SNVS902A October 2012 – October 2015 TPS92640 , TPS92641
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Controlled On-Time Architecture
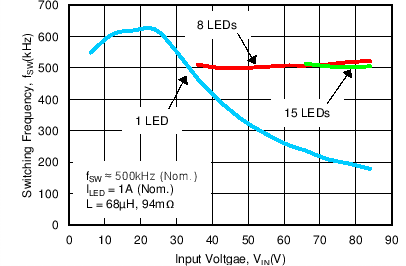
- 7.3.2 Switching Frequency
- 7.3.3 Average LED Current
- 7.3.4 Analog Dimming and True-Zero Operation
- 7.3.5 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.6 PWM Dimming Using the UDIM Pin
- 7.3.7 External Shunt FET PWM Dimming
- 7.3.8 VCC Regulation and Start-up
- 7.3.9 Precision Reference
- 7.3.10 Control Loop Compensation
- 7.3.11 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.13 Boot Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
TPS92640: Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Set Output Voltage Feedback Ratio
- 8.2.1.2.2 Set Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.3 Set Average LED Current
- 8.2.1.2.4 Set Inductor Ripple Current
- 8.2.1.2.5 Set LED Ripple Current and Determine Output Capacitance, COUT
- 8.2.1.2.6 Choose N-Channel MOSFETs
- 8.2.1.2.7 Choose Input Capacitance
- 8.2.1.2.8 Set the Turnon Voltage and Undervoltage Lockout Hysteresis
- 8.2.2
TPS92640 - PWM Dimming Application
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Calculate Operating Points
- 8.2.2.2.2 Output Voltage Feedback
- 8.2.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2.4 Set the Feedback Reference and LED Current
- 8.2.2.2.5 Calculate the Inductor Value
- 8.2.2.2.6 Calculate the Output Capacitor Value
- 8.2.2.2.7 Calculate the MOSFET Parameters
- 8.2.2.2.8 Calculate the Minimum Input Capacitance
- 8.2.2.2.9 Undervoltage Lockout and Hysteresis
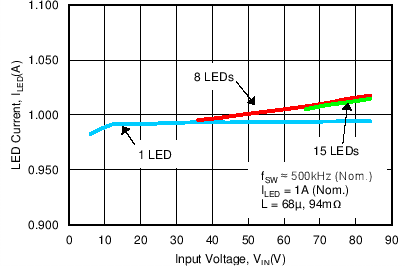
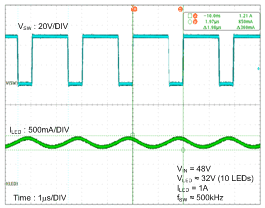
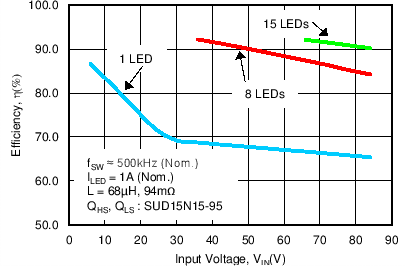
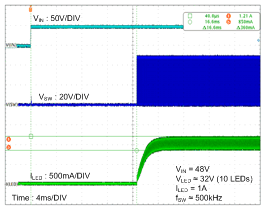
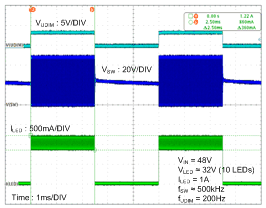
- 8.2.2.3 Application Curve
- 8.2.1
TPS92640: Design Procedure
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|16
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN, UDIM, SW | –0.3 | 90 | V | |
| –1 | mA | |||
| BOOT | –0.3 | 98.5 | V | |
| HG | –0.3 | 90 | V | |
| –2.5 (Pulse < 100 ns) | V | |||
| LG, SDRV, CS | –0.3 | +VCC | V | |
| –2.5 (Pulse < 100 ns) | V | |||
| VCC + 2.5 (Pulse < 100 ns) | V | |||
| VCC | –0.3 | 15 | V | |
| VREF, RON, COMP, VOUT, IADJ, SDIM | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| –200 | 200 | µA | ||
| GND | –0.3 | 0.3 | V | |
| –2.5 (Pulse < 100 ns) | 2.5 (Pulse < 100 ns) | V | ||
| Continuous power dissipation | Internally Limited | |||
| Maximum lead temperature (soldering and reflow) (2) | 260 | °C | ||
| Maximum junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) Refer to TI’s packaging website for more detailed information and mounting techniques.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS92640 PWP PACKAGE | ||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
| TPS92641 PWP PACKAGE | ||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | 7 | 85 | V | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS92640 | TPS92641 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWP (HTSSOP) | PWP (HTSSOP) | |||
| 14 PINS | 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 40.1 | 38.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 24.6 | 22.7 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 20.9 | 16.5 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.6 | 0.6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 20.7 | 16.3 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 2.5 | 1.7 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified VIN = 24 V. Typical specifications apply for TA = TJ = 25°C.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(1) | TYP(2) | MAX(1) | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| START-UP REGULATOR (VCC, VIN) | ||||||
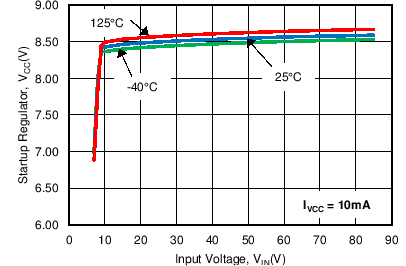
| VCCREG | VCC Regulation | ICC = 10 mA, VIN = 24 V, 85 V | 7.86 | 8.5 | 9.14 | V |
| ICCLIM | VCC Current Limit | VCC = 0 V | 48 | 63 | 78 | mA |
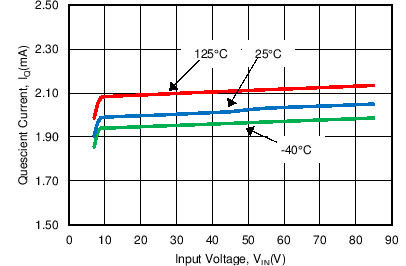
| IQ | Quiescent Current | VUDIM = 3 V, Static VIN = 7 V, 24 V, 85 V |
2 | 3 | mA | |
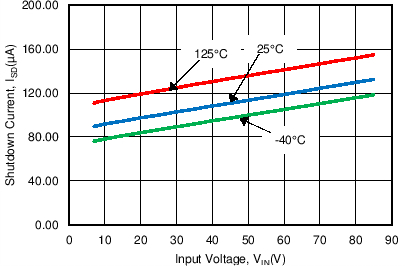
| ISD | Shutdown Current | VUDIM = 0 V | 100 | µA | ||
| VCC-UV | VCC UVLO Threshold | VCC increasing | 5.04 | 5.9 | V | |
| VCC decreasing | 4.5 | 4.9 | ||||
| VCC-HYS | VCC UVLO Hysteresis | 0.17 | V | |||
| REFERENCE VOLTAGE (VREF) | ||||||
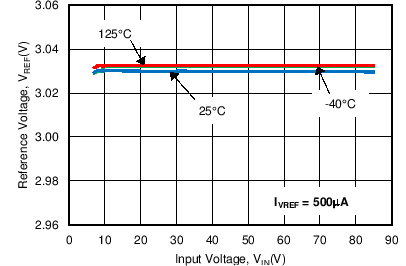
| VREF | Reference Voltage | No Load, VIN = 7 V, 24 V, 85 V | 2.97 | 3.03 | 3.09 | V |
| IVREFLIM | Current Limit | VREF = 0 V | 1.3 | 2.1 | 2.9 | mA |
| ERROR AMPLIFIER (CS, COMP) | ||||||
| VCSREF | CS Reference Voltage | With respect to GND | VIADJ/10 | V | ||
| VCSREF-OFF | Error Amp Input Offset Voltage | –600 | 0 | 600 | µV | |
| ICOMP | COMP Sink Current | 85 | µA | |||
| COMP Source Current | 110 | µA | ||||
| gM-CS | Transconductance | 500 | µA/V | |||
| Linear Input Range | See (3) | ±125 | mV | |||
| Transconductance Bandwidth | –6-dB unloaded response(3) | 400 | kHz | |||
| TIMERS / OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION (RON, VOUT) | ||||||
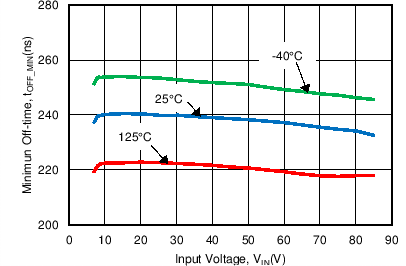
| tOFF-MIN | Minimum Off-time | CS = 0 V | 230 | ns | ||
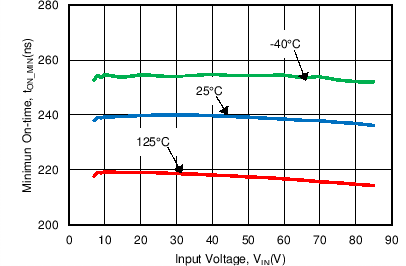
| tON-MIN | Minimum On-time | 235 | ns | |||
| tON | Programmed On-time | VVOUT = 2 V, RON = 25 kΩ, CON = 1 nF | 2.08 | µs | ||
| RRON | RON Pulldown Resistance | 35 | 120 | Ω | ||
| tCL | Current Limit Off-time | 270 | µs | |||
| tD-ON | RON Thresh - HG Falling Delay | 25 | ns | |||
| VTH-OVP | VOUT Overvoltage Threshold | VOUT rising | 2.85 | 3.05 | 3.25 | V |
| VHYS-OVP | VOUT Overvoltage Hysteresis | 0.13 | V | |||
| GATE DRIVER (HG, LG, BOOT, SW) | ||||||
| RSRC-LG | LG Sourcing Resistance | LG = High | 1.5 | 6 | Ω | |
| RSNK-LG | LG Sinking Resistance | LG = Low | 1 | 4.5 | Ω | |
| RSRC-HG | HG Sourcing Resistance | HG = High | 3.9 | 6 | Ω | |
| RSNK-HG | HG Sinking Resistance | HG = Low | 1.1 | 4.5 | Ω | |
| VTH-BOOT | BOOT UVLO Threshold | BOOT-SW rising | 1.9 | 3.4 | 4.5 | V |
| VHYS-BOOT | BOOT UVLO Hysteresis | BOOT-SW falling | 1.8 | V | ||
| TD-HL | HG to LG deadtime | HG fall to LG rise | 60 | ns | ||
| TD-LH | LG to HG deadtime | LG fall to HG rise | 60 | ns | ||
| PWM DIMMING (SDIM, SDRV) (TPS92641 only) | ||||||
| RSRC-DDRV | SDRV Sourcing Resistance | SDRV = High | 5.6 | 30 | Ω | |
| tSDIM-RIS | SDIM to SDRV Rising Delay | SDIM rising | 68 | 100 | ns | |
| tSDIM -FALL | SDIM to SDRV Falling Delay | SDIM falling | 29 | 70 | ns | |
| VSDIM-RIS | SDIM Rising Threshold | SDIM rising | 1.29 | 1.74 | V | |
| VSDIM -FALL | SDIM Falling Threshold | SDIM falling | 0.5 | V | ||
| RSDIM-PU | SDIM Pullup Resistance | 90 | kΩ | |||
| ANALOG ADJUST (IADJ) | ||||||
| VADJ-MAX | IADJ Clamp Voltage | 2.46 | 2.54 | 2.62 | V | |
| RADJ | IADJ Input Impedance | 1 | MΩ | |||
| UNDERVOLTAGE / PWM (UDIM) | ||||||
| VTH-UDIM | UDIM Start-up Threshold | UDIM rising | 1.21 | 1.276 | 1.342 | V |
| IHYS-UDIM | UDIM Hysteresis Current | 12 | 21 | 30 | µA | |
| tUDIM-RIS | UDIM to HG/LG Rising Delay | UDIM rising | 168 | 260 | ns | |
| tUDIM-FALL | UDIM to HG/LG Falling Delay | UDIM falling | 174 | 280 | ns | |
| VUDIM-LP | UDIM Low Power Threshold | 370 | mV | |||
| TUDIM-DET | UDIM Shutdown Detect Timer | UDIM falling | 8.5 | 13 | ms | |
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | ||||||
| TSD | Thermal Shutdown Threshold | See (3) | 165 | °C | ||
| THYS | Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis | See (3) | 20 | °C | ||
(1) All limits specified at room temperature (TYP values) and at temperature extremes (MIN/MAX values). All room temperature limits are 100% production tested. All limits at temperature extremes are specified via correlation using standard Statistical Quality Control (SQC) methods. All limits are used to calculate Average Outgoing Quality Level (AOQL).
(2) Typical numbers are at 25°C and represent the most likely norm.
(3) These electrical parameters are specified by design, and are not verified by test.
6.6 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise stated, –40°C ≤ TA = TJ ≤ 125°C, VIN = 24 V, VIADJ= 2 V, ILED = 1 A, CVCC = 2.2 μF, CCOMP = 0.47 μF