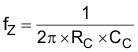JAJSJ29E May 2020 – October 2024 TPS61378-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VCC Power Supply
- 7.3.2 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.3 Enable and Soft Start
- 7.3.4 Shut Down
- 7.3.5 Switching Frequency Setting
- 7.3.6 Spread Spectrum Frequency Modulation
- 7.3.7 Adjustable Peak Current Limit
- 7.3.8 Bootstrap
- 7.3.9 Load Disconnect
- 7.3.10 MODE/SYNC Configuration
- 7.3.11 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.12 Output Short Protection/Hiccup
- 7.3.13 Power-Good Indicator
- 7.3.14 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTE|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTE|16
発注情報
8.2.2.7.1 Small Signal Model
The TPS61378-Q1 uses the fixed frequency peak current mode control. There is an internal adaptive slope compensation to avoid subharmonic oscillation. With the inductor current information sensed, the small-signal model of the power stage reduces from a two-pole system, created by L and COUT, to a single-pole system, created by ROUT and COUT. The single-pole system is easily used with the loop compensation. Figure 8-4 shows the equivalent small signal elements of a boost converter.
 Figure 8-4 TPS61378-Q1 Control Equivalent Circuitry Model
Figure 8-4 TPS61378-Q1 Control Equivalent Circuitry ModelThe small signal of power stage is:
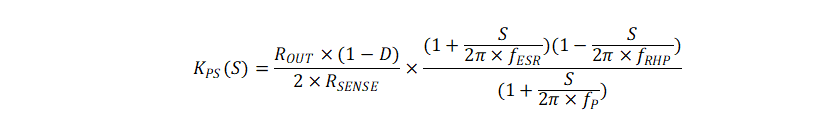
where
- D is the duty cycle
- ROUT is the output load resistor
- RSENSE is the equivalent internal current sense resistor, which is typically 118 mΩ
The single pole of the power stage is:
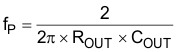
where
- COUT is the output capacitance. For a boost converter having multiple identical output capacitors in parallel, simply combine the capacitors with the equivalent capacitance
The zero created by the ESR of the output capacitor is:
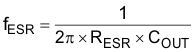
where
- RESR is the equivalent resistance in series of the output capacitor
The right-hand plane zero is:
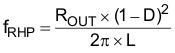
where
- D is the duty cycle
- ROUT is the output load resistor
- L is the inductance
Equation 20 shows the equation for feedback resistor network and the error amplifier.
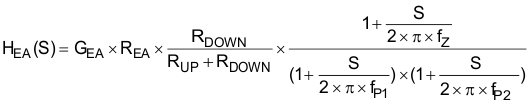
where
- REA is the output impedance of the error amplifier, typically REA = 500 MΩ
- ƒP1, ƒP2 is the pole's frequency of the compensation
- fZ is the zero’s frequency of the compensation network
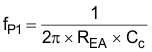
where
- CC is the zero capacitor compensation
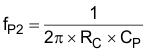
where
- CP is the pole capacitor compensation
- RC is the resistor of the compensation network