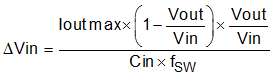SLVSEQ0A May 2019 – March 2020 TPS54A24
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Continuous Conduction Mode Operation (CCM)
- 7.3.3 VIN Pins and VIN UVLO
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference and Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Enable and Adjustable UVLO
- 7.3.7 Soft Start and Tracking
- 7.3.8 Safe Start-Up Into Prebiased Outputs
- 7.3.9 Power Good
- 7.3.10 Sequencing (SS/TRK)
- 7.3.11 Adjustable Switching Frequency (RT Mode)
- 7.3.12 Synchronization (CLK Mode)
- 7.3.13 Bootstrap Voltage and 100% Duty Cycle Operation (BOOT)
- 7.3.14 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.15 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Output Voltage Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 PGOOD Pullup Resistor
- 8.2.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTW|24
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTW|24
発注情報
8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
The TPS54A24 requires input decoupling ceramic capacitors type X5R, X7R or similar from VIN to PGND placed as close as possible to the IC. A total of at least 10 µF of capacitance is required and some applications may require a bulk capacitance. At least 1 µF of bypass capacitance is recommended near both VIN pins to minimize the input voltage ripple. A 0.1-µF to 1-µF capacitor must be placed by both VIN pins 2-3 and 16-17 to provide high frequency bypass to reduce the high frequency overshoot and undershoot on VIN and SW pins. The voltage rating of the input capacitor must be greater than the maximum input voltage. The capacitor must also have a ripple current rating greater than the maximum RMS input current of the TPS54A24. The RMS input current can be calculated using Equation 23.
For this example design, a ceramic capacitor with at least a 25-V voltage rating is required to support the maximum input voltage. Two 10-µF, 1210, X7R, 25-V and two 0.1-μF, 0603, X7R 25-V capacitors in parallel has been selected to be placed on both sides of the TPS54A24 near both VIN pins to PGND pins. Based on the capacitor manufacturer's website, the total ceramic input capacitance derates to 14 µF at the nominal input voltage of 12 V. A 100-µF bulk capacitance is also used in this circuit to bypass long leads when connected a lab bench top power supply.
The input capacitance value determines the input ripple voltage of the regulator. The input voltage ripple can be calculated using Equation 24. The maximum input ripple occurs when operating nearest to 50% duty cycle. Using the nominal design example values of Ioutmax = 10 A, CIN = 14 μF, and fSW = 500 kHz, the input voltage ripple with the 12 V nominal input is 150 mV and the RMS input ripple current with the 4.5 V minimum input is 4.9 A.
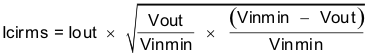
vertical spacer