JAJSHL1J August 2018 – May 2021 TLV803E , TLV809E , TLV810E
PRODMIX
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.3 Application Curves
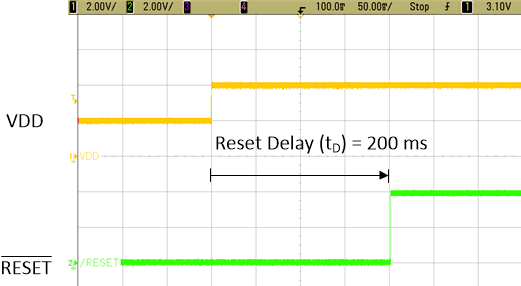
Figure 9-2 and Figure 9-3 show the TLV803EA29 functionality. In Figure 9-2, the VDD supply voltage drops from 30% above VIT- = 3.8 V to 10% below VIT- = 2.6 V with a 0.1-µF capacitor on VDD. The RESET output is connected to VDD through the pull-up resistor so when the VDD supply voltage drops. The RESET output discharges down to the VDD supply voltage through the pull-up resistor and RESET pin capacitance. Once the high-to-low propagation delay tPD_HL expires, the internal MOSFET turns on and asserts RESET to logic low. Note that tPD_HL varies with VDD specifically on how much VDD drops and how quickly in addition to the VDD and RESET pin capacitances. In Figure 9-3, VDD rises from 2 V to 4 V and the RESET output deasserts to logic high after the reset delay time (tD) expires.
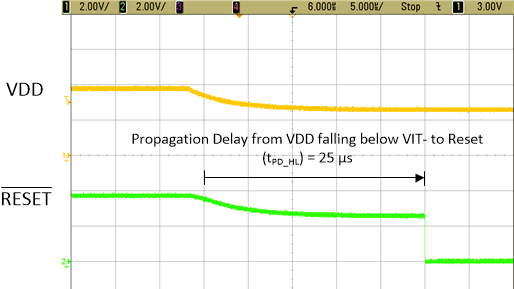
- Typical tPD_HL= 30 µs for VDD falling from (VIT+ + 30%) to (VIT- - 10%).
- VDD does not fall all the way to 0 V so RESET momentarily discharges to VDD until tPD_HL expires.