JAJSNR9B April 2016 – April 2022 INA301-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.1.3 INA301-Q1 Operation With Common-Mode Voltage Transients Greater Than 36 V
With a small amount of additional circuitry, the INA301-Q1 can be used in circuits subject to transients greater than 36 V. Use only Zener diodes or Zener-type transient absorbers (sometimes referred to as transzorbs). Any other type of transient absorber has an unacceptable time delay. Start by adding a pair of resistors as a working impedance for the Zener diode, as shown in Figure 8-3. Keep these resistors as small as possible; preferably, 10 Ω or less. Larger values can be used, but with an additional induced error resulting from less signal reaching the device input pins. Because this circuit limits only short-term transients, many applications are satisfied with a 10-Ω resistor along with conventional Zener diodes of the lowest power rating available. This combination uses the least amount of board space. These diodes can be found in packages as small as SOT-523 or SOD-523.
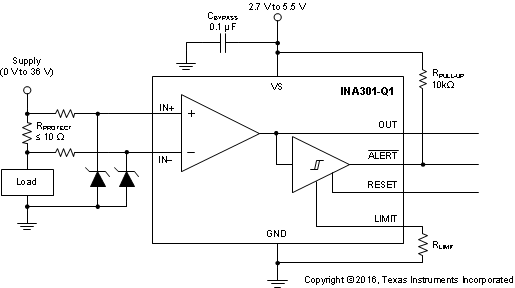 Figure 8-3 Transient Protection
Figure 8-3 Transient Protection