SLUSF22 November 2024 TPS54538
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode
- 6.3.2 Mode Selection
- 6.3.3 Voltage Reference
- 6.3.4 Output Voltage Setting
- 6.3.5 Switching Frequency Selection / Synchronization
- 6.3.6 Phase Shift
- 6.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 6.3.8 External Soft Start and Prebiased Soft Start
- 6.3.9 Power Good
- 6.3.10 Minimum On Time, Minimum Off Time, and Frequency Foldback
- 6.3.11 Frequency Spread Spectrum
- 6.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 6.3.13 Overcurrent and Undervoltage Protection
- 6.3.14 Thermal Shutdown
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Application
- 7.2.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 7.2.2.2 Output Voltage Resistors Selection
- 7.2.2.3 Choosing Switching Frequency
- 7.2.2.4 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.2.5 Output Inductor Selection
- 7.2.2.6 Output Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.2.8 Feedforward Capacitor CFF Selection
- 7.2.2.9 Maximum Ambient Temperature
- 7.2.3 Application Curves
- 7.3 Best Design Practices
- 7.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.5 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.4 Output Voltage Setting
A precision 0.6V reference voltage, VREF, is used to maintain a tightly regulated output voltage over the entire operating temperature range. The output voltage is set by a resistor divider from the output voltage to the FB pin. TI recommends using 1% tolerance resistors with a low temperature coefficient for the FB divider. Select the bottom-side resistor, RFBB, for the desired divider current and use Equation 1 to calculate the top-side resistor, RFBT. Lower RFBB increases the divider current and reduces efficiency at very light load. Larger RFBB makes the FB voltage more susceptible to noise, so larger RFBB values require a more carefully designed feedback path on the PCB. TI recommends setting RFBB = 10kΩ and RFBT in the range of 10kΩ to 300kΩ for most applications.
The tolerance and temperature variation of the resistor dividers affect the output voltage regulation.
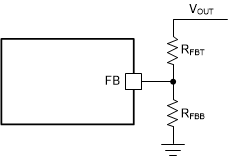 Figure 6-2 Output Voltage Setting
Figure 6-2 Output Voltage Settingwhere
- VREF is the 0.6V (the internal reference voltage).
- RFBB is 10kΩ (recommended).