JAJSGJ9A November 2018 – May 2019 TPS56339
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Advanced Emulated Current Mode Control
- 7.3.2 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.3 Soft Start and Pre-Biased Soft Start
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.5 Minimum ON-time, Minimum OFF-time and Frequency Foldback at Dropout Conditions
- 7.3.6 Overcurrent and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.7 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Light-Load Operation
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
The TPS56339 requires an input decoupling capacitor and a bulk capacitor is needed depending on the application. TI recommends a ceramic capacitor over 10 µF for the decoupling capacitor. An additional 0.1-µF capacitor (C3) from VIN pin to ground is recommended to provide additional high frequency filtering. The capacitor voltage rating needs to be greater than the maximum input voltage. The capacitor must also have a ripple current rating greater than the maximum input current ripple of the TPS56339. The input ripple current can be calculated using Equation 16.
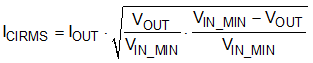
The value of a ceramic capacitor varies significantly over temperature and the amount of DC bias applied to the capacitor. The capacitance variations due to temperature can be minimized by selecting a dielectric material that is stable over temperature. X5R and X7R ceramic dielectrics are usually selected for power regulator capacitors because they have a high capacitance to volume ratio and are fairly stable over temperature. The output capacitor must also be selected with the DC bias taken into account. The capacitance value of a capacitor decreases as the DC bias across a capacitor increases. For this example design, a ceramic capacitor with at least a 35-V voltage rating is required to support the maximum input voltage. For this example, two Murata GRM21BR6YA106KE43L (10-μF, 35-V, 0805, X5R) capacitors have been selected. The effective capacitance under input voltage of 12 V for each one is 0.269 × 10 = 2.69 μF. The input capacitance value determines the input ripple voltage of the regulator. The input voltage ripple can be calculated using Equation 17. Using the design example values, IOUT_MAX = 3 A, CIN_E = 2 × 2.69 = 5.38 μF, fSW = 500 kHz, yields an input voltage ripple of 279 mV and a RMS input ripple current of 1.48 A.
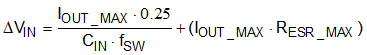
where
- RESR_MAX is the maximum series resistance of the input capacitor