SLVSH95 July 2024 TPS546C25
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 D-CAP4 Control
- 6.3.2 Internal VCC LDO and Using an External Bias on VCC Pin and VDRV Pin
- 6.3.3 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 6.3.4 Differential Remote Sense and Internal, External Feedback Divider
- 6.3.5 Set the Output Voltage and VORST#
- 6.3.6 Start-Up and Shutdown
- 6.3.7 Dynamic Voltage Slew Rate
- 6.3.8 Set Switching Frequency
- 6.3.9 Switching Node (SW)
- 6.3.10 Overcurrent Limit and Low-side Current Sense
- 6.3.11 Negative Overcurrent Limit
- 6.3.12 Zero-Crossing Detection
- 6.3.13 Input Overvoltage Protection
- 6.3.14 Output Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 6.3.15 Overtemperature Protection
- 6.3.16 Telemetry
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
-
7 Register Maps
- 7.1 Conventions for Documenting Block Commands
- 7.2 (01h) OPERATION
- 7.3 (02h) ON_OFF_CONFIG
- 7.4 (03h) CLEAR_FAULTS
- 7.5 (04h) PHASE
- 7.6 (09h) P2_PLUS_WRITE
- 7.7 (0Ah) P2_PLUS_READ
- 7.8 (0Eh) PASSKEY
- 7.9 (10h) WRITE_PROTECT
- 7.10 (15h) STORE_USER_ALL
- 7.11 (16h) RESTORE_USER_ALL
- 7.12 (19h) CAPABILITY
- 7.13 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK
- 7.14 (20h) VOUT_MODE
- 7.15 (21h) VOUT_COMMAND
- 7.16 (22h) VOUT_TRIM
- 7.17 (24h) VOUT_MAX
- 7.18 (25h) VOUT_MARGIN_HIGH
- 7.19 (26h) VOUT_MARGIN_LOW
- 7.20 (27h) VOUT_TRANSITION_RATE
- 7.21 (29h) VOUT_SCALE_LOOP
- 7.22 (2Ah) VOUT_SCALE_MONITOR
- 7.23 (2Bh) VOUT_MIN
- 7.24 (33h) FREQUENCY_SWITCH
- 7.25 (35h) VIN_ON
- 7.26 (36h) VIN_OFF
- 7.27 (39h) IOUT_CAL_OFFSET
- 7.28 (40h) VOUT_OV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.29 (41h) VOUT_OV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.30 (42h) VOUT_OV_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.31 (43h) VOUT_UV_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.32 (44h) VOUT_UV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.33 (45h) VOUT_UV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.34 (46h) IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.35 (48h) IOUT_OC_LV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.36 (49h) IOUT_OC_LV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.37 (4Ah) IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.38 (4Fh) OT_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.39 (50h) OT_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.40 (51h) OT_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.41 (55h) VIN_OV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.42 (60h) TON_DELAY
- 7.43 (61h) TON_RISE
- 7.44 (64h) TOFF_DELAY
- 7.45 (65h) TOFF_FALL
- 7.46 (78h) STATUS_BYTE
- 7.47 (79h) STATUS_WORD
- 7.48 (7Ah) STATUS_VOUT
- 7.49 (7Bh) STATUS_IOUT
- 7.50 (7Ch) STATUS_INPUT
- 7.51 (7Dh) STATUS_TEMPERATURE
- 7.52 (7Eh) STATUS_CML
- 7.53 (7Fh) STATUS_OTHER
- 7.54 (80h) STATUS_MFR_SPECIFIC
- 7.55 (88h) READ_VIN
- 7.56 (8Bh) READ_VOUT
- 7.57 (8Ch) READ_IOUT
- 7.58 (8Dh) READ_TEMPERATURE_1
- 7.59 (98h) PMBUS_REVISION
- 7.60 (99h) MFR_ID
- 7.61 (9Ah) MFR_MODEL
- 7.62 (9Bh) MFR_REVISION
- 7.63 (ADh) IC_DEVICE_ID
- 7.64 (AEh) IC_DEVICE_REV
- 7.65 (D1h) SYS_CFG_USER1
- 7.66 (D2h) PMBUS_ADDR
- 7.67 (D4h) COMP
- 7.68 (D5h) VBOOT_OFFSET_1
- 7.69 (D6h) STACK_CONFIG
- 7.70 (D8h) PIN_DETECT_OVERRIDE
- 7.71 (D9h) NVM_CHECKSUM
- 7.72 (DAh) READ_TELEMETRY
- 7.73 (79h) STATUS_ALL
- 7.74 (DDh) EXT_WRITE_PROTECTION
- 7.75 (A4h) IMON_CAL
- 7.76 (FCh) FUSION_ID0
- 7.77 (FDh) FUSION_ID1
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.6 Start-Up and Shutdown
Start-Up
The start-up and shutdown of the device is controlled by several PMBus programmable values including:
The tON_RISE time is selectable by pin-strapping through MSEL1, PMBus programming, or both.
With the default ON_OFF_CONFIG settings, the timing is as shown. See the Supported PMBus commands for full details on the implementation and use.
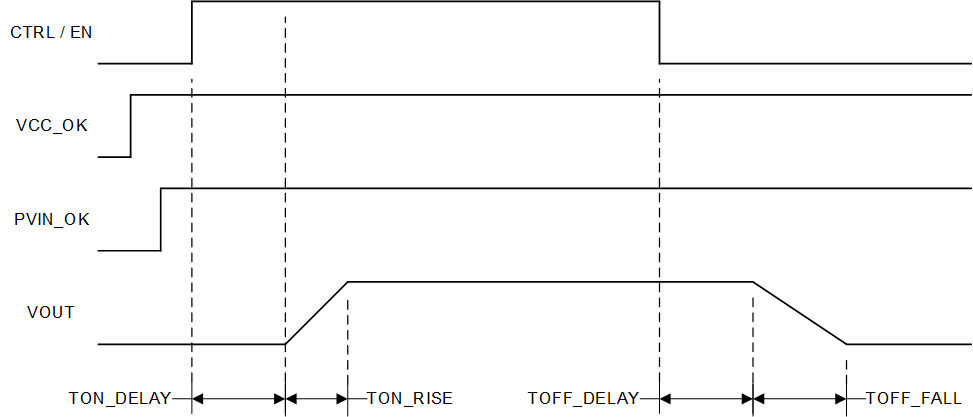 Figure 6-4 TPS546C25 Start-Up and Shutdown
Figure 6-4 TPS546C25 Start-Up and ShutdownThe startup sequence includes three sequential periods. During the first period, the device does initialization, which includes building up internal LDOs and references, register value initialization, pin strap detection, enabling digital interface, and so forth. The initialization, which is not gated by CTRL pin voltage, starts as long as VCC pin voltage is above the VCC_OK UVLO rising threshold (3.15V typical). The length of this period is about 200μs for TPS546C25 device. The PMBus communication including both read and write operations is allowed after finishing the initialization.
Once the CTRL pin voltage crosses above CTRL high threshold (typically 1.2V) the device moves to the second period, power-on delay. The power-on delay is programmable in TPS546C25 through register TON_DELAY with minimum 0.05ms delay and maximum 2ms delay.
The VOUT soft start is the third period. A soft-start ramp, which is an internal signal, starts when the chosen power-on delay finishes. The soft-start time can be selected in register TON_RISE with options of 1ms, 2ms, 4ms, 8ms, and 16ms. When starting up without prebias on the output, the VOUT ramps up from 0V to either the selected Vboot value or the programmable VOUT_COMMAND value to avoid the inrush current by the output capacitor charging, and also minimize VOUT overshoot.
For the startup with a prebiased output the device limits current from being discharged from the prebiased output voltage by preventing the low-side FET from forcing the SW node low until after the first PWM pulse turns on the high-side FET. After the increasing reference voltage exceeds the feedback voltage, which is internally divided down from (VOSNS−GOSNS) level, the high-side SW pulses start. This action enables a smooth start-up with a prebiased output.
Shutdown
The TPS546C25 device also offers programmable soft-stop feature through PMBus register TOFF_FALL with 0.5ms, 1ms, 2ms, and 4ms options. The soft-stop feature forces a controlled decrease of the output voltage from regulation to 200mV. After Vout is discharged to 200mV level the power stage stops switching and goes to tri-state. There can be negative inductor current forced during the TOFF_FALL time to discharge the output voltage.
After a stop condition is received and the selected TOFF_DELAY delay expires, the TPS546C25 device enters the soft-stop operation during which the control loop actively controls the discharge slew rate of the output voltage. The power stage continues switching while the internal reference ramps down linearly. The discharge slew rate during this phase is determined by the selected boot up voltage (not the current output voltage) and the selected TOFF_FALL time. After Vout is discharged to 200mV level the power stage stops switching and goes to tri-state. The Vout discharge continues but the discharge slew rate is controlled by the load current. With this discharge operation, the TPS546C25 device controls the soft-stop slew rate rather the total soft-stop time, thus the total VOUT discharge time (also known as, soft-stop time) can vary from the register TOFF_FALL value. The TOFF_FALL time is utilized to set the internal reference DAC ramp-down time from the regulation level to 0mV. For example, under heavy load condition, the total soft-stop time from VOUT regulation level to zero volt is likely shorter than the programmed TOFF_FALL value. Under light load, the total soft-stop time likely becomes longer than the programmed TOFF_FALL value.