SLUSDW0B May 2020 – May 2020 UCC28065
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Principles of Operation
- 8.3.2 Natural Interleaving
- 8.3.3 On-Time Control, Maximum Frequency Limiting, Restart Timer and Input Voltage Feed-Forward compensation
- 8.3.4 Zero-Current Detection and Valley Switching
- 8.3.5 Phase Management and Light-Load Operation
- 8.3.6 Burst Mode Operation
- 8.3.7 External Disable
- 8.3.8 Improved Error Amplifier
- 8.3.9 Soft Start
- 8.3.10 Brownout Protection
- 8.3.11 Line Dropout Detection
- 8.3.12 VREF
- 8.3.13 VCC
- 8.3.14
System Level Protections
- 8.3.14.1 Failsafe OVP - Output Over-voltage Protection
- 8.3.14.2 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.14.3 Open-Loop Protection
- 8.3.14.4 VCC Undervoltage Lock-Out (UVLO) Protection
- 8.3.14.5 Phase-Fail Protection
- 8.3.14.6 CS - Open, TSET - Open and Short Protection
- 8.3.14.7 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.14.8 Fault Logic Diagram
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.2 ZCD Resistor Selection RZA, RZB
- 9.2.2.3 HVSEN
- 9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Selecting RS For Peak Current Limiting
- 9.2.2.6 Power Semiconductor Selection (Q1, Q2, D1, D2)
- 9.2.2.7 Brownout Protection
- 9.2.2.8 Converter Timing
- 9.2.2.9 Programming VOUT
- 9.2.2.10 Voltage Loop Compensation
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor ( COUT ) is selected based on holdup requirements, as shown in Equation 28.
Equation 28. 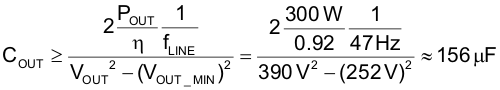
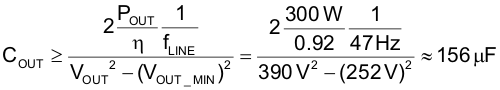
Two 100-μF capacitors were used in parallel for the output capacitor.
Equation 29. 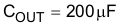
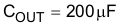
For this size capacitor, the low-frequency peak-to-peak output voltage ripple (VRIPPLE) is approximately 14 V, as shown in Equation 30:
Equation 30. 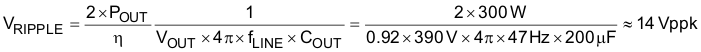
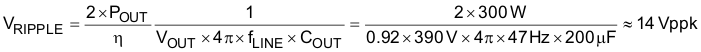
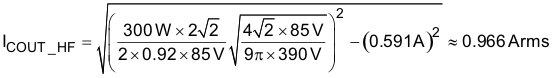
In addition to holdup requirements, a capacitor must be selected so that it can withstand the low-frequency RMS current (ICOUT_100Hz) and the high-frequency RMS current (ICOUT_HF); see Equation 31 to Equation 33. High-voltage electrolytic capacitors generally have both a low- and a high-frequency RMS current ratings on the product data sheets.
Equation 31. 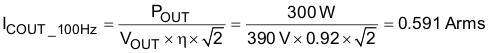
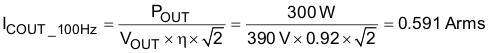
Equation 32. 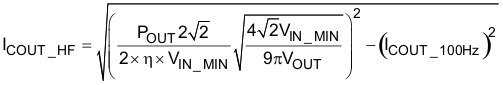

Equation 33.