JAJSHF7A May 2019 – November 2019 AMC1035-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
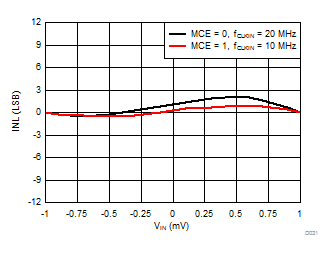
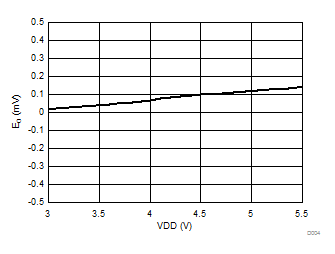
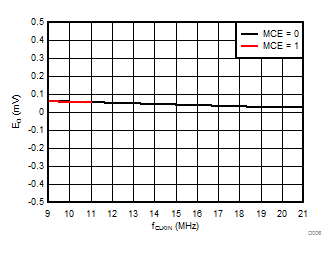
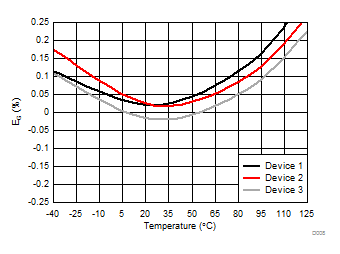
6.6 Typical Characteristics
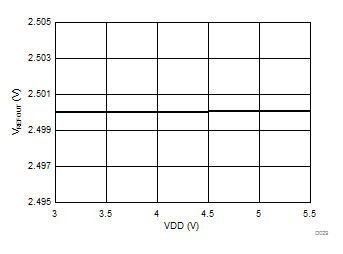
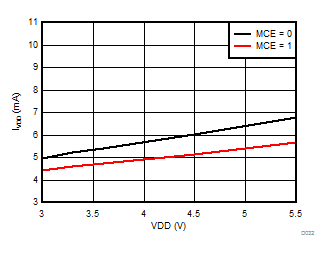
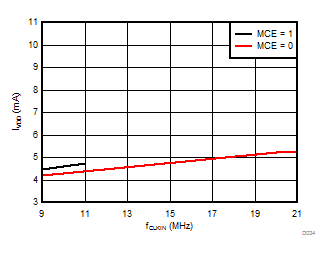
at VDD = 3.3 V, AINP = –1 V to 1 V, AINN = GND, fCLKIN = 20 MHz, MCE = 0, and sinc3 filter with OSR = 256 (unless otherwise noted)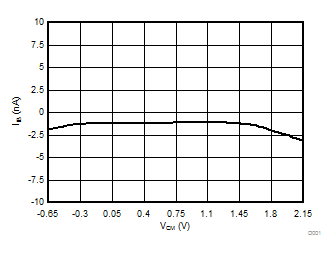
| VDD = 5.5 V |
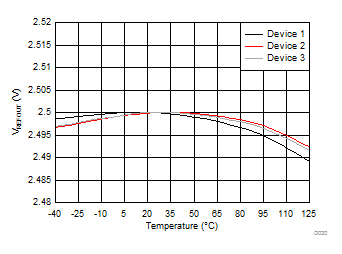
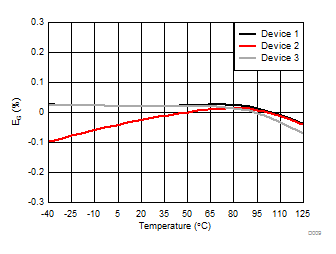
Common-Mode Input Voltage
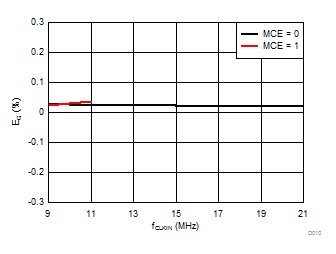
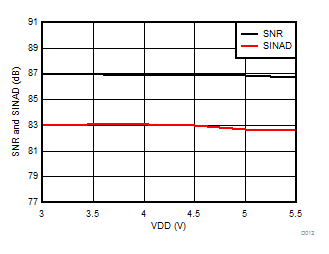
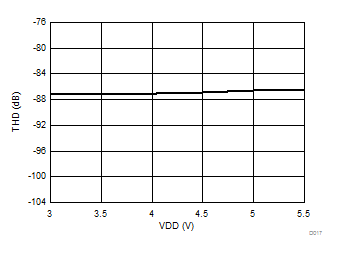
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion vs Supply Voltage
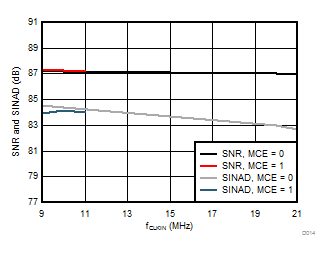
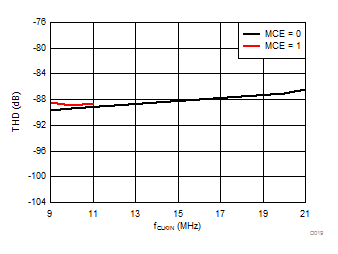
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion vs Clock Frequency
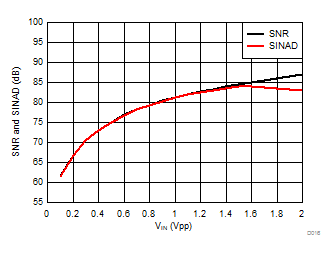
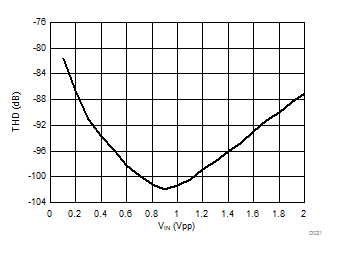
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion vs Input Signal Voltage
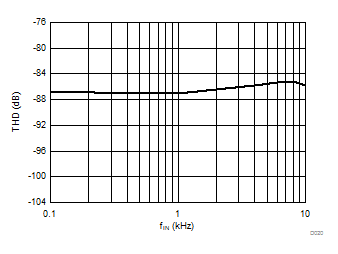
Input Signal Frequency
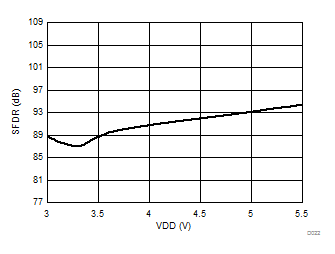
Supply Voltage
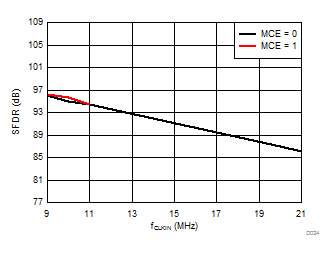
Clock Frequency
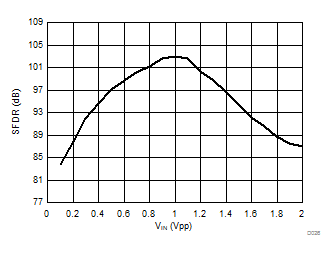
Input Signal Voltage
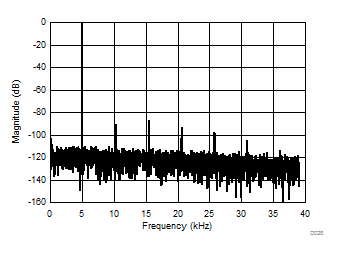
| 4096-point FFT, VIN = 2 VPP |
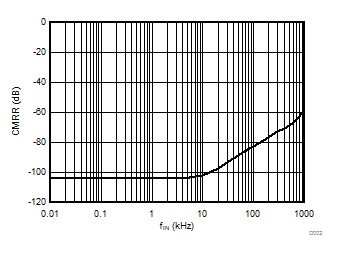
Input Signal Frequency
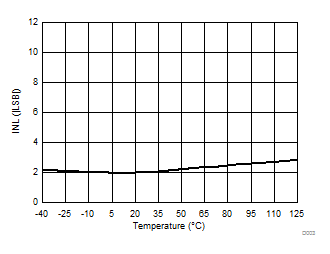
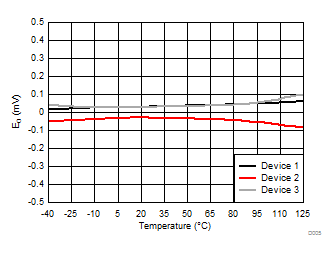
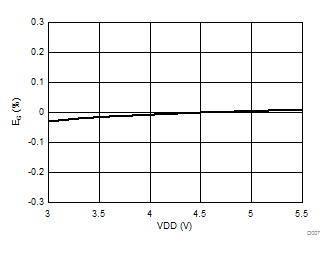
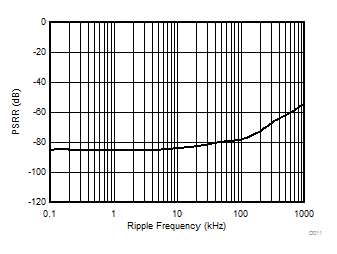
Ripple Frequency
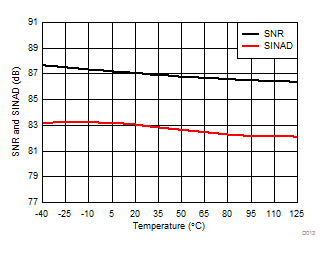
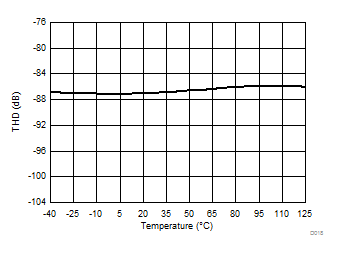
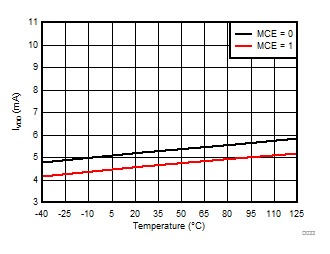
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion vs Temperature
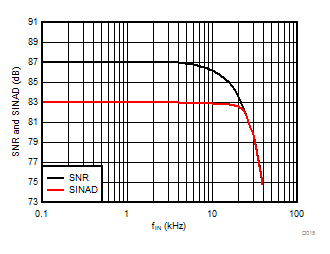
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion vs Input Signal Frequency
Input Signal Voltage
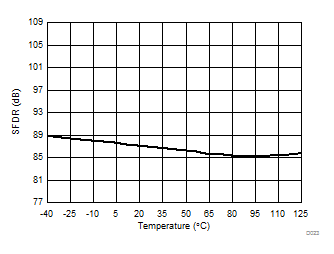
Temperature
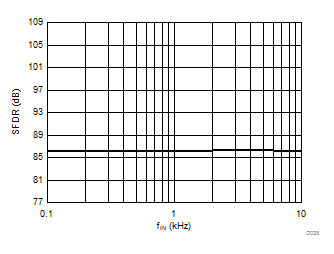
Input Signal Frequency
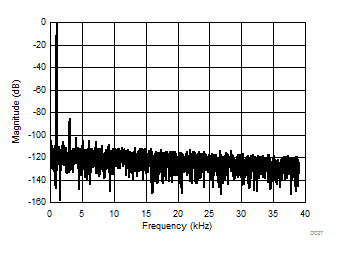
| 4096-point FFT, VIN = 2 VPP |