JAJSRP9 September 2024
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 説明
- 4 Device Options
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.4 Soft Start
After enabling the device, there is a 700µs (typical) enable delay (tdelay) before the device starts switching. After the enable delay, if the SS pin is left un-connected an internal soft start-up circuitry controls the output voltage ramp up with a period of 1.5ms (tRamp) for TPS6286A06 and with 500us for TP6286A08, TPS6286A10, TPS6286B08, and TPS6286B10. Leaving the SS pin disconnected provides the fastest start-up ramp. This action avoids excessive inrush current and creates a smooth output voltage rise-slope. This action also prevents excessive voltage drops of primary cells and rechargeable batteries with high internal impedance. The device is able to start into a prebiased output capacitor. The device starts with the applied bias voltage and ramps the output voltage to the nominal value. An external soft-start capacitor connected from SS to GND is charged 20µA by an internal current source during soft start until it reaches the reference voltage of 0.9V. The capacitance required to set a certain ramp-time (tramp) therefore is:
If the device is set to shutdown (EN = GND), undervoltage lockout, or thermal shutdown, an internal resistor pulls the SS pin to GND to make sure of a proper low level. Returning from those states causes a new start-up sequence.
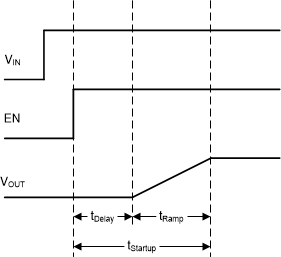 Figure 7-3 Start-up Sequence
Figure 7-3 Start-up Sequence