JAJSIN7 February 2020 TPS59632-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 PWM Operation
- 7.3.2 Current Sensing
- 7.3.3 Load-line (Droop)
- 7.3.4 Load Transients
- 7.3.5 Overshoot Reduction (OSR)
- 7.3.6 Undershoot Reduction (USR)
- 7.3.7 Autobalance Current Sharing
- 7.3.8 PWM And SKIP Signals
- 7.3.9 Bias Power (V5A, VDD, And VINTF) UVLO
- 7.3.10 Start-Up Sequence
- 7.3.11 Power Good Operation
- 7.3.12 Analog Current Monitor, IMON, And Corresponding Digital Output Current
- 7.3.13 Fault Behavior
- 7.3.14 Output Under Voltage Protection (UVP)
- 7.3.15 Output Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.16 Over Current Protection (OCP)
- 7.3.17 Over Current Warning
- 7.3.18 Input Voltage Limits
- 7.3.19 VID Table
- 7.4 User Selections
- 7.5 I2C Interface Operation
- 7.6 I2C Register Maps
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
3-Phase D-CAP+™, Step-Down Application
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Step 1: Select Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.2 Step 2: Set The Slew Rate
- 8.2.1.2.3 Step 3: Set The I2C Address
- 8.2.1.2.4 Step 4: Determine Inductor Value And Choose Inductor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Step 5: Current Sensing Resistance
- 8.2.1.2.6 Step 6: Select Over Current Protection (OCP) Setting
- 8.2.1.2.7 Step 7: Current Monitor (IMON) Setting
- 8.2.1.2.8 Step 8: Set the Load-Line Slope
- 8.2.1.2.9 Step 9: Voltage Feedback Resistor Calculation
- 8.2.1.2.10 Step 10: Ramp Compensation Selection
- 8.2.1.2.11 Step 11 Overshoot Reduction (OSR) selection
- 8.2.1.2.12 Step 12: Undershoot Reduction (USR) selection
- 8.2.1.2.13 Step 13: Loop Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Performance Plots
- 8.2.1
3-Phase D-CAP+™, Step-Down Application
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
RHB Package
32-Pin QFN
(Top View)
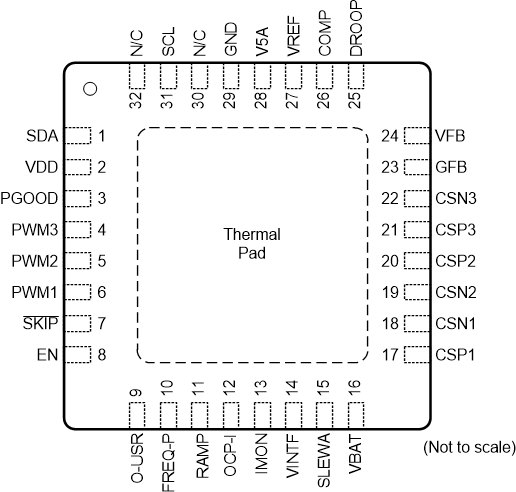
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| COMP | 26 | I | Error amplifier summing node. Resistors from VREF to COMP (RCOMP) and COMP to DROOP (RDROOP) set the droop gain. |
| CSP1 | 17 | I | Positive current sense inputs. Connect to the most positive node of current sense resistor or inductor DCR sense network. Tie CSP3, CSP2, or CSP1 (in that order) to 3.3 V to disable the phase. |
| CSP2 | 20 | ||
| CSP3 | 21 | ||
| CSN1 | 18 | I | Negative current sense inputs. Connect to the most negative node of current sense resistor or inductor DCR sense network. CSN1 has a secondary OVP comparator and includes the soft-stop pulldown transistor. |
| CSN2 | 19 | ||
| CSN3 | 22 | ||
| DROOP | 25 | O | Error amplifier output. A resistor pair from VREF to COMP to DROOP sets the droop gain. ADROOP = 1 + RDROOP / RCOMP. |
| EN | 8 | I | Enable; 100-ns de-bounce. Regulator enters low-power mode, but retains start-up settings when brought low. |
| FREQ-P | 10 | I | R to GND sets the per phase switching frequency. MUST connect a resistor to VREF to ensure this pin voltage is above 0.8 V for proper operation. |
| GFB | 23 | I | Voltage sense return. Tie to GND on PCB with a 10-Ω resistor to provide feedback when µP is not populated. |
| GND | 29 | – | Analog circuit reference; tie to a quiet point on the ground plane. |
| IMON | 13 | O | Analog current monitor output. VIMON = Σ VISENSE × (1 + RIMON / ROCP). |
| OCP-I | 12 | I/O | Voltage divider to IMON. Resistor ratio sets the IMON gain (see IMON pin). R to GND (ROCP) selects 1 of 8 OCP levels (per phase, latched at start-up). |
| O-USR | 9 | I | Voltage divider to the VREG pin. Connect a resistor to GND to select the pulse-truncation level and OSR level. Voltage at O-USR selects the USR level. |
| PU | 9 | I | Provides pullup resistance to VREF through 10-kΩ resistor. |
| PAD | GND | – | Thermal pad; tie to the ground plane with multiple vias. |
| PGOOD | 3 | O | Power Good output; Open-drain. PGOOD can be configured to go low when the current reaches 70% of the OCP setting value. |
| PWM1 | 6 | O | PWM controls for the external driver; 5-V logic level. Controller forces signal to the 3-state level when needed. |
| PWM2 | 5 | ||
| PWM3 | 4 | ||
| RAMP | 11 | I | Voltage divider to VREF. Connect a resistor to GND to set the ramp setting voltage. The RAMP setting can override the factory ramp setting. |
| NC | 30 | NC | No connect. Leave pins floating. |
| 32 | |||
| SCL | 31 | I | l2C digital clock line. |
| SDA | 1 | I/O | I2C digital data line. |
| SKIP | 7 | O | This pin is active high to operate synchronous buck MOSFETs in Forced Continuous Conduction Mode (FCCM) active low for skip mode operation. This pin must be connected to the corresponding pin of the drivers for this function. |
| SLEWA | 15 | I | The voltage sets the 3 LSBs of the I2C address. The resistance to GND selects 1 of 8 slew rates. The start-up slew rate (EN transitions high) is SLEWRATE / 2. The ADDRESS and SLEWRATE values are latched at start-up. |
| VINTF | 14 | I | Input voltage to power I2C interface logic. Can be tied to VDD if 3.3-V logic signals are needed. |
| V5A | 28 | I | 5-V power input for analog circuits; connect through resistor to 5-V plane and bypass to GND with ≥ 1-µF ceramic capacitor |
| VBAT | 16 | I | 10-kΩ resistor to VBAT provides VBAT information to the on-time circuits for both converters. |
| VDD | 2 | I | 3.3-V digital power input; bypass to GND with ≥ 1-µF capacitor. |
| VFB | 24 | I | Voltage sense line. Tie directly to VOUT sense point of processor. Tie to VOUT on PCB with a 10-Ω resistor to provide feedback when the microprocessor is not populated. The resistance between VFB and GFB is > 1 MΩ. |
| VREF | 27 | O | 1.7-V, 500-µA reference. Bypass to GND with a 0.22-µF ceramic capacitor. |