JAJSGV6 January 2019 TPS54560B
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) pin)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current-Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLK pin
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Minimum Input Voltage, VIN
- 8.2.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.2.12 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.2.14 Safe Operating Area
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Other System Examples
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7.3.10 Accurate Current-Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
The TPS54560B implements peak-current-mode control in which the COMP pin voltage controls the peak current of the high-side MOSFET. A signal proportional to the high-side switch current and the COMP pin voltage are compared each cycle. When the peak switch current intersects the COMP control voltage, the high-side switch is turned off. During overcurrent conditions that pull the output voltage low, the error amplifier increases switch current by driving the COMP pin high. The error amplifier output is clamped internally at a level which sets the peak switch-current limit. The TPS54560B provides an accurate current limit threshold with a typical current limit delay of 60 ns. With smaller inductor values, the delay results in a higher peak inductor current. The relationship between the inductor value and the peak inductor current is shown in Figure 23.
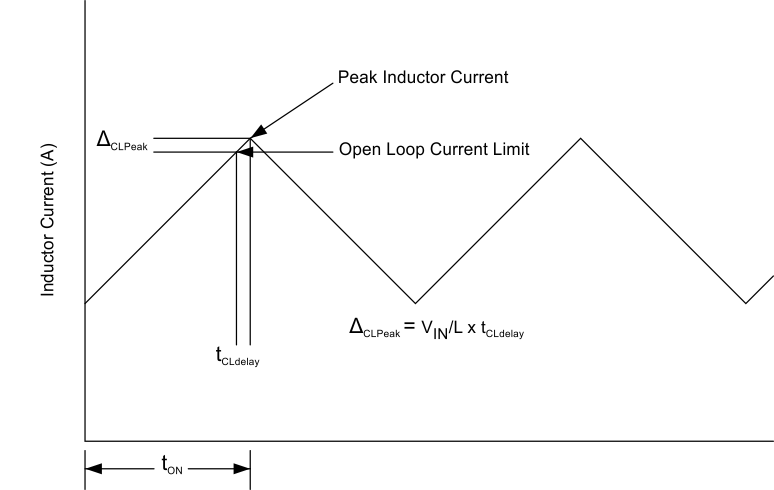 Figure 23. Current Limit Delay
Figure 23. Current Limit Delay To protect the converter in overload conditions at higher switching frequencies and input voltages, the TPS54560B implements a frequency foldback. The oscillator frequency is divided by 1, 2, 4, and 8 as the FB pin voltage falls from 0.8 V to 0 V. The TPS54560B uses a digital frequency foldback to enable synchronization to an external clock during normal start-up and fault conditions. During short-circuit events, the inductor current can exceed the peak current limit because of the high input voltage and the minimum controllable on-time. When the output voltage is forced low by the shorted load, the inductor current decreases slowly during the switch off-time. The frequency foldback effectively increases the off-time by increasing the period of the switching cycle providing more time for the inductor current to ramp down.
With a maximum frequency foldback ratio of 8, there is a maximum frequency at which the inductor current can be controlled by frequency foldback protection. Equation 10 calculates the maximum switching frequency at which the inductor current remains under control when VOUT is forced to VOUT(SC). The selected operating frequency must not exceed the calculated value.
Equation 9 calculates the maximum switching frequency limitation set by the minimum controllable on time and the input to output step down ratio. Setting the switching frequency above this value causes the regulator to skip switching pulses to achieve the low duty cycle required at maximum input voltage.
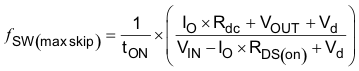
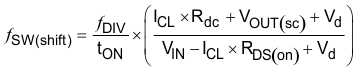
where
- IO — Output current
- ICL — Current limit
- Rdc — inductor resistance
- VIN — maximum input voltage
- VOUT — output voltage
- VOUTSC — output voltage during short
- Vd — diode voltage drop
- RDS(on) — switch on resistance
- tON — controllable on time
- ƒDIV — frequency divide equals (1, 2, 4, or 8)