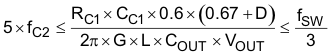JAJSH64B November 2012 – April 2019 TPS53819A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Enable and Soft-Start
- 7.3.2 Adaptive On-Time Control
- 7.3.3 Zero Crossing Detection
- 7.3.4 Output Discharge Control
- 7.3.5 Low-Side Driver
- 7.3.6 High-Side Driver
- 7.3.7 Power Good
- 7.3.8 Current Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.9 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.10 Out-of-Bound Protection
- 7.3.11 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 OPERATION [01h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.2 ON_OFF_CONFIG [02h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.3 WRITE_PROTECT [10h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.4 CLEAR_FAULTS [03h] (Send Byte)
- 7.6.5 STORE_DEFAULT_ALL [11h] (Send Byte)
- 7.6.6 RESTORE_DEFAULT_ALL [12h] (Send Byte)
- 7.6.7 STATUS_WORD [79h] (Read Word)
- 7.6.8 CUSTOM_REG (MFR_SPECIFIC_00) [D0h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.9 DELAY_CONTROL (MFR_SPECIFIC_01) [D1h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.10 MODE_SOFT_START_CONFIG (MFR_SPECIFIC_02) [D2h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.11 FREQUENCY_CONFIG (MFR_SPECIFIC_03) [D3h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.12 VOUT_ADJUSTMENT (MFR_SPECIFIC_04) [D4h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.13 Output Voltage Fine Adjustment Soft Slew Rate
- 7.6.14 VOUT_MARGIN (MFR_SPECIFIC_05) [D5h] (R/W Byte)
- 7.6.15 Output Voltage Margin Adjustment Soft-Slew Rate
- 7.6.16 UVLO_THRESHOLD (MFR_SPECIFIC_06) [D6h]
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Inductor (L1)
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitors (C10, C11, C12, C13, C14)
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitors (C1, C2, C3, C4, C5)
- 8.2.2.6 MOSFET (Q1, Q2)
- 8.2.2.7 VREG Bypass Capacitor (C18)
- 8.2.2.8 VDD Bypass Capacitor (C19)
- 8.2.2.9 VBST Capacitor (C7)
- 8.2.2.10 Snubber (C8 and R9)
- 8.2.2.11 Feedback Resistance, RFBH and RFBL (R17 and R18)
- 8.2.2.12 Overcurrent Limit (OCL) Setting Resistance (R10)
- 8.2.2.13 PMBus Device Address (R3 and R4)
- 8.2.2.14 PGOOD Pullup Resistor (R2)
- 8.2.2.15 SCL and SDA Pulldown Resistors (R14 and R15)
- 8.2.2.16 PMBus Pullup Resistors
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGT|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGT|16
発注情報
8.2.2.4 Output Capacitors (C10, C11, C12, C13, C14)
Determine the output capacitance to meet the load transient, ripple requirements, and to meet small-signal stability as shown in Equation 12.
Based on Equation 12, the value of COUT to ensure small signal stability can be calculated using Equation 13 and Equation 14. These equations assume MLCC are used and the ESR effects are negligible. If a high ESR output capacitor is used, the effects may reduce the minimum and maximum capacitance. In the design example using Table 1 for 425-kHz switching frequency, the time constant is 62 μs. The recommended minimum capacitance for a design with an 8-V minimum input voltage is 260 μF. The recommended maximum capacitance for design with a 14-V maximum input voltage is 4842 μF.
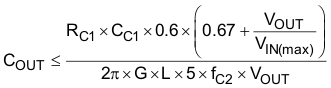
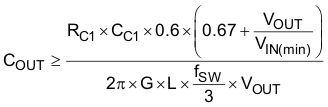
Select a larger output capacitance to decrease the output voltage change that occurs during a load transient and the output voltage ripple.
The minimum output capacitance to meet an output voltage ripple requirement can be calculated with Equation 15. In the example the minimum output capacitance for 12 mVPP ripple is 162 μF. If non ceramic capacitors are used Equation 16 calculates the maximum equivalent series resistance (ESR) of the output capacitor to meet the ripple requirement. Equation 17 calculates the required RMS current rating for the output capacitor. In this example with 12-V nominal input voltage it is 1.77 A. Finally the output capacitor must be rated for the output voltage.
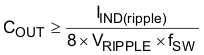
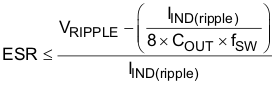
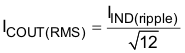
This example uses five 1210, 100-μF, 6.3-V, X5R ceramic capacitors with 2 mΩ of ESR. From the data sheet the estimated DC derating of 95% and AC derating of 70% for a total of 66.5% at room temperature. The total output capacitance is approximately 332.5 μF.