JAJSK02 October 2020 TPS23731
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 CLS Classification
- 8.3.2 DEN Detection and Enable
- 8.3.3 APD Auxiliary Power Detect
- 8.3.4 Internal Pass MOSFET
- 8.3.5 T2P and APDO Indicators
- 8.3.6
DC-DC Controller Features
- 8.3.6.1 VCC, VB, VBG and Advanced PWM Startup
- 27
- 8.3.6.2 CS, Current Slope Compensation and blanking
- 8.3.6.3 COMP, FB, EA_DIS, CP, PSRS and Opto-less Feedback
- 8.3.6.4 FRS Frequency Setting and Synchronization
- 8.3.6.5 DTHR and Frequency Dithering for Spread Spectrum Applications
- 8.3.6.6 SST and Soft-Start of the Switcher
- 8.3.6.7 SST, I_STP, LINEUV and Soft-Stop of the Switcher
- 8.3.7 Switching FET Driver - GATE
- 8.3.8 EMPS and Automatic MPS
- 8.3.9 VDD Supply Voltage
- 8.3.10 RTN, AGND, GND
- 8.3.11 VSS
- 8.3.12 Exposed Thermal pads - PAD_G and PAD_S
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 PoE Overview
- 8.4.2 Threshold Voltages
- 8.4.3 PoE Start-Up Sequence
- 8.4.4 Detection
- 8.4.5 Hardware Classification
- 8.4.6 Maintain Power Signature (MPS)
- 8.4.7 Advanced Start-Up and Converter Operation
- 8.4.8 Line Undervoltage Protection and Converter Operation
- 8.4.9 PD Self-Protection
- 8.4.10 Thermal Shutdown - DC-DC Controller
- 8.4.11 Adapter ORing
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1
Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.1.1 Input Bridges and Schottky Diodes
- 9.2.1.1.2 Input TVS Protection
- 9.2.1.1.3 Input Bypass Capacitor
- 9.2.1.1.4 Detection Resistor, RDEN
- 9.2.1.1.5 Classification Resistor, RCLS.
- 9.2.1.1.6 APD Pin Divider Network, RAPD1, RAPD2
- 9.2.1.1.7 Setting Frequency (RFRS) and Synchronization
- 9.2.1.1.8 Bias Supply Requirements and CVCC
- 9.2.1.1.9 APDO, T2P Interface
- 9.2.1.1.10 Output Voltage Feedback Divider, RAUX, R1,R2
- 9.2.1.1.11 Frequency Dithering for Conducted Emissions Control
- 9.2.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1
Design Requirements
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
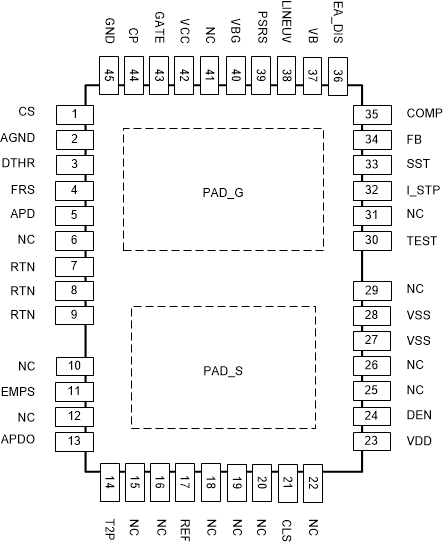 Figure 6-1 Package Pinout
Figure 6-1 Package PinoutTable 6-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | CS | I/O | DC-DC controller current sense input. Connect directly to the external power current sense resistor. |
| 2 | AGND | - | AGND is the DC-DC converter analog return. Tie to RTN and GND on the circuit board. |
| 3 | DTHR | O | Used for spread spectrum frequency dithering. Connect a capacitor (determines the modulating frequency) from DTHR to RTN and a resistor (determines the amount of dithering) from DTHR to FRS. If dithering is not used, short DTHR to VB pin. |
| 4 | FRS | I | This pin controls the switching frequency of the DC-DC converter. Tie a resistor from this pin to RTN to set the frequency. |
| 5 | APD | I | Primary auxiliary power detect input. Raise 1.5 V above RTN to disable pass MOSFET, also turning class off. If not used, connect APD to RTN. |
| 7, 8, 9 | RTN | - | RTN is the output of the PoE hotswap and the reference ground for the DC-DC controller. |
| 11 | EMPS | I | Automatic MPS enable input, referenced to RTN, internally pulled-up to 5-V internal rail. Tie to RTN to disable automatic MPS. |
| 13 | APDO | O | Active low output referenced to RTN, indicates that an auxiliary power adapter is detected via the APD input. |
| 14 | T2P | O | Active low output that indicates a PSE has performed the IEEE 802.3at Type 2 hardware classification, or APD is active. |
| 17 | REF | O | Internal 1.25-V voltage reference. Connect a 49.9-kΩ_1% resistor from REF to VSS. |
| 21 | CLS | O | Connect a resistor from CLS to VSS to program the classification current. |
| 23 | VDD | — | Positive input power rail for PoE interface circuit and source of DC-DC converter start-up current. Bypass with a 0.1 µF to VSS and protect with a TVS. |
| 24 | DEN | I/O | Connect a 25.5-kΩ resistor from DEN to VDD to provide the PoE detection signature. Pulling this pin to VSS during powered operation causes the internal hotswap MOSFET to turn off. |
| 27, 28 | VSS | - | Negative power rail derived from the PoE source. |
| 30 | TEST | O | Used internally for test purposes only. Leave open. |
| 32 | I_STP | I | This pin sets the SST discharge current during a soft-stop event independently from the setting used during a regular soft-start event. Connect a resistor from this pin to AGND to set the DC/DC soft-stop rate. |
| 33 | SST | I/O | A capacitor from SST to RTN pin sets the soft-start (ISSC charge current) and the hiccup timer (ISSD discharge current) for the DC-DC converter. Connect a capacitor from this pin to RTN to set the DC/DC startup rate. |
| 34 | FB | I | Converter error amplifier inverting (feedback) input. If flyback configuration with primary-side regulation, it is typically driven by a voltage divider and capacitor from the auxiliary winding, working with CP pin, FB also being connected to the COMP compensation network. If optocoupler feedback is enabled, tie FB to VB. |
| 35 | COMP | I/O | Compensation output of the DC-DC convertor error amplifier or control loop input to the PWM. If the internal error amplifier is used, connect the compensation networks from this pin to the FB pin to compensate the converter. If optocoupler feedback is enabled, the optocoupler and its network pulled up to VB directly drives the COMP pin. |
| 36 | EA_DIS | I | Error Amplifier disable input, referenced to AGND, internally pulled-up to 5V internal rail. Leave EA_DIS open to disable the Error amplifier, to enable optocoupler feedback for example. Connect to AGND otherwise. |
| 37 | VB | O | 5-V bias rail for DC/DC control circuits and the feedback optocoupler (when in use). Connect a 0.1-uF capacitor from this pin to AGND to provide bypassing. |
| 38 | LINEUV | I | LINEUV is used to monitor the bulk capacitor voltage to trigger a soft-stop event when an undervoltage condition is detected if APD is low. If not used, connect LINEUV to VB pin. |
| 39 | PSRS | I | PSR Sync enable input, referenced to AGND, internally pulled-up to 5V internal rail. PSRS works with CP pin to support flyback architecture using primary-side regulation. Leave PSRS open if the flyback output stage is configured with synchronous rectification and uses PSR. If diode rectification is used, or for applications not using PSR, connect PSRS to AGND. |
| 40 | VBG | O | 5-V bias rail for the switching FET gate driver circuit. For internal use only. Bypass with a 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor to GND pin. |
| 42 | VCC | I/O | DC/DC converter bias voltage. The internal startup current source and converter bias winding output power this pin. Connect a 1µF minimum ceramic capacitor to RTN. |
| 43 | GATE | O | Gate drive output for the main DC-DC converter switching MOSFET |
| 44 | CP | O | CP provides the clamp for the primary-side regulation loop. Connect this pin to the lower end of the bias winding of the flyback transformer. |
| 45 | GND | - | .Power ground used by the flyback power FET gate driver and CP. Connect to RTN. |
| 6, 10, 12, 15, 16, 18-20, 22, 25, 26, 29, 31, 41 | NC | - | No connect pin. Leave open. |
| 47 | PAD_S | - | The exposed thermal pad must be connected to VSS. A large fill area is required to assist in heat dissipation. |
| 46 | PAD_G | - | The exposed thermal pad must be connected to RTN. A large fill area is required to assist in heat dissipation. |