JAJSGV6 January 2019 TPS54560B
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) pin)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current-Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLK pin
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Minimum Input Voltage, VIN
- 8.2.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.2.12 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.2.14 Safe Operating Area
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Other System Examples
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLK pin
The RT/CLK pin can receive a frequency synchronization signal from an external system clock. To implement this synchronization feature connect a square wave to the RT/CLK pin through either circuit network shown in Figure 24. The square wave applied to the RT/CLK pin must switch lower than 0.5 V and higher than 1.7 V and have a pulse width greater than 15 ns. The synchronization frequency range is 160 kHz to 2300 kHz. The rising edge of the SW is synchronized to the falling edge of RT/CLK pin signal. Design the external synchronization circuit so that the default frequency set resistor is connected from the RT/CLK pin to ground when the synchronization signal is off. When using a low impedance-signal source, the frequency set resistor is connected in parallel with an AC-coupling capacitor to a termination resistor (for example, 50 Ω) as shown in Figure 24. The two resistors in series provide the default frequency setting resistance when the signal source is turned off. The sum of the resistance must set the switching frequency close to the external CLK frequency. TI recommends accoupling the synchronization signal through a 10-pF ceramic capacitor to the RT/CLK pin.
The first time the RT/CLK is pulled above the PLL threshold the TPS54560B switches from the RT resistor free-running frequency mode to the PLL synchronized mode. The internal 0.5-V voltage source is removed, and the RT/CLK pin becomes high impedance as the PLL starts to lock onto the external signal. The switching frequency can be higher or lower than the frequency set with the RT/CLK resistor. The device transitions from the resistor mode to the PLL mode and locks onto the external clock frequency within 78 microseconds. During the transition from the PLL mode to the resistor programmed mode, the switching frequency falls to 150 kHz and then increases or decreases to the resistor-programmed frequency when the 0.5-V bias voltage is reapplied to the RT/CLK resistor.
The switching frequency is divided by 8, 4, 2, and 1 as the FB pin voltage ramps from 0 to 0.8 volts. The device implements a digital frequency foldback to enable synchronizing to an external clock during normal start-up and fault conditions. Figure 25, Figure 26, and Figure 27 show the device synchronized to an external system clock in continuous conduction mode (CCM), discontinuous conduction (DCM), and pulse-skip mode (Eco-Mode).
SPACER
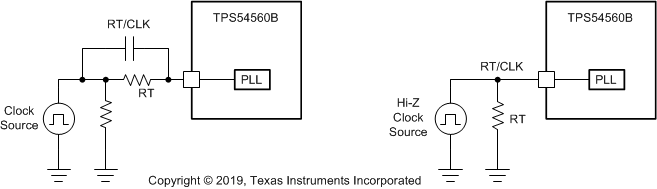 Figure 24. Synchronizing to a System Clock
Figure 24. Synchronizing to a System Clock 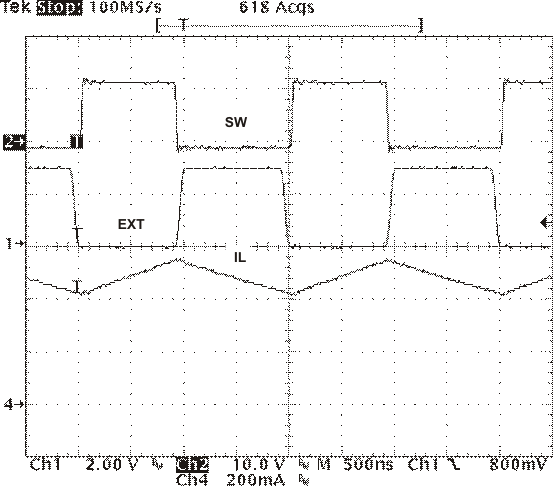 Figure 25. Plot of Synchronizing in CCM
Figure 25. Plot of Synchronizing in CCM 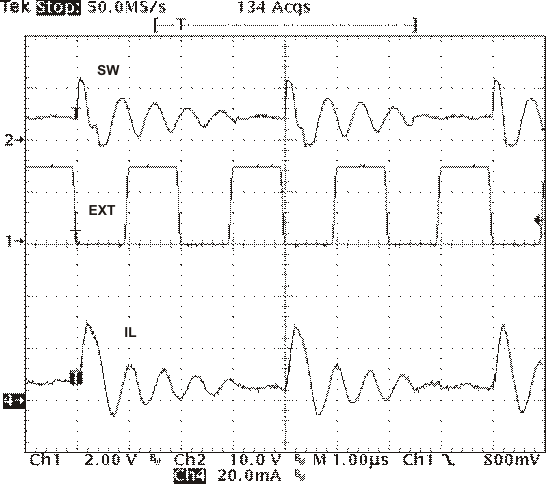 Figure 27. Plot of Synchronizing in Eco-mode
Figure 27. Plot of Synchronizing in Eco-mode 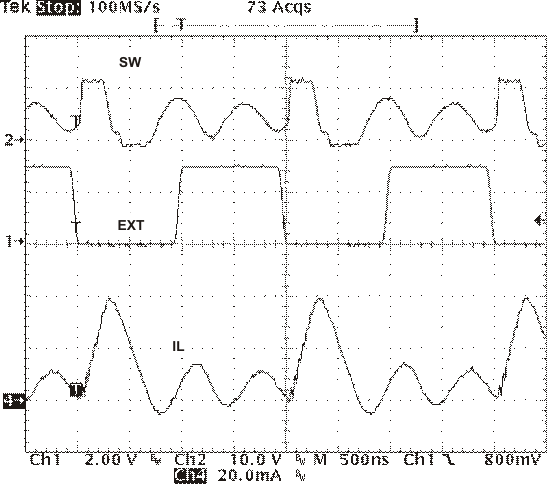 Figure 26. Plot of Synchronizing in DCM
Figure 26. Plot of Synchronizing in DCM