JAJSKK6A November 2020 – December 2021 TPS7H4010-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Synchronous Step-Down Regulator
- 7.3.2 Auto Mode and FPWM Mode
- 7.3.3 Fixed-Frequency Peak Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.4 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 7.3.5 Enable and UVLO
- 7.3.6 Internal LDO, VCC_UVLO, and BIAS Input
- 7.3.7 Soft Start and Voltage Tracking
- 7.3.8 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 7.3.9 Frequency Synchronization and Mode Setting
- 7.3.10 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 7.3.11 Bootstrap Capacitor and VBOOT-UVLO
- 7.3.12 Power-Good and Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 7.3.14 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 8.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Feed-Forward Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitors
- 8.2.2.8 VCC Capacitor
- 8.2.2.9 BIAS
- 8.2.2.10 Soft Start
- 8.2.2.11 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.12 PGOOD
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RNP|30
- KGD|0
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RNP|30
発注情報
7.3.8 Adjustable Switching Frequency
The internal oscillator frequency is controlled by the impedance on the RT pin. If the RT pin is open circuit, the TPS7H4010-SEP operates at its default switching frequency, 500 kHz. The RT pin is not designed to be connected directly to ground. To program the switching frequency by RT resistor, either Equation 13, Figure 7-12, or Table 7-1 can be used to find the resistance value.
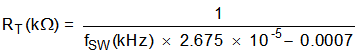
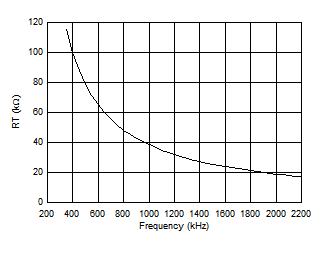 Figure 7-12 RT Resistance vs Switching Frequency
Figure 7-12 RT Resistance vs Switching Frequency| SWITCHING FREQUENCY fSW (kHz) | RT RESISTANCE (kΩ) |
|---|---|
| 350 | 115 |
| 400 | 100 |
| 500 | 78.7 (or open) |
| 750 | 52.3 |
| 1000 | 39.2 |
| 1500 | 26.1 |
| 2000 | 19.1 |
| 2200 | 17.4 |
The choice of switching frequency is usually a compromise between conversion efficiency and the size of the solution. Lower switching frequency has lower switching losses (including gate charge losses, switch transition losses, etc.) and usually results in higher overall efficiency. However, higher switching frequency allows the use of smaller power inductor and output capacitors, hence a more compact design. Lower inductance also helps transient response (higher large signal slew rate of inductor current), and has lower DCR. The optimal switching frequency is usually a trade-off in a given application and thus needs to be determined on a case-by-case basis. Factors that need to be taken into account include input voltage range, output voltage, most frequent load current level or levels, external component choices, solution size/cost requirements, efficiency, and thermal management requirements.
The choice of switching frequency may also be limited whether an operating condition triggers tON-MIN or tOFF-MIN. Minimum on-time, tON-MIN, is the smallest time that the HS switch can be on. Minimum off-time, tOFF-MIN, is the smallest duration that the HS switch can be off.
In CCM operation, tON-MIN and tOFF_MIN limits the voltage conversion range given a selected switching frequency, fSW. The minimum duty cycle allowed is:
The maximum duty cycle allowed is:
Given an output voltage, the choice of the switching frequency affects the allowed input voltage range, solution size and efficiency. The maximum operational supply voltage can be found by:
At lower supply voltage, the switching frequency decreases once tOFF-MIN is tripped. The minimum VIN without frequency foldback can be approximated by:
With a desired VOUT, the range of allowed VIN is narrower with higher switching frequency.
TPS7H4010-SEP has an advanced frequency fold-back algorithm under both tON_MIN and tOFF_MIN conditions. With frequency foldback, stable output voltage regulation is extended to wider range of supply voltages.
At very high VIN conditions, where tON-MIN limitation is met, the switching frequency reduces to allow higher VIN while maintaining VOUT regulation. Note that the peak to peak inductor current ripple will increase with higher VIN and lower frequency. TI does not recommend designing the circuit to operate with tON_MIN under typical conditions.
At very low VIN conditions, where tOFF-MIN limitation is met, the switching frequency decreases until tON-MAX condition is met. Such frequency foldback mechanism allows the TPS7H4010-SEP to have very low dropout voltage regardless of frequency setting.