JAJSE58E January 2014 – October 2017 LMT87
PRODUCTION DATA.
8.3.1 LMT87 Transfer Function
The output voltage of the LMT87, across the complete operating temperature range, is shown in Table 3. This table is the reference from which the LMT87 accuracy specifications (listed in the Accuracy Characteristics section) are determined. This table can be used, for example, in a host processor look-up table. A file containing this data is available for download at the LMT87 product folder under Tools and Software Models.
Table 3. LMT87 Transfer Table
| TEMP (°C) | VOUT (mV) | TEMP (°C) | VOUT (mV) | TEMP (°C) | VOUT (mV) | TEMP (°C) | VOUT (mV) | TEMP (°C) | VOUT (mV) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –50 | 3277 | –10 | 2767 | 30 | 2231 | 70 | 1679 | 110 | 1115 | ||||
| –49 | 3266 | –9 | 2754 | 31 | 2217 | 71 | 1665 | 111 | 1101 | ||||
| –48 | 3254 | –8 | 2740 | 32 | 2204 | 72 | 1651 | 112 | 1087 | ||||
| –47 | 3243 | –7 | 2727 | 33 | 2190 | 73 | 1637 | 113 | 1073 | ||||
| –46 | 3232 | –6 | 2714 | 34 | 2176 | 74 | 1623 | 114 | 1058 | ||||
| –45 | 3221 | –5 | 2700 | 35 | 2163 | 75 | 1609 | 115 | 1044 | ||||
| –44 | 3210 | –4 | 2687 | 36 | 2149 | 76 | 1595 | 116 | 1030 | ||||
| –43 | 3199 | –3 | 2674 | 37 | 2136 | 77 | 1581 | 117 | 1015 | ||||
| –42 | 3186 | –2 | 2660 | 38 | 2122 | 78 | 1567 | 118 | 1001 | ||||
| –41 | 3173 | –1 | 2647 | 39 | 2108 | 79 | 1553 | 119 | 987 | ||||
| –40 | 3160 | 0 | 2633 | 40 | 2095 | 80 | 1539 | 120 | 973 | ||||
| –39 | 3147 | 1 | 2620 | 41 | 2081 | 81 | 1525 | 121 | 958 | ||||
| –38 | 3134 | 2 | 2607 | 42 | 2067 | 82 | 1511 | 122 | 944 | ||||
| –37 | 3121 | 3 | 2593 | 43 | 2054 | 83 | 1497 | 123 | 929 | ||||
| –36 | 3108 | 4 | 2580 | 44 | 2040 | 84 | 1483 | 124 | 915 | ||||
| –35 | 3095 | 5 | 2567 | 45 | 2026 | 85 | 1469 | 125 | 901 | ||||
| –34 | 3082 | 6 | 2553 | 46 | 2012 | 86 | 1455 | 126 | 886 | ||||
| –33 | 3069 | 7 | 2540 | 47 | 1999 | 87 | 1441 | 127 | 872 | ||||
| –32 | 3056 | 8 | 2527 | 48 | 1985 | 88 | 1427 | 128 | 858 | ||||
| –31 | 3043 | 9 | 2513 | 49 | 1971 | 89 | 1413 | 129 | 843 | ||||
| –30 | 3030 | 10 | 2500 | 50 | 1958 | 90 | 1399 | 130 | 829 | ||||
| –29 | 3017 | 11 | 2486 | 51 | 1944 | 91 | 1385 | 131 | 814 | ||||
| –28 | 3004 | 12 | 2473 | 52 | 1930 | 92 | 1371 | 132 | 800 | ||||
| –27 | 2991 | 13 | 2459 | 53 | 1916 | 93 | 1356 | 133 | 786 | ||||
| –26 | 2978 | 14 | 2446 | 54 | 1902 | 94 | 1342 | 134 | 771 | ||||
| –25 | 2965 | 15 | 2433 | 55 | 1888 | 95 | 1328 | 135 | 757 | ||||
| –24 | 2952 | 16 | 2419 | 56 | 1875 | 96 | 1314 | 136 | 742 | ||||
| –23 | 2938 | 17 | 2406 | 57 | 1861 | 97 | 1300 | 137 | 728 | ||||
| –22 | 2925 | 18 | 2392 | 58 | 1847 | 98 | 1286 | 138 | 713 | ||||
| –21 | 2912 | 19 | 2379 | 59 | 1833 | 99 | 1272 | 139 | 699 | ||||
| –20 | 2899 | 20 | 2365 | 60 | 1819 | 100 | 1257 | 140 | 684 | ||||
| –19 | 2886 | 21 | 2352 | 61 | 1805 | 101 | 1243 | 141 | 670 | ||||
| –18 | 2873 | 22 | 2338 | 62 | 1791 | 102 | 1229 | 142 | 655 | ||||
| –17 | 2859 | 23 | 2325 | 63 | 1777 | 103 | 1215 | 143 | 640 | ||||
| –16 | 2846 | 24 | 2311 | 64 | 1763 | 104 | 1201 | 144 | 626 | ||||
| –15 | 2833 | 25 | 2298 | 65 | 1749 | 105 | 1186 | 145 | 611 | ||||
| –14 | 2820 | 26 | 2285 | 66 | 1735 | 106 | 1172 | 146 | 597 | ||||
| –13 | 2807 | 27 | 2271 | 67 | 1721 | 107 | 1158 | 147 | 582 | ||||
| –12 | 2793 | 28 | 2258 | 68 | 1707 | 108 | 1144 | 148 | 568 | ||||
| –11 | 2780 | 29 | 2244 | 69 | 1693 | 109 | 1130 | 149 | 553 | ||||
| 150 | 538 |
Although the LMT87 is very linear, the response does have a slight umbrella parabolic shape. This shape is very accurately reflected in Table 3. The transfer table can be calculated by using the parabolic equation (Equation 1).
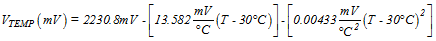
The parabolic equation is an approximation of the transfer table and the accuracy of the equation degrades slightly at the temperature range extremes. Equation 1 can be solved for T resulting in:
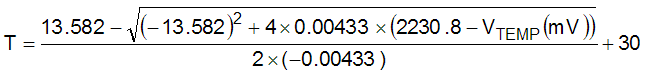
For an even less accurate linear transfer function approximation, a line can easily be calculated over the desired temperature range from Table 3 using the two-point equation (Equation 3):
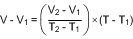
where
- V is in mV,
- T is in °C,
- T1 and V1 are the coordinates of the lowest temperature,
- and T2 and V2 are the coordinates of the highest temperature.
For example, if the user wanted to resolve this equation, over a temperature range of 20°C to 50°C, they would proceed as follows:
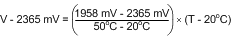
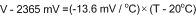
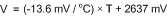
Using this method of linear approximation, the transfer function can be approximated for one or more temperature ranges of interest.