when the device is enabled
- dVOUT = change in VOUT during the ramp up of VOUT when the device is enabled
An appropriate CL value should be placed on VOUT such that the IMAX and IPLS specifications of the device are not violated.
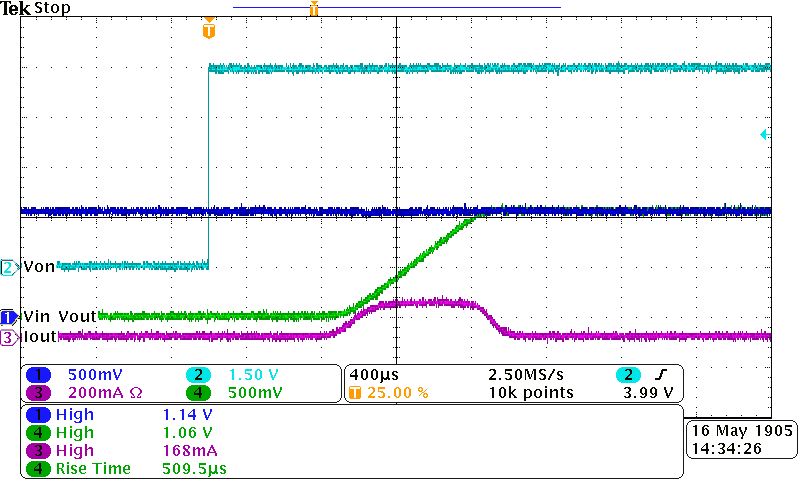 Figure 28. Inrush current (VBIAS = 5 V, VIN = 1.05 V, CL = 100 µF)
Figure 28. Inrush current (VBIAS = 5 V, VIN = 1.05 V, CL = 100 µF)
Thermal Considerations
The maximum IC junction temperature should be restricted to 125°C under normal operating conditions. To calculate the maximum allowable dissipation, PD(max) for a given output current and ambient temperature, use Equation 3.
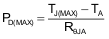
where
- PD(max) = maximum allowable power dissipation
- TJ(max) = maximum allowable junction temperature (125°C for the TPS22969)
- TA = ambient temperature of the device
- ΘJA = junction to air thermal impedance. See Thermal Information section. This parameter is highly dependent upon board layout.
8.2.3 Application Curves
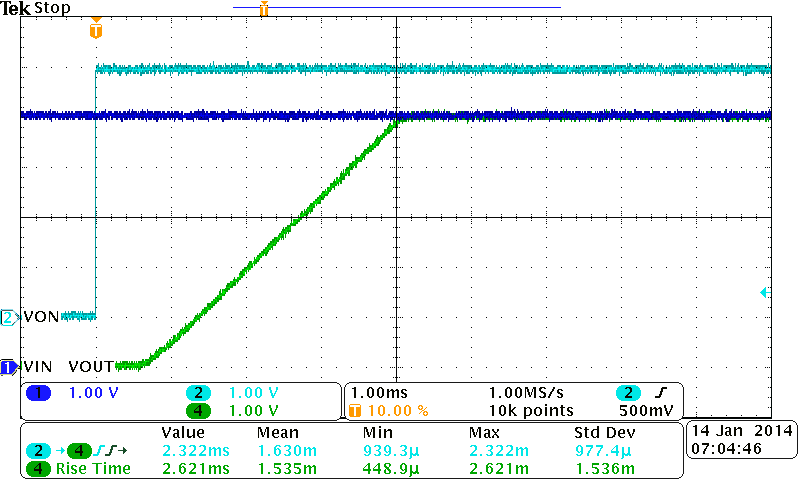
| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 5 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |
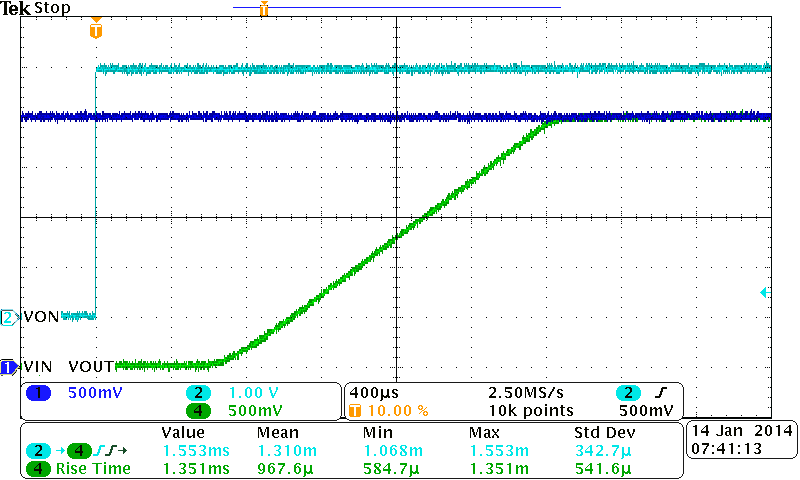
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 2.5 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |
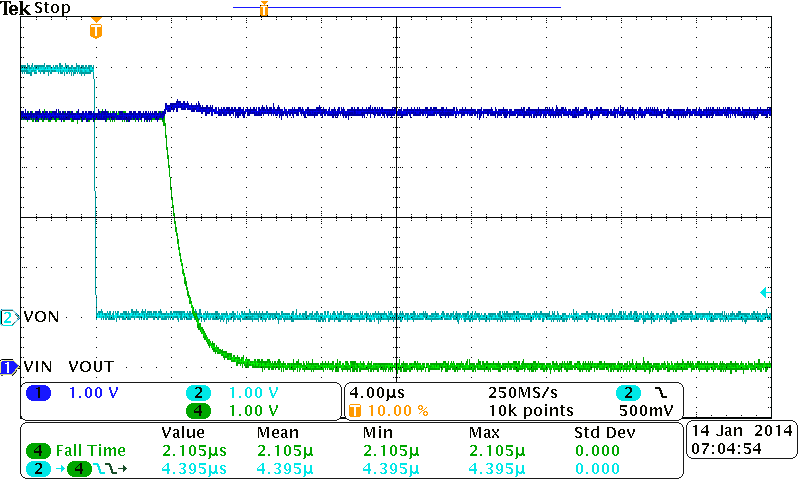
| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 5 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |
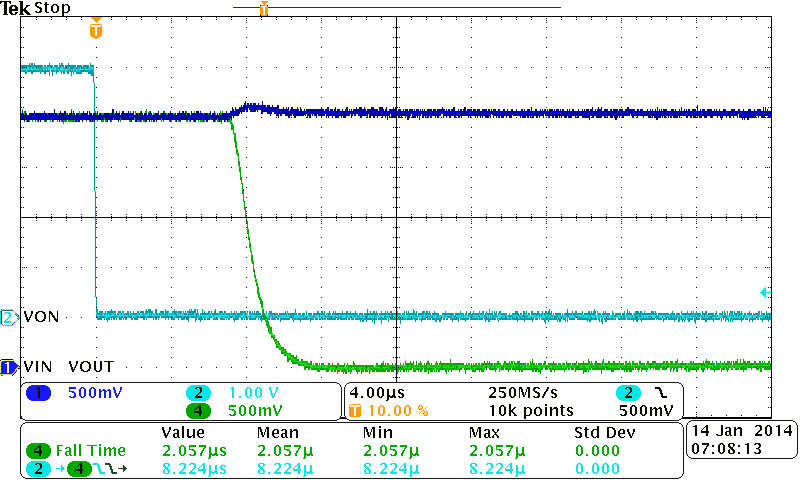
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 2.5 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |
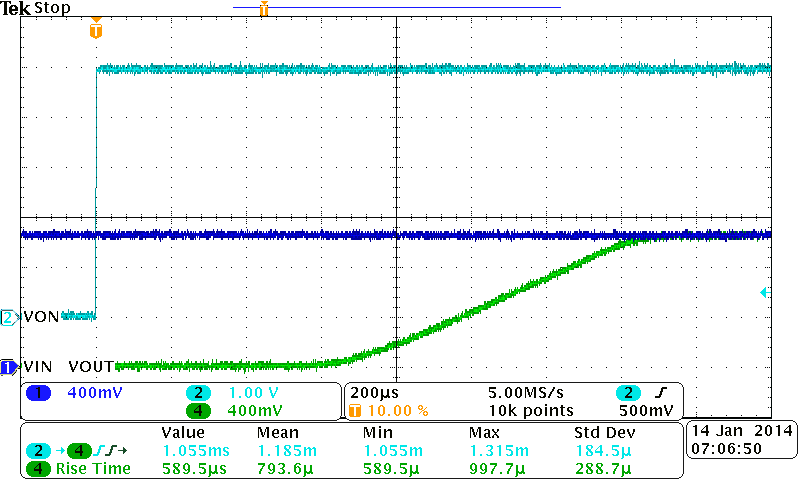
| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 1.05 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |
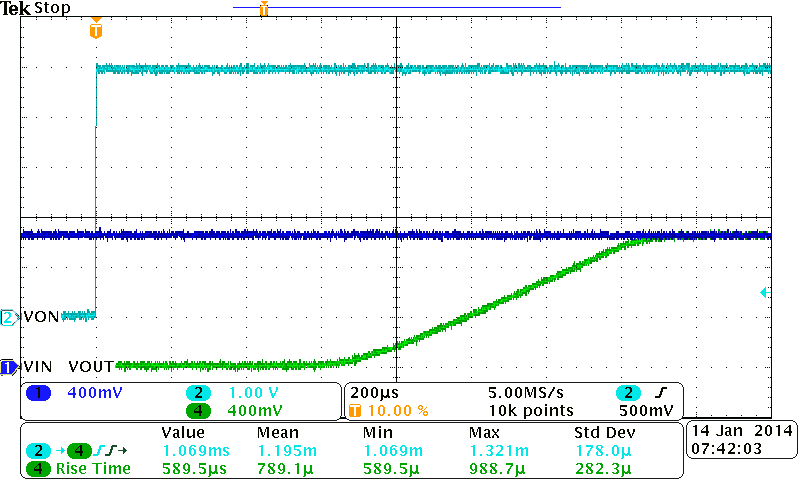
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 1.05 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |

| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 2.5 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |
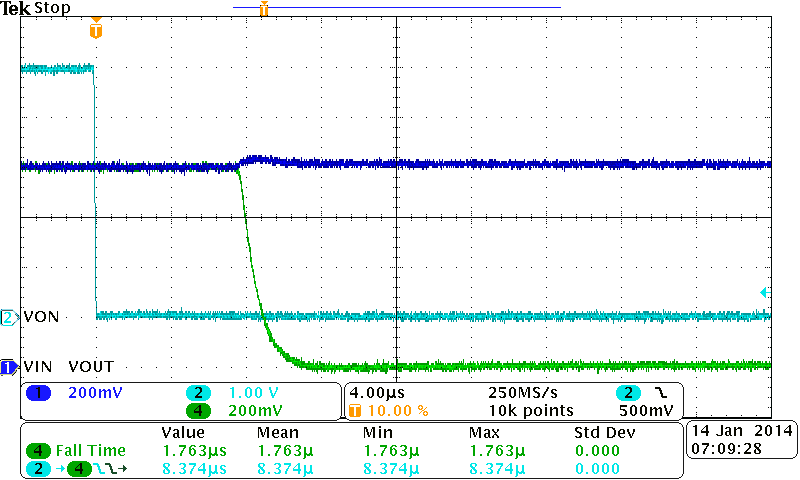
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 0.8 V | CIN = 1 µF |
| CL = 0.1 µF |