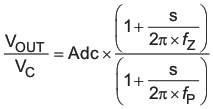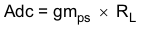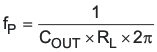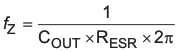JAJSLY1G July 2013 – June 2021 TPS54561
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Soft Start/Tracking Pin (SS/TR)
- 7.3.9 Sequencing
- 7.3.10 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) Pin)
- 7.3.11 Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.12 Synchronization to RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.13 Accurate Current Limit Operation
- 7.3.14 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.17 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.18 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.19 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter for 7-V to 60-V Input to 5-V at 5-A Output
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.1.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.7 Slow Start Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.10 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.1.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.12 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.1.2.13 Safe Operating Area
- 8.2.1.2.14 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Inverting Buck-Boost Topology for Positive Input to Negative Output
- 8.2.3 Split-Rail Topology for Positive Input to Negative and Positive Output
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter for 7-V to 60-V Input to 5-V at 5-A Output
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.18 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
Figure 7-18 describes a simple small signal model that can be used to design the frequency compensation. The TPS54561 power stage can be approximated by a voltage-controlled current source (duty cycle modulator) supplying current to the output capacitor and load resistor. The control to output transfer function is shown in Equation 14 and consists of a dc gain, one dominant pole, and one ESR zero. The quotient of the change in switch current and the change in COMP pin voltage (node c in Figure 7-17) is the power stage transconductance, gmPS. The gmPS for the TPS54561 is 17 A/V. The low-frequency gain of the power stage is the product of the transconductance and the load resistance as shown in Equation 15.
As the load current increases and decreases, the low-frequency gain decreases and increases, respectively. This variation with the load may seem problematic at first glance, but fortunately the dominant pole moves with the load current (see Equation 16). The combined effect is highlighted by the dashed line in the right half of Figure 7-18. As the load current decreases, the gain increases and the pole frequency lowers, keeping the 0-dB crossover frequency the same with varying load conditions. The type of output capacitor chosen determines whether the ESR zero has a profound effect on the frequency compensation design. Using high ESR aluminum electrolytic capacitors may reduce the number frequency compensation components needed to stabilize the overall loop because the phase margin is increased by the ESR zero of the output capacitor (see Equation 17).
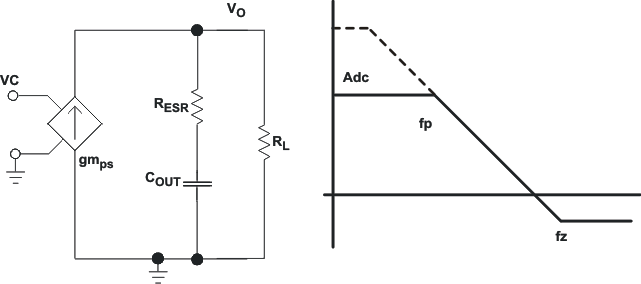 Figure 7-18 Simple Small Signal Model and Frequency Response for Peak Current Mode Control
Figure 7-18 Simple Small Signal Model and Frequency Response for Peak Current Mode Control